Abstract
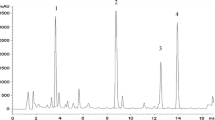
The genus Yucca is among the promising source with regard to their valuable steroidal sapogenin contents. Variety of Yucca species have been examined by wall M.E. and co-workers (1–5). Tomova and Panova (6) has examined sapogenins from leaves of Yucca aloefolia L. grown in Bulgaria. Recently Bedour and co-workers (7) have reported seasonal variation in sapogenin contents of Y. aloefolia. We have investigated steroidal sapogenin contents of Y. aloefolia L., leaves rhizomes, flowers and its eight month old callus tissue established on revised Murashige and Skoog’s (RT) medium from leaves.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.E. Wall, et.al., J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. Sci. Ed., 43:1 (1954).
M.E. Wall, et.al., J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. Sci. Ed., 43:503 (1954).
M.E. Wall, et.al., J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. Sci. Ed., 44:438 (1955).
M.E. Wall, et.al., J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. Sci. Ed., 46:653 (1957).
M.E. Wall, et.al., J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. Sci. Ed., 50:1001 (1961).
M. Tomova, D. Panova, Arch. Pharm., 296:553–556 (1963).
M.S. Bedour, M.H.A. Elgamal, International Research Congress of Natural Products as Medicinal Agents, Strasbourg, France, July 6–11, 24:11–44 (1980).
B. Kaul, E.J. Staba, Lloydia, 31:171 (1968).
T. Murashige, F. Skoog, Physiol Pl., 15:473 (1962).
Y. Tomita, A. Vomori and H. Minato, Phytochemistry, 9:111 (1970).
G.L. Sanches, J.C. Medina Achevedo and R.R. Sato, Analyst, 97:973 (1972).
P. Khanna, O.O. Sharma and S.C. Jain, Indian J. Exp. Biol., 17:446 (1979).
P. Khanna, O.P. Sharma, Jour. of Nat. Prod., 43:4–459 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1983 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Khanna, P., Purohit, P.V. (1983). Studies of Steroidal Sapogenins from Yucca aloefolia L. In Vivo and In Vitro Tissue Cultures. In: Sen, S.K., Giles, K.L. (eds) Plant Cell Culture in Crop Improvement. Basic Life Sciences, vol 22. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-4379-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-4379-0_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-4381-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-4379-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive