Abstract
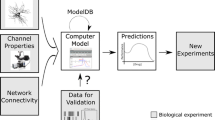
ModelDB is an online database (senselab.med.yale.edu/senselab/ModelDB) of published neuronal models, including models of ion channels, dendrites, axons, neurons, synapses and networks of neurons. Having ready access to the code for a model facilitates testing and verification of a model, re-use of model components to speed development of new models, and comparing a model to new experimental data. The database is useful for archiving models and for collaboration on modeling projects, and is a resource for teachers and students in both theoretical and experimental neuroscience. We describe here how to use the database: how to find specific models, how to obtain model code, how to run models, and how to contribute a model to the database.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bower, J.M. and Beeman, D. (1998) The Book of GENESIS: Exploring Realistic Neural Models with the GEneral NEural Simulation System. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Courtemanche, M., Ramirez, R.J., and Nattel, S. (1998) Ionic mechanisms underlying human atrial action potential properties: insights from a mathematical model. Am. J. Physiol. 275, H301–21.
Crane, G.J., Hines, M.L., and Neild, T.O. (2001) Simulating the spread of membrane potential changes in arteriolar networks. Microcirculation 8, 33–43.
Hines, M.L. and Carnevale, N.T. (1997) The NEURON simulation environment. Neural Comput. 9, 1179–209.
Migliore, M., Hoffman, D.A., Magee, J.C., and Johnston, D. (1999) Role of an A-type K+ conductance in the back-propagation of action potentials in the dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 7, 5–15.
Miller, P.L., Nadkarni, P., Singer, M., Marenco, L., Hines, M., and Shepherd, G. (2001) Integration of multidisciplinary sensory data: a pilot model of the human brain project approach. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 8, 34–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Davison, A.P., Morse, T.M., Migliore, M., Marenco, L., Shepherd, G.M., Hines, M.L. (2003). ModelDB: A Resource for Neuronal and Network Modeling. In: Kötter, R. (eds) Neuroscience Databases. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1079-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1079-6_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-5384-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-1079-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive