Abstract
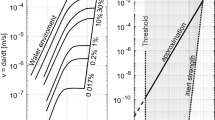
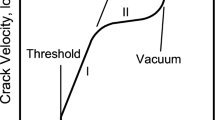
The decrease in the strength of glass under load results from reaction of the glass with water in the surrounding atmosphere. Hillig and Charles have proposed a model to explain the static fatigue of glass in which this reaction is enhanced by the concentration of stress at crack tips in the glass. This stress-enhanced corrosion leads to a sharpening of the crack tip, a still higher stress there, and ultimately failure when the theoretical cohesive stress of the glass is reached. This theory can explain some experimental results on delayed failure in glass but other results, such as the effect of surface treatment on delayed failure, are inconsistent with the theory.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.E. Mould, R.D. Southwick, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 42 582 (1959).
W.B. Hillig, R.J. Charles, in High Strength Materials, V.F. Zackey, ed., Wiley, New York (1965) 682.
J.E. Burke, R.H. Doremus, W.B. Hillig, A.M. Turkalo, in Ceramics in Severe Environments, W.W. Kriegel and H. Palmour, eds., Plenum Press, New York (1971) 435.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1974 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Doremus, R.H. (1974). Static Fatigue in Glass. In: Bishay, A. (eds) Recent Advances in Science and Technology of Materials. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-4538-1_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-4538-1_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-4540-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4613-4538-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive