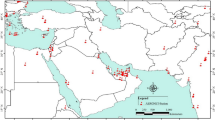
Airborne dust is of concern due to hazards in the localities affected by erosion, transport and deposition, but it is also of global concern due to uncertainties over its role in radiative forcing of climate. In order to model the environmental impact of dust, we need a better knowledge of sources and transport processes. Satellite remote sensing has been instrumental in providing this knowledge, through long time series of observations of atmospheric dust transport. Three remote sensing methodologies have been used, and are reviewed briefly in this paper. Firstly the use of observations from the Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS), secondly the use of the Infrared Difference Dust Index (IDDI) from Meterosat infrared data, thirdly the use of MODIS images from the rapid response system. These data have highlighted the major global sources of dust, mist of which are associated with endoreic drainage basins in deserts, which held lakes during Quaternary humid climate phases, and identified the Bodélé Depression in Tchad as the dustiest place on Earth.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
Armitage S.J., Drake N.A., Stokes S., El-hawat A., Salem M.J., White K., Turner P., McLaren, S.J. 2007. Multiple phases of North African humidity recorded in lacustrine sedi ments from the Fazzan basin, Libyna Sahara, in Quaternary Geochronology, n.2, 181–186
Brooks, N. 1999. Dust-climate interactions in the Sahel-Sahara zone of northern Africa, with particular reference to late twentieth century Sahelian drought. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, University of East Anglia
Brooks N., Legrand, M. 2000. Dust variability and rainfall in the Sahel, in McLaren S. and Kniveton D. (Eds.) Linking Climate Change to Land-Surface Change. Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1–25
Bryant R.G., Gigg G.R., Mahowald N.M., Eckardt F.D., Ross S.G. 2007. Dust emission response to climate in southern Africa, in Journal of Geophysical Research, n.112, D09207, doi: 10.1029/2005JD007025
Bullard, J.E., White, K. 2005. Dust production and the release of iron oxides resulting from the aeolian abrasion of natural dune sands, in Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, n.30, 95–106, doi: 10.1002/esp.1148
Buritt B., Hyers A.D. 1981. Evaluation of Arizona's highway dust warning system, in Geological Society of America Special Paper, n.186, 281–292
Cakmur R.V., Miller R.L., Torres O. 2004. Incorporating the effect of small-scale circulations upon dust emission in an atmospheric general circulation model, in Journal of Geophysical Research, n.109, D07201, doi: 10.1029/2003JD004067
Chiapello, I., Moulin C. 2002. TOMS and METEOSAT satellite records of the variability of Saharan dust transport over the Atlantic during the last two decades (1979–1997), in Geophysical Research Letters, n.29 (8), 1176, doi: 10.1029/2001GL013767
Drake N., Bristow C.S. 2006. Shorelines in the Sahara: geomorphological evidence for an enhanced monsoon from palaeolake Megachad, Holocene n.16 (6), 901–911
Ganor, E., Mamane Y. 1982. Transport of Saharan dust across the eastern Mediterranean, in Atmospheric Environment, n.16, 581–587
Goudie A.S. 1999. Wind erosional landforms: yardangs and pans, in Goudie, A.S., Livingstone, I., and Stokes, S. (Eds.) Aeolian Environments, Sediments and Landforms. Wiley, Chichester, 167–180
Goudie A.S., Middleton, N.J. 1992. The changing frequency of dust storms through time, in Climatic Change, n.20, 197–225
Goudie A.S., Middleton N.J. 2001. Saharan dust storms: nature and consequences, in Earth-Science Reviews, n.56, 179–204
Herman J.R., Bhartia P.K., Torres O., Hsu C., Seftor, C., Celarier E. 1997. Global dis tribution of UV-absorbing aerosols from Nimbus 7/TOMS data, in Journal of Geophysical Research. n.102, 16911–16922
IPCC 2001. Climate Change 2001. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kaufman Y.J., Koren I., Remer L.A., Tanre D., Ginoux P., Fan S. 2005. Dust transport and deposition observed from the Terra-Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) spacecraft over the Atlantic Ocean, in Journal of Geophysical Research, n.110, D10S12, doi: 10.1029/2003JD004436
Leathers C.R. 1981. Plant component of desert dust in Arizona and their significance for man, in Geological Society of America Special Paper, n.186, 191–206
Legrand M., N'Doume C., Jankowiak I. 1994. Satellite-derived climatology of the Saharan aerosol, in Lynch D.K. (Ed.) Passive Infrared Remote Sensing of Clouds and the Atmosphere II. Proceedings of SPIE 2309, 127–135
Legrand M., Plana-Fattori A., N'Doume C. 2001. Satellite detection of dust using the IR imagery of Meteosat: 1. Infrared difference dust index, in Journal of Geophysical Research, n.106 (D16), 18251–18274
Leon J.F., Legrand M. 2003. Mineral dust sources in the surroundings of the north Indian Ocean, in Geophysical Research Letters, n.30 (6), 1309, doi: 10.1029/2002GL016690
Leys J. 1999. Wind erosion on agricultural land, in Goudie, A.S., Livingstone, I. and Stokes, S. (Eds.) Aeolian Environments, Sediments and Landforms. Wiley, Chichester, 143–166
Liss P.S., Turner S.M. 2000. The influence of iron on ocean biology and climate; insights from the IronEx studies in the Equatorial Pacific, in Hanson R.B., Ducklow H.W. and Field J.G. (Eds.) The Changing Ocean Carbon Cycle, A Midterm Synthesis of Joint Global Ocean Flux Study. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Livingstone I., Warren A. 1996. Aeolian Geomorphology. Longman, Harlow
McFadden L.D., Wells S.G., Jercinovich M.J. 1987. Influences of aeolian and pedogenic processes on the origin and evolution of desert pavements, in Geology, n.15, 504–508
McTainsh G. 1999. Dust transport and deposition, in Goudie, A.S., Livingstone, I. and Stokes, S. (Eds.) Aeolian Environments, Sediments and Landforms. Wiley, Chichester, 181–211
Middleton N.J. 1985. Effect of drought on dust production in the Sahel,, in Nature, n.316 (6027), 431–435
Middleton N.J. 1986. Dust storms in the Middle East, Journal of Arid Environments, n.10, 83–96
Middleton N.J., Goudie A.S. 2001. Saharan dust, sources and trajectories, in Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers, n.26 (2), 165–181
Middleton N.J., Goudie A.S., Wells G.L. 1986. The frequency and source areas of dust storms, in Nickling, W.G. (Ed.) Aeolian Geomorphology. Allen & Unwin, Boston, pp. 237–260
Prospero J.M., Glaccum R.A., Nees R.T. 1983. Atmospheric transport of soil dust from Africa to South America, in Nature, n.320, 570–572
Torres O., Bhartia P.K., Herman J.R., Sinyuk A., Holben B. 2002. A long term record of aerosol optical thickness from TOMS observations and comparison to AERONET measurements, in Journal of Atmospheric Science, n.59, 398–413
Warren A., Chappell A., Todd M.C., Bristow C.S., Drake N.A., Engelstaedter S., Martins V., M'bainayel S., Washington R. 2007. Dust-raising in the dustiest place on earth, in Geomorphology, n.92, 25–37, doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.02.007
Washington R., Todd M.C. 2005. Atmospheric controls on mineral dust emission from the Bodélé Depression, Chad: the role of the low level jet, in Geophysical Research Letters, n.32, L17701, doi: 10.1029/2005GL023597
Washington R., Todd, M. Middleton, N.J., Goudie, A.S. 2003. Dust-storm source areas determined by the total ozone monitoring spectrometer and surface observations, in Annals of the Association of American Geographers, n.93 (2), 297–313
Washington R., Todd, M.C., Engelstaedter, S., Mbainayel, S., Mitchell F. 2006a. Dust and the low-level circulation over the Bodélé Depression, Chad: observations from BoDEx 2005, Journal of Geophysical Research, n.111, D03201, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006502
Washington R., Todd M.C., Lizcano G., Tegen I., Flamant C., Koren, I., Ginoux P., Engelstaedter S., Bristow C.S., Zender C.S., Goudie A.S., Warren A., Prospero J.M. 2006b. Links between topography, wind, deflation, lakes and dust: the case of the Bodélé Depression, Chad, in Geophysical Research Letters, n.33, L09401, doi: 10.1029/2006GL025827
Wasson R.J., Nanninga P.M. 1986. Estimating wind transport of sand on vegetated surfaces, in Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, n.11, 505–514
Wheaton E.E. 1992. Prairie dust storms, a neglected hazard, in Natural Hazards, n.5, 53–63
White K., Eckardt F.D. 2006. Geochemical mapping of carbonate sediments in the Makgadikgadi basin, Botswana, using moderate resolution remote sensing data, in Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, n.31, 665–681, doi: 10.1002/esp.1289
White K., Livingstone I., Gurney S., Dearing J., Bateman M. 2002. Post-processing of mineral mixture maps for mapping surficial materials: the example of the Matmata loess, southern Tunisia, in International Journal of Remote Sensing, n.23, 3091–3106, doi: 10.1080/01431160110104674
Worster D. 1979. Dust Bowl; the Southern High Plains in the 1930s. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer Science + Business Media B.V
About this paper
Cite this paper
White, K. (2009). Remote Sensing Of Aeolian Dust Production And Distribution. In: Marini, A., Talbi, M. (eds) Desertification and Risk Analysis Using High and Medium Resolution Satellite Data. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8937-4_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8937-4_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-8936-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-8937-4
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)