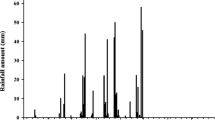
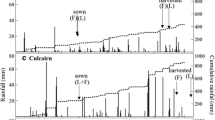
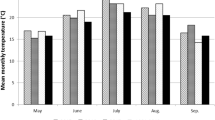
Soybean production is being encouraged in Malawi to supply protein to its population. Cultivation of soybean varieties currently recommended in Malawi requires seed inoculation with a highly effective rhizobium strain. Using rhizobial inoculants ensures that the correct rhizobial bacteria associate with the plant. Until the late 1980s and early 1990s, seed-applied peat-based inoculants dominated the commercial inoculant market. However, although peat was recognized as a very good carrier of rhizobia, there was interest in developing alternate formulations because it was considered time-consuming and impractical. As alternative liquid formulations were introduced, along with new packaging, this allowed farmers to treat seed directly from the packaged product as it was passing through the grain auger into the seeding equipment. Brockwell et al. (1980) reported that, when conditions were stressful and generally unfavourable, soil inoculation, such as granular soil implants, resulted in better nodulation and better yield than seed-applied inoculants. Hynes et al. (2001) reported that of eight lentil trials, six indicated that liquid and peat formulations were equally effective at enhancing final yields relative to the control. In contrast, Clayton et al. (2003) reported that seed yield by peatbased powder typically out-performed the liquid inoculant, which did not differ significantly from uninoculated. However, there were no data in the country on which to base rhizobia-inoculation recommendations. A trial was initiated in Malawi to determine the best method of inoculation and the rate of application of rhizobial inoculants for optimal biological nitrogen fixation and grain yield of soybean.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer Science + Business Media B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chilimba, A.D.C. (2008). Evaluation of Seed and Liquid Inoculation on Biological Nitrogen Fixation and Grain Yield of Soybean. In: Dakora, F.D., Chimphango, S.B.M., Valentine, A.J., Elmerich, C., Newton, W.E. (eds) Biological Nitrogen Fixation: Towards Poverty Alleviation through Sustainable Agriculture. Current Plant Science and Biotechnology in Agriculture, vol 42. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8252-8_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8252-8_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-8251-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-8252-8
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)