Abstract
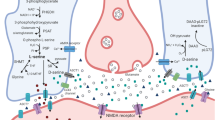
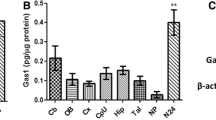
Recently, d-serine has been identified as an important NMDA-receptor co-agonist, which might play a role in central nervous system development. We investigated this by studying rat P19 cells, an established model for neuronal and glial differentiation. Our results show that (1) the d-serine synthesizing enzyme serine racemase was expressed upon differentiation, (2) extracellular d-serine concentrations increased upon differentiation, which was inhibited by serine racemase antagonism, and (3) inhibition of d-serine synthesis or prevention of d-serine binding to the NMDA-receptor increased synaptophysin expression and intercellular connections, supporting a role for NMDA-receptor activation by d-serine, synthesized by serine racemase, in shaping synaptogenesis and neuronal circuitry during central nervous system development. In conjunction with recent evidence from literature, we therefore suggest that d-serine deficiency might be responsible for the severe neurological phenotype seen in patients with serine deficiency disorders. In addition, this may provide a pathophysiological mechanism for a role of d-serine deficiency in psychiatric disorders.
Competing interests: None declared
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adesnik H, Li G, During MJ, Pleasure SJ, Nicoll RA (2008) NMDA receptors inhibit synapse unsilencing during brain development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:5597–5602
Bain G, Ray WJ, Yao M, Gottlieb DI (1994) From embryonal carcinoma cells to neurons: the P19 pathway. Bioessays 16:343–348
Basu AC, Tsai GE, Ma CL, Ehmsen JT, Mustafa AK, Han L, Jiang ZI et al (2009) Targeted disruption of serine racemase affects glutamatergic neurotransmission and behavior. Mol Psychiatry 14:719–727
Da Silva Lde B, Leipnitz G, Seminotti B, Fernandes CG, Beskow AP, Amaral AU, Wajner M (2009) D-serine induces lipid and protein oxidative damage and decreases glutathione levels in brain cortex of rats. Brain Res 1256:34–42
De Koning TJ, Klomp LW (2004) Serine deficiency syndromes. Curr Opin Neurol 17:197–204
De Koning TJ, Jaeken J, Pineda M, van Maldergem L, Poll-The BT, van der Knaap MS (2000) Hypomyelination and reversible white matter attenuation in 3-phophoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency. Neuropediatrics 31:287–292
De Koning TJ, Duran M, van Maldergem L, Pindeda M, Dorland L, Gooskens R, Jaeken J et al (2002) Congenital microcephaly and seizures due to 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency: outcome of treatment with amino acids. J Inherit Metab Dis 25:119–125
De Koning TJ, Klomp LW, van Oppen AC, Beemer FA, Dorland L, van den Berg I, Berger R (2004) Prenatal and early postnatal treatment in 3-phosphoglycerate-dehydrogenase deficiency. Lancet 364:2221–2222
Detera-Wadleigh SD, McMahon FJ (2006) G72/G30 in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: review and meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry 60:106–114
Eastwood SL (2004) The synaptic pathology of schizophrenia: is aberrant neurodevelopment and plasticity to blame? Int Rev Neurobiol 59:47–72
Fuchs SA, Dorland L, de Sain-van der Velden MG, Hendriks M, Klomp LW, Berger R, de Koning TJ (2006) D-serine in the developing human central nervous system. Ann Neurol 60:476–480
Fuchs SA, Klomp LWJ, de Koning TJ (2008a) D-serine in the developing human central nervous system: clinical implications. In: Heresco-Levy U, Javitt DC (eds) Glutamate in neuropsychiatric disorders. Research Signpost, Trivandrum, Kerala, India, pp 75–97
Fuchs SA, de Sain-van der Velden MG, de Barse MM, Roeleveld MW, Hendriks M, Dorland L, Klomp et al (2008b) Two mass-spectrometric techniques for quantifying serine enantiomers and glycine in cerebrospinal fluid: potential confounders and age-dependent ranges. Clin Chem 54:1443–1450
Heresco-Levy U, Vass A, Bloch B, Wolosker H, Dumin E, Balan L, Deutsch L et al (2009) Pilot controlled trial of D-serine for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:1275–1282
Jaeken J, Detheux M, van Maldergem L, Foulon M, Carchon H, van Schaftingen E (1996) 3-Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency: an inborn error of serine biosynthesis. Arch Dis Child 74:542–545
Kim PM, Aizawa H, Kim PS, Huang AS, Wickramasinghe SR, Kashani AH, Barrow RK et al (2005) Serine racemase: activation by glutamate neurotransmission via glutamate receptor interacting protein and mediation of neuronal migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:2105–2110
Leipnitz G, da Silva LB, Fernandes CG, Seminotti B, Amaral AU, Dutra-Filho CS, Wahner M (2010) D-serine administration provokes lipid oxidation and decreases the antioxidant defenses in rat striatum. Int J Dev Neurosci 28:297–301
Mothet JP, Parent AT, Wolosker H, Brady RO Jr, Linden DJ, Ferris CD, Rogawski MA et al (2000) D-serine is an endogenous ligand for the glycine site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4926–4931
Pape HC, Pare D (2010) Plastic synaptic networks of the amygdala for the acquisition, expression, and extinction of conditioned fear. Physiol Rev 90:419–463
Rabacchi S, Bailly Y, Delhaye-Bouchaud N, Mariani J (1992) Involvement of the N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor in synapse elimination during cerebellar development. Science 256:1823–1825
Ramirez-Amaya V, Balderas I, Sandoval J, Escobar ML, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2001) Spatial long-term memory is related to mossy fiber synaptogenesis. J Neurosci 21:7340–7348
Scarr E, Gray L, Keriakous D, Robinson PJ, Dean B (2006) Increased levels of SNAP-25 and synaptophysin in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in bipolar I disorder. Bipolar Disord 8:133–143
Schell MJ, Molliver ME, Snyder SH (1995) D-serine, an endogenous synaptic modulator: localization to astrocytes and glutamate-stimulated release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:3948–3952
Takarada T, Hinoi E, Takahata Y, Yoneda Y (2008) Serine racemase suppresses chondrogenic differentiation in cartilage in a Sox9-dependent manner. J Cell Physiol 215:320–328
Takarada T, Takahata Y, Iemata M, Hinoi E, Uno K, Hirai T, Yamamoto T et al (2009) Interference with cellular differentiation by D-serine through antagonism at N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors composed of NR1 and NR3A subunits in chondrocytes. J Cell Physiol 220:756–764
Yang Y, Ge W, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Shen W, Wu C, Poo M et al (2003) Contribution of astrocytes to hippocampal long-term potentiation through release of D-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:15194–15199
Yoshida K, Furuya S, Osuka S, Mitoma J, Shinoda Y, Watanabe M, Azuma N et al (2004) Targeted disruption of the mouse 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase gene causes severe neurodevelopmental defects and results in embryonic lethality. J Biol Chem 279:3573–3577
Zanatta A, Schuck PF, Viegas CM, Knebel LA, Busanello EN, Moura AP, Wajner M (2009) In vitro evidence that D-serine disturbs the citric acid cycle through inhibition of citrate synthase activity in rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res 1298:186–193
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (grant 920-03-345). We thank O. van Beekum for directing our attention to and supplying us with rat P19 cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by: Jaak Jaeken
Appendices
Concise 1 Sentence Take-Home Message
d-serine, synthesized by serine racemase might play an important role in shaping synaptogenesis and neuronal circuitry during central nervous system development.
Details of the Contributions of Individual Authors
-
Sabine A. Fuchs: planned the study, designed and performed the experiments (with the exception of the LC-MS analyses), interpreted results, and wrote the manuscript
-
Martin W. Roeleveld: performed all LC-MS analyses, revised and agreed with the manuscript
-
Leo W.J. Klomp: participated in study conception and design, data interpretation and manuscript revision
-
Ruud Berger: supervised study conception and design, data interpretation and manuscript revision.
-
Tom J. de Koning: participated in study conception and design, data interpretation and manuscript revision
Guarantor for the Article
Tom J. de Koning
A Competing Interest Statement
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to declare, thus none of the authors has
-
In the past 5 years accepted the following from an organization that may in any way gain or lose financially from the results of your study or the conclusions of your review, editorial, or letter:
-
Received reimbursement for attending a symposium
-
Received a fee for speaking or for organizing education
-
Received funds for research or for a member of staff
-
Received a fee for consulting
-
In the past 5 years been employed by an organization that may in any way gain or lose financially from the results of your study or the conclusions of your review, editorial, or letter.
-
Any stocks or shares in such an organization
-
Acted as an expert witness on the subject of your study, review, editorial, or letter
-
Any other competing financial interests
Details of Funding
Financial support was provided from The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (personal grant to S.A. Fuchs 920-03-345).
The author(s) confirm(s) independence from the sponsors; the content of the article has not been influenced by the sponsors
Details of Ethics Approval, Patient Consent Statement or Approval from the Institutional Committee for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals
No ethics approval, patient consent statement or approval from the Institutional Committee for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals was required for these research studies
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 SSIEM and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Fuchs, S.A., Roeleveld, M.W., Klomp, L.W.J., Berger, R., de Koning, T.J. (2012). D-Serine Influences Synaptogenesis in a P19 Cell Model. In: JIMD Reports - Case and Research Reports, 2012/3. JIMD Reports, vol 6. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/8904_2011_116
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/8904_2011_116
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-28128-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-28129-7
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)