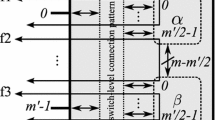
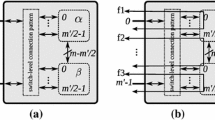
Abstract
With the increasing demand and growth of high-speed networks, it is imperative to develop high performance network switches that also have low complexity. Over the years, many high performance ATM switches have been proposed. The majority of these switches has high performances but also have very high hardware complexities. Therefore, there is a need for switch designs with lower complexity and high performance. The authors are proposing the use of the folded hypercube (FHC) as a new infrastructure for ATM switches. This paper presents two novel ATM switches that are implemented from the FHC networks. It presents the design of the two switches, discusses how the simulation models are developed, and gives the analysis of the simulation results. Finally, the performances of the two switch models are compared to other switches in the literature.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Ahmadi and W. E. Denzel, “A Survey of modern high-performance switching techniques,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 7, no. 7, pp. 1091–1103, Sep. 1989.
R. Y. Awdeh and H. T. Mouftah, “Survey of ATM switch architectures,” Computer Networks and ISDN Systems, vol. 27, no. 12, pp. 1567–1613, Nov. 1995.
J. H. Patel, “Performance of processor-memory interconnection network,” IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol. 30, no. 10, pp. 771–780, Oct. 1981.
T. Matsunaga, “Sorting-based routing algorithms of a photonic ATM cell switch: HiPower,” IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 41, no. 9, pp. 1356–1363, Sep. 1993.
D. C. W. Pao and W. N. Chau, “Design of ATM switch using hypercube with distributed shared input buffers and dedicated output buffer,” International Conference on Network Protocols, pp. 92–99, 1995.
H. J. Siegel, “Analysis Techniques for SIMD Machine Interconnection Networks and the Effects of Processor Address Masks,” IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol. C-26, pp. 153–161, Feb. 1977.
A. El-Amawy and S. Latifi, “Properties of folded hypercubes,” IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 31–42, Jan. 1991.
S. Latifi and A. El-Amawy, “On folded hypercubes,” International Conference on Parellel Processing, vol. 1, pp. 180–187, 1989.
J. S. Park and N. J. Davis IV, “Modeling the Folded Hypercube Network with OPNET,” The Proceedings of OPNETWORK’ 99, Washington, DC, August 1999.
A. G. Greenberg and B. Hajek, “Deflection routing in hypercube networks,” IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 1070–1081, Jun. 1982.
E. A. Varvarigos and D. P. Bertsekas, “Performance of hypercube routing schemes with or without buffering,” IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 299–311, Jun. 94.
F. B. Chedid and R. B. Chedid, “A new variation on hypercubes with smaller diameter,” Information Processing Letters, vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 275–280, Jul. 26 1993.
B. R. Collier and H. S. Kim, “Efficient analysis of shared buffer management strategies in ATM networks under non-uniform bursty traffic,” IEEE INFOCOM’96, pp. 671–678, 1996.
S. C. Liew, “Performance of various input-buffered and output-buffered ATM switch design principles under bursty traffic: simulation study,” IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 42, no. 2/3/4, pp. 1371–1379, 1994.
D. M. Dias and J. R. Jump, “Packet switching interconnection networks for modular systems,” IEEE Computer, vol. 14, pp. 43–53, Dec. 1981.
A. L. DeCegama, The Technology of Parallel Processing, Volume 1, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1989.
G. F. Pfister and V. A. Norton, “Hot spot contention and combining in multistage interconnection networks,” IEEE International Conference on Parallel Processing, pp. 790–797, 1985.
J. S. Park, Performance analysis of partitioned multistage cube network and adaptive routed single-stage cube network, Master’s Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Park, J.S., Davis, N.J. (2001). The Folded Hypercube ATM Switches. In: Networking — ICN 2001. ICN 2001. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2094. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-47734-9_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-47734-9_37
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-42303-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-47734-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive