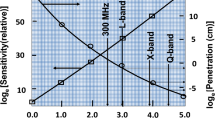
Abstract
A brief introduction to magnetic resonance and imaging is followed by a discussion of the challenges of performing low-frequency (ca. 300 MHz) pulsed EPR. The 300 MHz parallel coil resonator and the data acquisition system used in the authors’ spectrometer is described in detail, as are mathematical techniques of image reconstruction. 3D oxymetric images of mice were obtained using pulsed FID detection of T2*of triarylmethyl radicals injected into the mice. Single-point imaging, a technique developed for solid-state NMR, applied to pulsed EPR imaging yields artifact-free spatial images.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
8. References
Abragam, A.,1961, The Principles of Nuclear Magnetism, Oxford University Press, London.
Afeworki, M., Miller, N. R., Devasahayam, N., Cook, J., Mitchell, J. B., Subramanian, S. and Krishna, M. C., 1998, Preparation and EPR studies of lithium phthalocyanine radical as an oxymetric probe, Free. Radical. Bio. Med. 25: 72–78.
Afeworki, M., van Dam, G. M., Devasahayam, N., Murugesan, R., Cook, J., Coffin, D., ALarsen, J. H. A., Mitchell, J. B., Subramanian, S. and Krishna, M. C., 2000, Three-dimensional whole body imaging of spin probes in mice by time-domain radiofrequency electron paramagnetic resonance, Magn. Reson. Med. 43: 375–382.
Alecci, M., Brivati, J. A., Placidi, G. and Sotgiu, A., 1998a, A radiofrequency (220-MHz) Fourier transform EPR spectrometer, J. Magn. Reson. 130: 272–280.
Alecci, M., Brivati, J. A., Placidi, G., Testa, L., Lurie, D. J. and Sotgiu, A., 1998b, A submicrosecond resonator and receiver system for pulsed magnetic resonance with large samples, J. Magn. Reson. 132: 162–166.
Alecci, M., Ferrari, M., Quaresima, V., Sotgiu, A. and Ursini, C. L., 1994, Simultaneous 280-MHz EPR Imaging of rat organs during nitroxide free-radical clearance, Biophys. J. 67: 1274–1279.
Alecci, M., Gualtieri, G., Sotgiu, A., Testa, L. and Varoli, V., 1991, Multipolar Magnet for Low-Frequency Esr Imaging, Meas. Sci. Technol. 2: 32–37.
Alecci, M., Nicholson, I. and Lurie, D. J., 1996, A novel multiple-tuned radiofrequency loop-gap resonator for use in PEDRI, J Magn Reson B 110: 82–86.
Alecci, M., Penna, S. D., Sotgiu, A., Testa, L. and Vannucci, I., 1992, Electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometer for three-dimensional in vivo imaging at very low frequency, 63: 4263–4270.
Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J. H., Laursen, I., Leunbach, I., Ehnholm, G., G., W. L., Petersson, J. S. and Golman, K., 1998, EPR and DNP properties of certain novel single electron contrast agents intended for oximetric imaging, J. Magn. Reson. 133: 1–12.
Axelson, D. E., Kantzas, A. and Eads, T., 1995, Single point H-1 magnetic resonance imaging of rapid solids, Can. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 40: 16–26.
Balcom, B., Beyea, S. D., Green, D. P., Armstrong, R. L. and Bremner, T. W., 1996, Single-Point Ramped Imaging with T1 Enhancement (SPRITE), J. Magn. Reson. 123: 131–134.
Bandettini, P. A.; Wong, E. C.; Hinks, R. S.; Tikofsky, R. S., and Hyde, J. S., 1992, Time course EPI of human brain function during task activation, Magn. Reson. Med. 25: 390–397
Bendel, P., Davis, M., Berman, E. and Kabalka, G. W., 1990, A method for imaging nuclei with short T2 relaxation and its application to Boron-11 NMR imaging of a BNCT agent in an intact rat, J. Magn. Reson. 88: 369–375.
Beyea, S. D., Balcom, B. J., Mastikhin, I. V., Bremner, T. W., Armstrong, R. L. and Grattan-Bellew, P. E., 2000, Imaging of heterogeneous materials with a turbo spin echo single-point imaging technique, J. Magn. Reson. 144: 255–265.
Bloch, F., Hansen, W. W. and Packard, H. E., 1946, Nuclear Induction, Phys. Rev. 69: 127–131.
Botto, R. E., Gody, G. D., Dieckman, S. L., French, D. C., Gopalsmai, N. and Rizo, P., 1996, Three-dimensional magnetic resonance microscopy of materials, Solid. State. Nucl. Magn Reson. 6: 389–402.
Bourg, J., Krishna, M. C., Mitchell, J. B., Tschudin, R. G., Pohida, T. J., Friauf, W. S., Smith, P. D., Metcalfe, J., Harrington, F. and Subramanian, S., 1993, Radiofrequency FT EPR spectroscopy and imaging, J. Magn. Reson. B 102: 112–115.
Bracewell, R. N., 1994, Two dimensional imaging, Prentice Hall, New York.
Brivati, J. A., Stevens, A. D. and Symons, M. C. R., 1991, A radiofrequency ESR spectrometer for in vivo imaging, J. Magn. Reson. 92: 480–489.
Choi, S., Tang, X. W. and Cory, D. G., 1997, Constant time imaging approaches to NMR microscopy, Int. J. Imag. Tech. Sys. 8: 263–276.
Crepeau, R. H., Dulcic, A., Gorchester, J., Saarinen, T. R., and Freed, J. H., 1989, Composite pulses in time-domain ESR, J. Magn. Reson. 84: 184–190.
Devasahayam, N., Subramanian, S., Murugesan, R., Cook, J. A., Afeworki, M., Tschudin, R. G., Mitchell, J. B. and Krishna, M. C., 2000, Parallel coil resonators for time-domain radiofrequency electron paramagnetic resonance imaging of biological objects, J. Magn. Reson. 142: 168–176.
Eaton, G. R., Eaton, S. E. and Ohno, K., ed., 1991, EPR imaging and in vivo EPR, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Eaton, G. R., Eaton, S. S. and Maltempo, M. M., 1989, Three approaches to spectral spatial EPR imaging, Appl. Radiat. Isotopes 40: 1227–1231.
Eaton, G. R., Eaton, S. S. and Rinard, G. A., 1998, Frequency dependence of EPR sensitivity, in Spatially Resolved Magnetic Resonance: Methods, Materials, Medicine, Biology, Rheology, Geology, Ecology, Hardware, P. Blümler, B. Blümich, R. Botto, R. Botto and E. Fukushima.ed.), Wiley-VCH. Weinheim
Eaton, S. S. and Eaton, G. R., 1986, EPR imaging, Spectroscopy 1: 32–35.
Eaton, S. S. and Eaton, G. R., 2000, Relaxation times of organic radicals and transition metal ions. in Biological Magnetic Resonance, vol. 19 L. J. Berliner, S. S. Eaton and G. R. Eaton.eds.) pp. 29–154
Eaton, S. S., Maltempo, M. M., Stemp, E. D. A. and Eaton, G. R., 1987, Three-dimensional EPR imaging with one spectral and two spatial diemnsions, Chem. Phys. Lett. 142: 567–569.
Edelstein, W. A., Hutchison, J. M. S., Johnson, G. and Redpath, T. W., 1980, Spin-warp NMR imaging and applications to human whole-body imaging, Phys. Med. Biol. 25: 751–756.
Emid, S. and Creyghton, J. H. N., 1985, High-resolution NMR imaging in solids, Physica B 128: 81–83.
Ernst, R. R., 1966, Sensitivity enhancement in magnetic resonance, Adv. Magn. Reson. 2: 1–135.
Ernst, R. R., 1970, Magnetic resonance with stochastic excitation, J. Magn. Reson. 3: 10–27.
Ernst, R. R. and Anderson, J. R., 1966, Application of Fourier spectroscopy to nuclear magnetic resonance, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 37: 93–103.
Ewert, U. and Herrling, T., 1986, Spectrally resolved EPR tomography with stationary gradient, Chem. Phys. Lett. 129: 516–520.
Farrar, T. C. and Becker, E. D.,1971, Pulse and Fourier Transform NMR: Introduction to Theory and Methods, Academic Press, New York.
Field, L. D., Sternhill, S. and Sternhill, L. S.,1989, Analytical NMR John Wiley & Son, New York.
Fowler, J. S., Volkow, N. D., Wang, G. J., Ding, Y. S. and Dewey, S. L., 1999, PET and drug research and development, J. Nucl. Med. 40: 1154–1163.
Freeman, R., 1998, Shaped radiofrequency pulses in high resolution NMR, Progress in NMR Spectroscopy 32: 59–106.
Froncisz, W. and Hyde, J. S., 1982, The Loop-Gap Resonator-a New Microwave Lumped Circuit Electron-Spin-Resonance Sample Structure, J. Magn. Reson. 47: 515–521.
Fujii, H. and Berliner, L. J., 1985, One-dimensional and two-dimensional Electron-Paramagnetic-Resonance imaging studies on phantoms and plant specimens, Magn. Reson. Med. 2: 275–282.
Gadian, D. G.,1995, NMR and its Applications to Living Systems, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Gallez, B., Debuyst, R., Dejehet, F., Liu, K. J., Walczak, T., Goda, F., Demeure, R., Taper, H. and Swartz, H. M., 1998, Small particles of fusinite and carbohydrate chars coated with aqueous soluble polymers: Preparation and applications for in vivo EPR oximetry, Magn. Reson. Med. 40: 152–159.
Golman, K., Leunbach, I., Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J. H., Ehnholm, G. J., Wistrand, L. G., Petersson, J. S., Jarvi, A. and Vahasalo, S., 1998, Overhauser-enhanced MR imaging (OMRI), Acta. Radiol. 39: 10–17.
Golman, K., Petersson, J. S., Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J. H., Leunbach, I., Wistrand, L. G., Ehnholm, G. and Liu, K. C., 2000, Dynamic in vivo oxymetry using Overhauser enhanced MR imaging, J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 12: 929–938.
Gravina, S. and Cory, D. G., 1994, Sensitivity and resolution of constant-time imaging, J. Magn. Reson. B 104:53–61.
Griffiths, D. J.,1989, Introduction to Electrodynamics Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Haacke, E. M, Brown, R. W., Thompson, M. R. and Venkatesan, R.,1999, Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Physical Principles and Sequence Design John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Halpern, H. J. and Bowman, M. K., 1991, Low frequency EPR spectrometers: MHz range, in EPR Imaging and in vivo EPR G. R. Eaton, S. S. Eaton and K. Ohno.ed.), CRC Press. Boca Raton
Halpern, H. J., Spencer, D. P., van Polen, J., Bowman, M. K., Nelson, A. C., Dowey, E. M. and Teicher, B. A., 1989, Imaging radio frequency electron-spin-resonance spectrometer with high resolution and sensitivity for in vivo measurements, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 60: 1040–1050.
Halpern, H. J., Yu, C., Peric, M., Barth, E., Grdina, D. J. and Teicher, B. A., 1994, Oximetry deep in tissues with low-frequency electron paramagnetic resonance, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 13047–13051.
Halpern, H. J., Yu, C., Peric, M., Barth, E. D., Karczmar, G. S., River, J. N., Grdina, D. J. and Teicher, B. A., 1996, Measurement of differences in pO2 in response to perfluorocarbon carbogen in FSa and NFSa murine fibrosarcomas with low-frequency electron paramagnetic resonance oximetry, Radiat. Res. 145: 610–618.
Herman, G. T.,1980, Image Reconstruction from Projections: The Fundamentals of Computerized Tomography Acadmic Press, New York.
Hirata, H., Walczak, T. and Swartz, H. M., 1997, An improved inductive coupler for suppressing a shift in the resonance frequency of electron paramagnetic resonance resonators, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 68: 3187–3191.
Hyde, J. S., Froncisz, W. and Oles, T., 1989, Multipurpose loop gap resonator, J. Magn. Reson. 82: 223–230.
Hyde, J. S., Mchaourab, H. S., Camenisch, T. G., Ratke, J. J., Cox, R. W. and Froncisz, W., 1998, Electron paramagnetic resonance detection by time-locked subsampling, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 69: 2622–2628.
Ilangovan, G., Zweier, J. L. and Kuppusamy, P., 1999, Preparation and characterization of a highly sensitive EPR oximetry probe for biological application, Free. Radical. Bio. Med. 27: S106–S106.
Ilangovan, G., Zweier, J. L. and Kuppusamy, P., 2000a, Electrochemical preparation and EPR studies of lithium phthalocyanine. Part 2: Particle-size-dependent line broadening by molecular oxygen and its implications as an oximetry probe, J. Phys. Chem. B 104: 9404–9410.
Ilangovan, G., Zweier, J. L. and Kuppusamy, P., 2000b, Electrochemical preparation and EPR studies of lithium phthalocyanine: Evaluation of the nucleation and growth mechanism and evidence for potential-dependent phase formation, J. Phys. Chem. B 104: 4047–4059.
Jiang, J. J., Nakashima, T., Liu, K. J., Goda, F., Shima, T. and Swartz, H. M., 1996, Measurement of pO2 in liver using EPR oximetry, J. Appl. Physiol. 80: 552–558.
Johnson, C. C. and Guy, A. W., 1972, Nonionizing electromagnetic wave effects in biological materials and systems, Proc. I. E. E. E. 60: 6.
Kak, A. C. and Slaney, M.,1988, Principles of Computerized Tomographic Imaging IEEE Press, New York.
Kevan, L. and Bowman, M. K., ed., 1990, Modern Pulsed and Continuous-wave Electron Spin Resonance John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Krishna, M. C., Afeworki, M., Devasahayam, N., Cook, J., Subramanian, S. and Mitchell, J. B., 1999, In vivo free radical detection and imaging by EPR: Non-invasive mapping of tissue oxygen status., Free. Radical, Bio. Med. 27: S154–S154.
Kumar, A., Welti, D. and Ernst, R. R., 1975, NMR Fourier zeugmatography, J. Magn. Reson. 18: 69–83.
Kuppusamy, P., Afeworki, M., Shankar, R. A., Coffin, D., Krishna, M. C., Hahn, S. M, Mitchell, J. B. and Zweier, J. L., 1998, In vivo electron paramagnetic resonance imaging of tumor heterogeneity and oxygenation in a murine model, Cancer. Res. 58: 1562–1568.
Kuppusamy, P., Chzhan, M., Vij, K., Shteynbuk, M., Lefer, D. J., Giannelia, E. and Zweier, J. L., 1994, Three-dimensional spectral-spatial EPR imaging of free radicals in the heart: A technique for imaging tissue metabolism and oxygenation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 3388–3392.
Kuppusamy, P., Chzhan, M., Wang, P. H. and Zweier, J. L., 1996, 3D gated EPR imaging of the beating heart, Biophys. J. 70: Su409–Su409.
Kuppusamy, P., Li, H. Q., Ilangovan, G., Cardounel, A. J., Zweier, J. L., Yamada, K., Krishna, M. C. and Mitchell, J. B., 2002, Noninvasive imaging of tumor redox status and its modification by tissue glutathione levels, Cancer. Res. 62: 307–312.
Kwong, K. K., Belliveau, J. W., Chesler, D. A., Goldberg, I. E., Weisskoff, R. M., Poncelet, B. P., Kennedy, D. N., Hoppel, B. E., Cohen, M. S., Turner, R., Cheng, H.-M., Brady, T. J., and Rosen, B. R., 1992, Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of brain activity during primary sensory stimulation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 5675–5679.
Lauterbur, P. C., 1973, Image formation by induced local interactions: Examples employing nuclear magnetic resonance, Nature 242: 190–191.
Lauterbur, P. C., Levin, D. N. and Marr, R. B., 1984, Theory and simulation of NMR spectroscopic imaging and field plotting by projection reconstruction involving an intrinsic frequency dimension, J. Magn. Reson. 59: 536–541.
Liu, K. J., Gast, P., Moussavi, M., Norby, S. W., Vahidi, N., Walzak, T., Wu, M. and Swartz, H. M., 1993, Lithium phthalocyanine: a probe for electron paramagnetic resonance oximetry in viable biologic systems, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 5438–5442.
Liu, K. J., Hoopes, P. J., Rolett, E. L., Beerle, B. J., Azzawi, A., Goda, F., Dunn, J. F. and Swartz, H. M., 1997, Effect of anesthesia on cerebral tissue oxygen and cardiopulmonary parameters in rats, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 411: 33–39.
Lowe, I. J. and Norberg, R. E., 1957, Free-induction decays in solids, Phys. Rev. 107: 46–61.
Lurie, D. J., Bussell, D. M., Bell, L. H. and Mallard, J. R., 1988, Proton-electron double magnetic resonance imaging of free radical solutions, J. Magn. Reson. 76: 366–370.
Lurie, D. J., Hutchison, J. M. S., Bell, J. H., Nicholson, I., Bussell, D. M. and Mallard, J. R., 1989, Field cycled proton-electron double resonance imaging of free radicals in large aquous samples, J. Magn. Reson. 84: 431–437.
Maltempo, M. M., 1986, Differentiation of spectral and spatial components in EPR imaging using 2-D image reconstruction algorithms, J. Magn. Reson. 69: 156–163.
Maltempo, M. M., Eaton, S. S. and Eaton, G. R., 1987, Spectral-spatial two dimensional EPR imaging, J. Magn. Reson. 72: 449–455.
Maltempo, M. M., Eaton, S. S. and Eaton, G. R., 1988, Reconstruction of spectral-spatial two dimensional images from incomplete sets of projections without prior knowledge of the component spectra, J. Magn. Reson. 77: 75–83.
Maresch, G. G., Mehring, M. and Emid, S., 1986, High resolution ESR imaging, Physica 138B: 261–263.
Marr, R. B., Chen, C.-N. and Lauterbur, P. C., 1981, Mathematical Aspects of Computerized Tomography Springer-verlag, New York.
Moonen, C. T. W., Bandettini, P. A., Aquirre, G. K. and Heilman, H. P., 1999, Functional MRI Springer Verlag, New York.
Murugesan, R., Afeworki, M., Cook, J. A., Devasahayam, N., Tschudin, R., Mitchell, J. B., Subramanian, S. and Krishna, M. C., 1998, A broadband pulsed radio frequency electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometer for biological applications, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 69: 1869–1876.
Murugesan, R., Cook, J. A., Devasahayam, N., Afeworki, M., Subramanian, S., Tschudin, R., Larsen, J. A., Mitchell, J. B., Russo, A. and Krishna, M. C., 1997, In vivo imaging of a stable paramagnetic probe by pulsed-radiofrequency electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, Magnet. Reson. Med. 38: 409–414.
Natterer, F.,1986, The Mathematics of Computerized Tomography Wiley, Chichester.
Ogawa, S., Tank, D. W., Menon, R., Ellerman, J. M., Kim, S. G., Merkle, H. and Ugurbill, K., 1992, Intrinsic signal changes accompanying sensory stimulation-functional brain mapping with magnetic resonance imaging, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 89: 5951–5955.
Ohara, J. A., Goda, F., Liu, K. J., Bacic, G., Hoopes, P. J. and Swartz, H. M., 1995, The pO2 in a Murine Tumor after Irradiation-an in-vivo Electron-Paramagnetic-Resonance oximetry study, Radiat. Res. 144: 222–229.
Ono, M., Ogata, T., Hsieh, K. C., Suzuki, M., Yoshida, E. and Kamada, H., 1986, L-band electron-spin-resonance spectrometer using a loop-gap resonator for in vivo analysis, Chem. Lett.: 491–494.
Panagiotelis, I., Nicholson, I., Foster, M. A. and Hutchison, J. M. S., 2001, T*(1e) and T*(2e) maps derived in vivo from the rat using longitudinally detected electron spin resonance phase imaging; Application to abdominal oxygen mapping. Magnet. Reson. Med. 46:1223–1232.
Pfenninger, S., Forrer, J., Schweiger, A. and Weiland, T., 1988, Bridged loop gap resonator-a resonant structure for pulsed electron-spin-resonance transparent to high-frequency radiation, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 59: 752–760.
Pfenninger, S., Froncisz, W., Forrer, J., Luglio, J. and Hyde, J. S., 1995, General-method for adjusting the quality factor of EPR resonators, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66: 4857–4865.
Placidi, G., Alecci, M., Colacicchi, S. and Sotgiu, A., 1998, Fourier reconstruction as a valid alternative to filtered back projection in iterative applications: Implementation of Fourier spectral spatial EPR imaging, J. Magn. Reson. 134: 280–286.
Polk, C, and Postow, E., 1996, Handbook of Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields, 2nd Edition CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Poole, C, P., 1997, Electron Spin Resonance: A Comprehensive Treatise on Experimental Techniques John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Purcell, E. H., Torrey, H. C. and Pound, R. V., 1946, Resonance absorption by nuclear moments in solid, Phys. Rev. 69: 37–38.
Pursley, R., Kakareka, J., Salem, G., Devasahayam, N., Subramanian, S., Tschudin, R. G., Krishna, M. C. and Pohida, T. J., 2003, Stochastic excitation and Hadamard correlation spectroscopy with bandwidth extension in RF FT-EPR, J. Magn. Reson. 162: 35–45.
Quine, R. W., Rinard, G. W., Eaton, S. S. and Eaton, G. R., 2002, A pulsed and continuous wave 250 MHz electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometer, Conc. Magn. Reson. (Magn. Reson. Engineer.) 15: 59–91.
Ramachandran, G. N. and Lakshminarayanan, A. V., 1971, Three-dimensional reconstruction from radiographs and electron-micrographs: application of convolutions instead of Fourier transforms, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68: 2236–2240.
Rinard, G. A., Quine, R. W., Eaton, S. S. and Eaton, G. R., 1993, Microwave coupling structures for spectroscopy, J. Magn. Reson. A 105: 137–144.
Rinard, G. A., Quine, R. W., Eaton, S. S., Eaton, G. R. and Froncisz, W., 1994, Relative benefits of overcoupled resonators vs inherently low-Q resonators for pulsed magnetic resonance, J. Magn. Reson. A. 108: 71–81.
Rinard, G. A., Quine, R. W., Harbridge, J. R., Song, R. T., Eaton, G. R, and Eaton, S. S., 1999a, Frequency dependence of EPR signal-to-noise, J. Magn. Reson. 140: 218–227.
Rinard, G. A., Quine, R. W., Song, R. T., Eaton, G. R. and Eaton, S. S., 1999b, Absolute EPR spin echo and noise intensities, J. Magn. Reson. 140: 69–83.
Rinard, G. A., Eaton, S. S., Eaton, G. R., Poole, Jr., C. P. and Frach, H. A., 1999c, Electron spin resonance sensitivity, in Handbook of Electronm Spin Resonance, vol. 2, C. P. Poole, Jr., and H. A. Farach, eds., API Press.
Rinard, G. A., Quine, R. W., Eaton, S. and Eaton, G. R., 2002a, Frequency dependence of EPR signal intensity, 250 MHz to 9.1 GHz, J. Magn. Reson. 156: 113–121.
Rinard, G. A., Quine, R. W., Eaton, G. R. and Eaton, S. S. 2002b, 250 MHz Crossed loop resonator for pulsed electron paramagnetic resonance, Magn. Reson. Engineer. 15, 37–46.
Rinard, G. A., Quine, R. W., Eaton, S. S., G. R. Eaton, S. S., 2004, Frequency dependence of EPR sensitivity, Biological Magnetic Resonance, 21, in press.
Rollett, J. S. and Higgs, L. S., 1962, Correction of spectroscopic line profiles for instrumental broadening by a Fourier analysis method, Proc. Roy. Soc. Land. 79: 87–91.
Sakamoto, Y., Hirata, H. and Ono, M., 1995, Design of a Multicoupled Loop-Gap Resonator Used for Pulsed Electron-Paramagnetic-Resonance Measurements, IEEET Microw. Theory 43: 1840–1847.
Savitzky, A. and Golay, M. J. E., 1964, Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures, Anal. Chem. 36: 1627–1639.
Shepp, L. A., 1980, Computerized tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance, J. Comp. Assist. Tomogr. 4: 94–107.
Shepp, L. A. and Logan, B. F., 1974, The Fourier reconstruction of a head section, IEEE Trans. Nuc. Sci. NS-21: 21–43.
Subramanian, S., Murugesan, R., Devasahayam, N., Cook, J. A., Afeworki, M., Pohida, T., Tschudin, R. G., Mitchell, J. B. and Krishna, M. C., 1999, High-speed data acquisition system and receiver configurations for time-domain radiofrequency electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging, J. Magn. Reson. 137: 379–388.
Subramanian, S., Yamada, K., Irie, A., Murugesan, R., Cook, J. A., Devasahayam, N., Van Dam, G. M., Mitchell, J. B. and Krishna, M. C., 2002, Noninvasive in vivo oximetric imaging by radiofrequency FT EPR, Magn. Reson. Med. 47: 1001–1008.
Swartz, H. M. and Walczak, T., 1998, Developing in vivo EPR oximetry for clinical use, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 454: 243–252.
Utsumi, H., Takeshita, K., Miura, Y., Masuda, S. and Hamada, A., 1993, In vivo EPR measurement of radical reaction in whole mice-influence of inspired oxygen and ischemia-reperfusion injury on nitroxide reduction, Free Rad. Res. Comm. 19: S219–227.
Von Schulthess, G. K., ed., 2000, Clinical Positron Emission Tomography (PET): Correlation with Morphological Cross-Sectional Imaging Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia.
Weil, J. A., Bolton, J. R. and Wertz, J. E.,1994, Electron Paramagnetic Resonance-Elementary Theory and Practical Applications, Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Wuthrich, K.,1995, NMR in Structural Biology World Scientific, London.
Yamada, K. I., Murugesan, R., Devasahayam, N., Cook, J. A., Mitchell, J. B., Subramanian, S. and Krishna, M. C., 2002, Evaluation and comparison of pulsed and continuous wave Radiofrequency electron paramagnetic resonance techniques for in vivo detection and imaging of free radicals, J. Magn. Reson. 154: 287–297.
Yong, L., Harbridge, J., Quine, R. W., Rinard, G. A., Eaton, S. S., Eaton, G. R., Mailer, C., Barth, E. and Halpern, H. J., 2001, Electron spin relaxation of triarylmethyl radicals in fluid solution, J. Magn. Reson. 152: 156–161.
Zavoisky, E., 1945, Spin-magnetic resonance in paramagnetics, J. Phys. E 9: 245–249.
Ziessow, D. and Bluemich, B., 1974, Hadamard-NMR-spektroskopie, Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 11: 1168–1179.
Zweier, J. L., Wang, P. H. and Kuppusamy, P., 1995, Direct measurement of nitric-oxide generation in the ischemic heart using electron-paramagnetic-resonance spectroscopy, J. Biol. Chem. 270: 304–307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer Science + Business Media, Inc.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Subramanian, S., Krishna, M.C. (2005). Time-Domain Radio Frequency EPR Imaging. In: Eaton, S.R., Eaton, G.R., Berliner, L.J. (eds) Biomedical EPR, Part A: Free Radicals, Metals, Medicine, and Physiology. Biological Magnetic Resonance, vol 23. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-26741-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-26741-7_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-0-306-48506-0
Online ISBN: 978-0-387-26741-8
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)