Conclusion
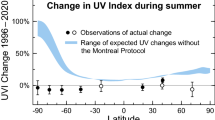
Exposure of biota to UV radiation is now recognized as largely detrimental even at levels typical of the natural atmosphere. The main factors controlling atmospheric UV radiation (solar zenith angle, ozone column amount, clouds and aerosols, surface reflections) are fairly well understood in principle, but usually at least some of these are not known for an arbitrary location and time of interest. Reductions in stratospheric ozone have so far caused increases in biologically effective UV radiation of some 5–15% at middle latitudes, with larger percent increases in polar regions, but no significant increases in the tropics. Such increases, while difficult to detect directly, are estimated to have substantial public health impacts, e.g., on skin cancer incidence. International agreements to phase out the production and release of ozone-destroying chemicals are intended to prevent further depletion of stratospheric ozone, and lead to full recovery by the middle of the next century. The success of such agreements is contingent on strict global compliance, and assumes that our current understanding of ozone chemistry, which in many details is still evolving, is at least sufficient today to allow prediction of future atmospheric responses to anthropogenic emissions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACGIH, 1992, 1991–1992 Threshold Limit Values, American Conference of Governmental and Industrial Hygienists.
Andrady, A. L., Torikai, A., and Fueki, K., 1989, Photodegradation of rigid PVC formulations III. Wavelength sensitivity to light-induced yellowing by monochromatic light, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 37:935–946.
Bates, D. R., and Nicolet, M., 1950, Atmospheric hydrogen, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 62:106.
Booth, R. C., and Madronich, S., 1994, Radiation amplification factors—improved formulation accounts for large increases in ultraviolet radiation associated with Antarctic ozone depletion, in Ultraviolet Radiation and Biological Research in Antarctica (C. S. Weiler and P. A. Penhale, eds.), pp. 39–42, American Geophysical Union Antarctic Research Series, Washington, DC.
Boucher, N., Prezelin, B. B., Evens, T, Jovine, R., Kroon, B., Moline, M. A., and Schofield, O., 1994, Icecolors’ 93: Biological weighting function for the ultraviolet inhibition of carbon fixation in a natural antarctic phytoplankton community, Antarct. J.-Review 1994, pp. 272–275.
Brasseur, G. P., Granier, C., and Walters, S., 1990, Future changes in stratospheric ozone and the role of heterogeneous chemistry, Nature 348:626–628.
Brûhl, C., and Crutzen, P. J., 1989, On the disproportionate role of tropospheric ozone as a filter against solar UV-B radiation, Geophys. Res. Lett. 16:703–706.
Caldwell, M. M., Camp, L. B., Warner, C. W., and Flint, S. D., 1986, Action spectra and their key role in assessing biological consequences of solar UV-B radiation change, in Stratospheric Ozone Reduction, Solar Ultraviolet Radiation and Plant Life (R. C. Worrest and M. M. Caldwell, eds.), pp. 87–111, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Chapman, S., 1930, On ozone and atomic oxygen in the upper atmosphere, Philos. Mag. 10:369.
Crutzen, P. J., 1970, The influence of nitrogen oxide concentrations on the atmospheric ozone content, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 96:320.
De Fabo, E. C., and Noonan, F. P., 1983, Mechanism of immune suppression by ultraviolet radiation in vivo. I. Evidence for the existence of a unique photoreceptor in skin and its role in photoimmunology, J. Exp. Med. 158:84–98.
de Gruijl, F. R., and van der Leun, J. C., 1994, Estimate of the wavelength dependency of ultraviolet carcinogenesis and its relevance to the risk assessment of a stratospheric ozone depletion, Health Phys. 4:317–323.
DeLuisi, J. J., 1993, Possible calibration shift in the U.S. surface UV network instrumentation 1979 to 1985, Paper presented at the U.S. Department of Energy UV-B Critical Issues Workshop, Cocoa Beach, FL, 24–26 February.
Farman, J. C., Gardiner, B. G., and Shanklin, J. D., 1985, Large losses of total ozone in Antarctica reveal seasonal ClOχ/NOχ interaction, Nature 315:207–210.
Frederick, J. E. and Snell, H. E., 1990, Tropospheric influence on solar ultraviolet radiation: The role of clouds, J. Climate 3:373–381.
Herman, J. R., Bharlia, P. K., Ziemke, J., Ahmad, Z., and Larko, D., 1996, UV-B increases (1979–1992) from decreases in total ozone, Geophys. Res. Lett. 23:2117–2120.
Hoffman, D. J., and Solomon, S., 1989, Ozone destruction through heterogeneous chemistry following the eruption of El Chichon, J. Geophys. Res. 94:5029–5041.
Liu, S. C., McKeen, S. A., and Madronich, S., 1991, Effects of anthropogenic aerosols on biologically active ultraviolet radiation, Geophys. Res. Lett. 18:2265–2268.
Long, C. S., Miller, A. J., Lee, H.-T, Wild, J. D., Przywarty, R. C., and Hufford, D., 1996, Ultraviolet index forecasts issued by the National Weather Service, Hull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 77:729–748.
Madronich, S., 1993a, The atmosphere and UV-B radiation at ground level, in Environmental UV Photobiology (L. O. Björn and A. R. Young, ed.s.), pp. 1–39, Plenum Press, New York.
Madronich, S., 1993b, UV radiation in the natural and perturbed atmosphere, in Environmental Effects of UV (Ultraviolet) Radiation (M. Tevini, ed.), pp. 17–69, Lewis Publisher, Boca Raton, FL.
Madronich, S., and de Gruijl, F. R., 1993, Skin cancer and UV radiation. Nature 366:23.
Madronich, S. and Granier, C., 1994, Tropospheric chemistry changes due to increases in UV-B radiation, in Stratospheric Ozone Depletion/UV-B Radiation in the Biosphere (H. R. Biggs and M. E. B. Joyner, eds.), pp. 3–10, NATO Advanced Research Workshop, Springer-Verlag.
Madronich, S., McKenzie, R. L., Bjorn, L., and Caldwell, M. M., 1995, Changes in ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth’s surface, Ambio 24:143–152.
McKinlay, A. F., and Diffey, B. L., 1987, A reference action spectrum for ultraviolet induced erythema in human skin, in Human Exposure to Ultraviolet Radiation: Risks and Regulations (W. R. Passchler and B. F. M. Bosnajokovic, eds.), pp. 83–87, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Pitts, D. G., Cullen, A. P., and Hacker, P. D., 1977, Ocular effects of ultraviolet radiation from 295 to 365 nm, Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 16:932–939.
Quaite, F. E., Sutherland, B. M., and Sutherland, J. C., 1992, Action spectrum for DNA damage in alfalfa lowers predicted impact of ozone depletion, Nature 358:576–578.
Rowland, F. S., and Molina, M. J., 1975, Chlorofluoromethanes in the environment, Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 13:1–35.
Schafer, J. S., Saxena, V. K., Wenny, B. N., Barnard, W., and DeLuisi, J. J., 1996, Observed influence of clouds on ultraviolet-B radiation, Geophys. Res. Lett. 23:2625–2628.
Scotto, J., Cotton, G., Urbach, F., Berger, D., and Fears, T., 1988, Biologically effective ultraviolet radiation: Surface measurements in the United States, 1974 to 1985, Science 239:762–764.
Setlow, R. B., 1974, The wavelengths in sunlight effective in producing skin cancer: A theoretical analysis, Proc.. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 71:3363–3366.
Setlow, R. B., Grist, E., Thompson, K., and Woodhead, A. D., 1993, Wavelengths effective in induction of malignant melanoma, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:6666–6670.
Slaper, H., Velders, G. J. M., Daniel, J. S., de Gruijl, F. R., and van der Leun, J. C., 1996, Scenario study on ozone depletion and skin cancer incidence illustrating the Vienna Convention achievements, Nature 384:256–258.
Smith, R. C., Prezelin, B. B., Baker, K. S., Bidigare, R. R., Boucher, N. P., Coley, T, Karentz, D., Maclntyre, S., Matlick, H. A., Menzies, D., Ondrusek, M., Wan, Z., and Waters, K. J., 1992, Ozone depletion: Ultraviolet radiation and phytoplankton biology in Antarctic waters, Science 255:952–959.
Solomon, S., 1990, Progress towards a quantitative understanding of Antarctic ozone depletion. Nature 347:347–354.
Steinmetz, V, and Wellmann, E., 1986, The role of solar UV-B in growth regulation of cress (Lepidium sativum l.) seedlings, Photochem. Photobiol. 43:189–193.
Stolarski, R. S., and Cicerone, R. J., 1974, Stratospheric chlorine: A possible sink for ozone, Can. J. Chem. 52:1610.
Stolarski, R. S., Bloomfield, P., McPeters, R. D., and Herman, J. R., 1991, Tolal ozone trends deduced from Nimbus 7 TOMS data, Geophys. Res. Lett. 18:1015–1018.
UNHP, 1994, Environmental Effects of Stratospheric Ozone Depletion-1994 Update (J. van der Leun, M. Tevini, and X. Tang, eds.). United Nations Environmental Programme, Nairobi, Kenya.
US Standard Atmosphere, 1976, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, United States Air Force, Washington, October.
Weatherhead, E. C, Tiao, G. C., Reinsel, G. C, Frederick, J. E., DeLuisi, J. J., Choi, D., and Tam, W., 1997, Analysis of long-term behavior of ultraviolet radiation measured by Robertson-Berger meters at 14 sites in the United States, J. Geophys. Res. 102:8737–8754.
WMO, 1994a, Scientific Assessment of Stratospheric Ozone: 1994 (D. Albritton and R. Watson, eds.), World Meteorological Organization, Global Of.one Research and Monitoring Project, Report No. 37.
WMO, 1994b, Report of the WMO Meeting of Experts on UV-B Measurements, Data Quality and Standardization of UV Indices, World Meteorological Organization Global Atmosphere Watch, Report No. 95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Madronich, S. (2002). Stratospheric Ozone and Its Effects on the Biosphere. In: Reactive Oxygen Species in Biological Systems. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-46806-9_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-46806-9_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-0-306-45756-2
Online ISBN: 978-0-306-46806-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive