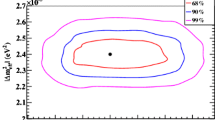
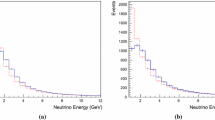
Abstract
The main goal of the magnetized Iron CALorimeter detector (ICAL), proposed to be built in the India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO) laboratory, is to study atmospheric neutrino oscillations. The interactions of atmospheric neutrinos with the rock material around the detector produces upward-going muons which carries the signature of oscillation. We therefore present the oscillation sensitivity results using upward-going muons and discuss their significance in INO.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Nitta, Neutrino oscillation analysis of upward through-going and stopping Muons in super-kamiokande. PhD thesis, Department of Physics, Osaka University, 2003. http://www-sk.icrr.u-tokyo.ac.jp/sk/pub/nitta.pdf
M.S. Athar et al., India-based neutrino observatory: project report volume I. http://www.ino.tifr.res.in/ino/OpenReports/INOReport.pdf
R. Kanishka et al., Simulations study of Muon response in the peripheral regions of the iron calorimeter detector at the India-based neutrino observatory, submitted to JINST 2014
B. Satyanarayana, Design and characterisation studies of resistive plate Chambers. PhD thesis, Department of Physics, IIT Bombay, PHY-PHD-10-701 (2009)
A. Chatterjee et al., A simulations study of the Muon response of the iron calorimeter detector at the India-based neutrino observatory. JINST 9 P07001 (2014). arXiv:1405.7243
Infolytica Corp., Electromagnetic field simulation software. http://www.infolytica.com/en/products/magnet/
D. Casper, The Nuance neutrino physics simulation, and the future. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 112 161–170 (2002). arXiv:0208030
S. Agostinelli et al. GEANT4 collaboration. Geant4: a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 506 250–303 (2003). http://geant4.cern.ch
T. Thakore, A. Ghosh, S. Choubey, A. Dighe, The reach of INO for atmospheric neutrino oscillation parameters. JHEP 1305, 058 (2013). arXiv:1303.2534
Acknowledgments
We thank INO collaboration for the help and support. We also thank all the INO Physics group coordinators for their comments and suggestions. R. Kanishka acknowledges UGC/DAE/DST (Govt. of India) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kanishka, R., Bhatnagar, V., Indumathi, D. (2016). Oscillation Studies with Upward-Going Muons Using INO-ICAL. In: Bhuyan, B. (eds) XXI DAE-BRNS High Energy Physics Symposium. Springer Proceedings in Physics, vol 174. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25619-1_46
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25619-1_46
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-25617-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-25619-1
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)