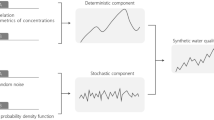
Abstract
Discussed are the methods of stochastic modeling the precipitation runoff time series and fields. Discussed are the structural attributes, scope, boundary conditions and various improvements of the univariate Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and the multivariate Transfer Function Model (TFM). Presented are the comparative studies of existing models of the neural network. An attempt is made to investigate various geographical locations and various applications of the river runoff forecast.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
R. J. Abrahart and L. See, “Comparing Neural Network and Autoregressive Moving Average Techniques for the Provision of Continuous River Flow Forecasts in Two Contrasting Catchments,” Hydrol. Processes, No. 11—12, 14 (2000).
R. J. Abrahart and L. See, “Multi-model Data Fusion for River Flow Forecasting: An Evaluation of Six Alternative Methods Based on Two Contrasting Catchments,” Hydrol. and Earth Syst. Sci., No. 4, 6 (2002).
S. Abudu, C. L. Cui, J. P. King, and A. Kaiser, “Comparison of Performance of Statistical Models in Forecasting Monthly Streamflow of Kizil River, China,” Water Sci. and Eng., No. 3, 3 (2010).
A. Agarwal, R. K. Rai, and A. Upadhyay, “Forecasting of Runoff and Sediment Yield Using Artificial Neural Networks,” J. Water Res. and Protec., 1 (2009).
H. Akaike, “A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification,” IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr., No. 6, 19 (1974).
ASCE Committee on Surface—Water Hydrology, “Research Needs in Surface-Water Hydrology,” J. Hydraul. Div. Proc. Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng., 91 (1965).
A. G. Awadallah and J. Rousselle, “Improving Forecasts of Nile Flood Using SST Inputs in TFN Model,” J. Hydrol. Eng., No. 4, 5 (2000).
H. Awwad, J. Valdes, and P. Restrepo, “Streamflow Forecasting for Han River Basin, Korea,” J. Water Resour. Planning Management, No. 5, 120 (1994).
S. K. K. Babu, K. Karthikeyan, M. V. Ramanaiah, and D. Ramanah, “Prediction of Rainfall Flow Time Series Using Autoregressive Models,” Adv. Appl. Sci. Res., No. 2, 2 (2011).
P. Bartolini and J. D. Salas, “Modeling of Streamflow Processes at Different Time Scales,” Water Resour. Res., No. 8, 29 (1993).
M. F. P. Bierkens and G. Frans, Course Guide Stochastic Hydrology (GE04-44200) (Faculty of Geosciences, Department of Physical Geography, Utrecht University, Utrecht, 2014).
G. E. P. Box and G. M. Jenkins, Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control (Holden Day, San Francisco, CA, 1970).
G. E. P. Box and G. M. Jenkins, Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control (Holden Day, San Francisco, CA, 1976).
G. E. P. Box, G. M. Jenkins, and G. C. Reinsel, Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 3rd ed. (Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1994).
R. L. Bras and I. Rodriguez Iturbe, Random Functions and Hydrology (Addison Wesley Publishing Company, Reading, MA, 1985).
P. J. Brockwell and R. A. Davis, Time Series: Theory and Methods (Springer, New York, 1987).
P. J. Brockwell and R. A. Davis, Introduction to Time Series and Forecasting (Springer-Verlag, Inc., New York, 2002).
P. M. T. Broersen and A. H. Weerts, “Automatic Error Correction of Rainfall—Runoff Models in Flood Forecasting Systems,” in Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (Ottawa, Canada, 2005).
M. Bruen and J. Yang, “Functional Networks in Real-time Flood Forecasting—A Novel Application,” J. Hydrol., 28 (2005).
P. Burlando, R. Rosso, L. G. Cadavid, and J. D. Salas, “Forecasting of Short-term Rainfall Using ARMA Models,” J. Hydrol., 144 (1993).
L. Cao, A. Mees, and K. Judd, “Dynamics from Multivariate Time Series,” Physica D, 121 (1998).
M. Castellano, M. W. Gonzalez, B. M. Febrero, et al., “Modeling of The Monthly and Daily Behavior of the Runoff of the Xallas River Using Box—Jenkins and Neural Networks Methods,” J. Hydrol., 296 (2004).
T. J. Chang, “Microcomputer Application in Stochastic Hydrology Process,” J. Hydraul. Div. Proc. Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng. (1985).
T. J. Chang, M. L. Kavas, and I. W. Delleur, “Modeling of Sequences of Wet and Dry Days by Binary Discrete Autoregressive Moving Average Processes,” J. Appl. Meteorol. (1984).
T. J. Chang, M. L. Kavas, and I. W. Delleur, “Daily Precipitation Modeling by Discrete Autoregressive Moving Average Processes,” Res. J. Water Res., No. 5, 20 (1984).
T. J. Chang, M. L. Kavas, and I. W. Delleur, “Application of Discrete Autoregressive Moving Average Model for Estimation of Daily Runoff,” J. Hydrol., 91 (1987).
C. Chatfield, The Analysis of Time Series: An Introduction, 5th ed. (Chapman and Hall, London, 1996).
S. Chattopadhyay and G. Chattopadhyay, “Univariate Modelling of Summer-Monsoon Rainfall Time Series: Comparison between ARIMA and ARNN,” Comptes Rendus Geoscience, No. 2, 342 (2010).
Y. Cheng, “Evaluating an Autoregressive Model for Stream Flow Forecasting,” in Conference Proceeding of Hydraulic Engineering (1994).
F. H. S. Chiew, M. J. Stewardson, and T. A. McMahon, “Comparison of Six Rainfall-Runoff Modelling Approaches,” J. Hydrol., 147 (1993).
H. K. Cigizoglu, “Incorporation of ARMA Models into Flow Forecasting by Artificial Neural Networks,” Environmetrics, No. 4, 14 (2003).
P. Claps, F. Rossi, and C. Vitale, “Conceptual Stochastic Modeling of Seasonal Runoff Using Autoregressive Moving Average Models and Different Time Scales of Aggregation,” J. Water Resour. Res., No. 8, 29 (1993).
Chaitanya Damle, Flood Forecasting Using Time Series Data Mining, A thesis (M.S.) (Department of Industrial and Management Systems Engineering, College of Engineering, University of South Florida, 2005).
M. A. P. DeSilva, “A Time Series Model to Predict the Runoff of Catchment of The Kalu Ganga Basin,” J. National Science Foundation, Sri Lanka, No. 2, 34 (2006).
M. El-Fandy, Z. Ashour, and S. Taiel, “Time Series Models Adoptable for Forecasting Nile Floods and Ethiopian Rainfalls,” Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc., No. 1, 75 (1994).
C. H. Fajardo Toro, D. Gonzalez Peca, B. Soto Gonzalez, and F. F. Riverola, “Water Flows Modelling and Forecasting Using a RBF Neural Network,” Sistemas & Telematica, ICESI No. 12, 6 (2008).
M. R. Ghanbarpour, K. C. Abbaspour, G. Jalalvand, and G. A. Moghaddam, “Stochastic Modeling of Surface Stream Flow at Different Time Scales: Sangsoorakh Karst Basin, Iran,” J. Cave and Karst Studies, No. 1, 72 (2010).
D. Graupe, D. Isailovic, and V. Yevjevich, “Prediction Model for Runoff from Karstified Catchments,” in Proceedings of the U.S.—Yugoslavian Symposium on Karst Hydrology and Water Resources (Dubrovnik, June 2–7, 1975).
K. Helman, “SARIMA Models for Temperature and Precipitation Time Series in the Czech Republic for the Period 1961–2008,” J. Appl. Mathem., No. 3, 4 (2011).
K. W. Hipel and A. I. McLeod, Time Series Modeling of Water Resources and Environmental Systems (Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 1994).
K. Hsu, H. V. Gupta, and S. Sorooshian, “Artificial Neural Network Modeling of the Rainfall-Runoff Process,” J. Water Resour. Res., No. 10, 31 (1995).
A. J. Jakeman and G. M. Hornberger, “How Much Complexity Is Warranted in a Rainfall-Runoff Model?” J. Water Resour. Res., 29 (1993).
A. J. Jakeman, M. A. Greenway, and J. N. Jenings, “Time-series Models for the Prediction of Stream Flow in a Karst Drainage System,” J. Hydrol., No. 1, 23 (1984).
A.W. Jayawardena and F. Lai, “Analysis and Prediction of Chaos in Rainfall and Stream Flow Time Series,” J. Hydrol., 153 (1994).
A. M. B Karim, A. F. Sheta, and A. K. Khaled, “Forecasting River Flow in the USA: A Comparison between Auto-regression and Neural Network Non-parametric Models,” J. Comp. Sci., No. 10, 2 (2006).
J. M. Kihoro, R. O. Otieno, C. Wafula, “Seasonal Time Series Forecasting: A Comparative Study of ARIMA and ANN Models,” Afric. J. Sci. and Technol., No. 2, 5 (2004).
T. W. Kim and J. B. Valdes, “Nonlinear Model for Drought Forecasting Based on a Conjunction of Wavelet Transforms and Neural Networks,” J. Hydrol. Eng. (of ASCE), No. 6, 8 (2003).
C. C. Kisiel, “Time Series Analysis of Hydrologic Data,” in Advances in Hydroscience, Ed. by V. T. Chow, Vol. 5 (Academic Press, New York, 1969).
O. Kisi, “Daily River Flow Forecasting Using Artificial Neural Networks and Autoregressive Models,” Turk. J. Eng. and Environ. Sci., No. 1, 29 (2005).
U. C. Kothyari and V. P. Singh, “A Multiple-input Single-output Model for Flow Forecasting,” J. Hydrol., 220 (1999).
D. Koutsoyiannis, “Generalized Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Simulation and Forecast of Hydrologic Time Series,” J. Water Resour. Res., 36 (2000).
J. T. Kuo and Y. H. Sun, “An Intervention Model for Average 10 Day Stream Flow Forecast and Synthesis,” J. Hydrol., No. 1, 151 (1993).
E. M. Langu, “Detection of Changes in Rainfall and Runoff Patterns,” J. Hydrol., 147 (1993).
P. Lardet and C. Obled, “Real-time Flood Forecasting Using a Stochastic Rainfall Generator,” J. Hydrol., 162 (1994).
A. J. Lawrance and N. T. Kottegoda, “Stochastic Modelling of Riverflow Time Series,” J. Roy. Statis. Soc. Amer., 140 (1977).
C. C. Lu, C. H. Chen, I. F. Yau, et al., “Integration of Transfer Function Model and Back Propagation Neural Network for Forecasting Storm Sewer Flow in Taipei Metropolis,” Stochastic Environ. Res. Risk Assessment, 20 (2005).
H. Madson, M. B. Butts, S. T. Khu, and S. Y. Liong, “Data Simulation in Rainfall-runoff Forecasting,” in 4th International Conference on Hydroinformatics (Cedar Rapids, Iowa, USA, 2000).
M. Mahsin, Y. Akhter, M. Begum, “Modeling Rainfall in Dhaka Division of Bangladesh Using Time Series Analysis,” J. Math. Modelling and Application, No. 5, 1 (2012).
D. R. Maidment, Handbook of Hydrology (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1993).
S. Makridakis, S. C. Wheelwright, and R. J. Hyndman, Forecasting: Methods and Applications, 3rd ed. (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998).
C. M. Maria, G. M. Wenceslao, F. B. Manuel, et al., “Modelling of the Monthly and 13 Daily Behaviour of the Discharge of the Xallas River Using Box—Jenkins and Neural Networks Methods,” J. Hydrol., 296 (2004).
A. Mauludiyanto, G. Hendrantoro, M. H. Purnomo, et al., “ARIMA Modeling of Tropical Rain Attenuation on a Short 28-GHz Terrestrial Link,” IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Lett., 9 (2010).
A. I. McKerchar and J. W. Delleur, “Applications of Seasonal Parametric Linear Stochastic Models to Monthly Flow Data,” J. Water Resour. Res., No. 2, 10 (1974).
J. Meher and R. Jha, “Time-series Analysis of Monthly Rainfall Data for the Mahanadi River Basin, India,” Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions (SCAR), No. 1, 5 (2013).
A. Mishra, T. Hata, and A. W. Abdelhadi, “Models for Recession Flows in the Upper Blue Nile River,” Hydrol. Processes, 18 (2004).
R. Modarres and T. B. M. J. Ouarda, “Modelling Heteroscedasticty of Streamflow Times Series,” Hydrol. Sci. J., No. 1, 58 (2013).
B. R. Mohamad and N. Mojtaba, “Developing of Halil River Rainfall Runoff Model Using Conjuction of Wavelet Transform and ANN,” Res. J. Environ. Sci., No. 5, 2 (2008).
K. Mohammadi, H. R. Eslami, and D. Dardashti, “Comparison of Regression, ARIMA and ANN Models for Reservoir Inflow Forecasting Using Snowmelt Equivalent (a Case Study of Karaj),” J. Agr. and Sci. Technol., 7 (2005).
M. S. Mondal and S. A. Wasimi, “Periodic Transfer Function-Noise Model for Forecasting,” J. Hydrol. Eng., No. 5, 10 (2005).
P. E. Naill and M. Momani, “Time Series Analysis Model for Rainfall Data in Jordan: Case Study for Using Time Series Analysis,” Amer. J. Environ. Sci., No. 5, 5 (2005).
R. Nigam, Development of Computational Modeling Framework for River Flow Forecasting, Ph.D. Thesis, (Dept. of Mathematics, M.A.N.I.T., Bhopal, 2012).
R. Nigam, S. Nigam, and S. K. Mittal, “Modeling Tropical River Runoff: A Time Dependant Approach,” Science in Cold and Arid Regions, No. 3, 6 (2014).
D. J. Noakes, A. I. McLeod, and K. W. Hipel, “Forecasting Monthly River Flow Time Series,” Int. J. Forecast., No. 2, 1 (1985).
B. W. Otok and Suhartono, “Development of Rainfall Forecasting Model in Indonesia by Using ASTAR, Transfer Function, and ARIMA Methods,” Europ. J. Sci. Res., No. 3, 38 (2009).
U. Ozis and N. Keloglu, “Some Features of Mathematical Analysis of Karst,” in Proceedings of U.S.—Yugoslavian Symposium on Karst Hydrology and Water Resources (Dubrovnik, 1976).
A. Porporato and L. Ridolfi, “Clues to Existence of Deterministic Chaos in River Flow,” Int. J. Modern Physics B, 10 (1996).
A. Porporato and L. Ridolfi, “Nonlinear Analysis of River Flow Time Sequences,” J. Water Resour. Res., No. 6, 33 (1997).
A. Porporato and L. Ridolfi, “Multivariate Nonlinear Prediction of River Flows,” J. Hydrol., No. 1—4, 248 (2001).
R. Price, “The Growth and Significance of Hydroinformatics,” in River Basin Modelling for Flood Risk Mitigation, Ch. 5 (Springer, 2005).
A. T. Rabenja, A. Ratiarison, and J. M. Rabeharisoa, “Forecasting of the Rainfall and the Discharge of the Namorona River in Vohiparara and FFT Analyses of These Data,” in Proceedings of 4th International Conference in High-Energy Physics (Antananarivo, Madagascar, 2009).
A. Reddy, S. Babu, and P. Mallikarjuna, “Rainfall—Runoff Modeling: Combination of Simple Time-series, Linear Autoregressive and Artificial Neural Network Models,” WSEAS Transactions on Fluid Mechanics, No. 2, 3 (2008).
J. D. Salas, J. W. Deulleur, V. Yevjevich, and W. L. Lane, Applied Modeling of Hydrologic Time Series (Water Resources Publications, Littleton, Colorado, USA, 1980).
J. D. Salas, J. W. Deulleur, V. Yevjevich, and W. L. Lane, Applied Modeling of Hydrologic Time Series (Water Resources Publications, Littleton, Colorado, USA, 1985).
R. Samsudin, P. Saad, and A. Shabri, “River Flow Time Series Using Least Squares Support Vector Machines,” Hydrol. and Earth Syst. Sci., 15 (2011).
BuHamra Sana, S. Nejib, and G. Mahmoud, “The Box—Jenkins Analysis and Neural Networks: Prediction and Time Series Modeling,” Appl. Math. Modeling, 27 (2003).
G. Schwarz, “Estimating the Dimension of a Model,” Ann. Statist., 6 (1978).
S. A. Shamsnia, N. Shahidi, A. Liaghat, et al., “Modeling of Weather Parameters Using Stochastic Methods (ARIMA Model) (Case Study: Abadeh Region, Iran),” in International Conference on Environment and Industrial Innovation, Vol. 12 (2011).
S. Sharma, S. Isik, P. Srivastava, and L. Kalin, “Deriving Spatially Distributed Precipitation Data Using the Artificial Neural Network and Multi-linear Regression Models,” J. Hydrol. Eng., No. 2, 18 (2013).
M. Shiiba, X. Laurenson, and Y. Tachikawa, “Real-time Stage and Discharge Estimation by a Stochastic-dynamic Flood Routing Model,” Hydrol. Processes, 14 (2000).
M. Shiiba, T. Takasao, and E. Nakakita, “Investigation of Short-term Rainfall Prediction Method by a Translation Model,” in Proceedings of 28th Japanese Conference on Hydraulics (JSCE, 1984).
D. P. Solomatine, “Data-driven Modeling and Computational Intelligence Methods in Hydrology,” in Encyclopedia of Hydrological Sciences (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2005).
V. K. Somvanshi, O. P. Pandey, P. K. Agrawal, et al., “Modelling and Prediction of Rainfall Using Artificial Neural Network and ARIMA Techniques,” J. Ind. Geophys. Union, No. 2, 10 (2006).
Y. Tachikawa, Y. Komatsu, and M. Shiiba, “Stochastic Modelling of the Error Structure of Real-time Predicted Rainfall and Rainfall Field Generation,” Weather Radar Information and Distributed Hydrological Modelling, IAHS, 282 (2003).
T. Takasao, M. Shiiba, and E. Nakakita, “A Real-time Estimation of the Accuracy of Short-term Rainfall Prediction Using Radar,” Stochastic and Statistical Methods in Hydrology and Environmental Engineering, 2 (1994).
P. C. Tao and J. W. Delleur, “Seasonal and Nonseasonal ARMA Models in Hydrology,” J. Hydraul. Eng., ASCE, HY10, 102 (1976).
R. M. Thompstone, K. W. Hipel, and A. I. Mcleod, “Forecasting Quarter-monthly River Flow,” J. Amer. Water Res. Associat., No. 5, 21 (1985).
E. Todini, “Using a Desk-top Computer for an Online Flood Warning System,” IBM, J. Res. and Develop., 22 (1978).
E. Todini, “Hydrological Catchment Modeling: Past, Present and Future,” Hydrol. and Ear. Syst. Sci., No. 3, 11 (2007).
E. Toth, A. Brath, A. Montanari, “Comparison of Short-term Rainfall Prediction Models for Real-time Flood Forecasting,” J. Hydrol. (Elsevier), 239 (2000).
F. M. Tseng, H. C. Yub, G. H. Tzeng, “Combining Neural Network Model with Seasonal Time Series ARIMA Model,” Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 69 (2002).
W. Vandaele, Applied Time Series and Box-Jenkins Models (Academic Press, New York, 1983).
B. Volkan and A. Onkur, “A Study on Modeling Daily Mean Flow with MLR, ARIMA and RBFNN,” in BALWOIS 2010—Ohrid, Republic of Macedonia—25, 2010.
Y. C. Wang, S. T Chen, P. S. Yu, and T. C. Yang, “Storm-even Rainfall-Runoff Modelling Approach for Ungauged Sites in Taiwan,” Hydrol. Processes, 22 (2008).
W. D. Weeks and W. C. Boughton, “Tests of ARMA Model Forms for Rainfall-Runoff Modeling,” J. Hydrol., 91 (1987).
A. Weigend and N. Gershenfeld, Time Series Prediction: Forecasting the Future and Understanding the Past (Perseus Books, Santa Fe, 1995).
C. L. Wu, K. W. Chau, and Y. S. Li, “Predicting Monthly Streamflow Using Data-driven Models Coupled with Data-preprocessing Techniques,” Water Resour. Res., 45 (2009).
S. K. Yoon, M. Young, O. Tae-Suk, et al., “Application to Evaluation of Hydrological Time Series Forecasting for Long-term Runoff Simulation,” Geophys. Res. Abstracts, 12 (2010).
P. C. Young, “Advances in Real-time Flood Forecasting,” Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A, 360 (2002).
P. S. Yu, C. L. Liu, T. Y. Lee, “Application of Transfer Function Model to a Storage Runoff Process,” Stochast. and Statistical Methods in Hydrology and Environ. Eng., 3 (1994).
K. Yurekli, A. Kurung, and F. Ozturk, “Testing the Residuals of an ARIMA Model on the Cekerek Stream Watershed in Turkey,” Turk. J. Eng. and Environ. Sci., No. 2, 29 (2005).
X. Y. Yu, S. Y. Liong, and V. Babovic, “EC-SVM Approach for Real-time Hydrologic Forecasting,” J. Hydro-informatics, No. 3, 6 (2004).
J. M. Zaldivar, E. Gutierrez, I. M. Galvan, et al., “Forecasting High Waters at Venice Lagoon Using Chaotic Time Series Analysis and Non-linear Neural Networks,” J. Hydroinformatics, No. 1, 2 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R. Nigam, S. Nigam, S.K. Mittal, 2014, published in Meteorologiya i Gidrologiya, 2014, No. 11, pp. 56–73.
About this article
Cite this article
Nigam, R., Nigam, S. & Mittal, S.K. The river runoff forecast based on the modeling of time series. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 39, 750–761 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068373914110053
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068373914110053