Abstract
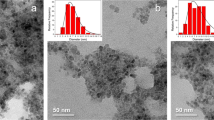
In this paper, water colloidal solutions of nanoparticles of magnetite (magnetic nanofluids, (MNFs)) are investigated by synchrotron X-ray diffraction (XRD) and small-angle scattering (SAXS). To prevent aggregation, nanoparticles are coated with polyacrylic acid (PAA) in a single solution and citric (CA) in the other solutions. In both cases, the maxima of the particle size distribution from SAXS (9–10 nm) correspond to the sizes of the magnetite crystallites that were estimated from the broadening of the diffraction lines. In addition, the SAXS data indicate the presence of a significant proportion of aggregates (up to 60 nm in diameter) in both colloidal solutions, although fundamental differences in the structures of aggregates between the MNFs stabilized by PAA and CA were not observed. In this study determination of the structural characteristics of MNFs were carried out in order to obtain stable dispersive non-aggregating nanoparticles of magnetite for use as contrast agents in magnetic resonance tomography, drug carriers, and other biomedical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. I. Baraton, Synthesis, Functionalization, and Surface Treatment of Nanoparticles (Am. Sci. Publ., Los-Angeles, CA, 2002).
M. V. Avdeev and V. L. Aksenov, Phys. Usp. 53, 971 (2010).
R. E. Rosensweig, Ferrohydrodynamics (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1985).
S. Taketomi and S. Chikazumi, Magnetic Fluids — Principle and Application (Nikkan Kogyo Shinbun, Tokyo, 1988; Mir, Moscow, 1993), p. 69.
S. Odenbach, Ferrofluids. Magnetically Controllable Fluids and their Applications, Lect. Notes in Physics, Vols. 233–251 (Springer, Berlin, 2002).
D. V. Orlov, Yu. A. Mikhalev, and A. P. Sizov, Magnetic Fluids in Engineering (Mashinostroenie, Moscow, 1993) [in Russian].
Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Magnetic Fluids, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 289 (2005).
Q. A. Pankhurst, J. Connolly, S. K. Jones, and J. Dobson, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36, R167 (2003).
I. Brigger, C. Dubernet, and P. Couvreur, Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 54, 631 (2002).
S. Mornet, S. Vasseur, F. Grasset, and E. Duguet, J. Mater. Chem. 14, 2161 (2004).
S. C. Wuang, K. G. Heoh, E. T. Kang, et al., Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 1723 (2006).
E. Duguet, S. Mornet, S. Vasseur, et al., Nanomedicine 1, 157 (2006).
J. P. Fortin, C. Wilhelm, J. Servais, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 2628 (2007).
M. V. Abdeev, B. Mucha, K. Lamszus, et al., Langmuir 26, 8503 (2010).
L. Vtkas, M. V. Avdeev, and D. Bica, “Magnetic Nanofluids: Synthesis and Structure,” in Nanoscience and Its Applications in Biomedicine, Ed. by D. Shi (Springer, Berlin, 2009), p. 645.
R. Massart, E. Dubois, V. Cabuil, and E. Hasmonay, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 149, 1 (1995).
A. Hajdu, E. Tombacz, E. Illes, et al., Progr. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 135, 29 (2008).
L. Vekas, M. V. Avdeev, and D. Bica, China Particuol. 5, 43 (2007).
E. Tombacz, D. Bica, A. Hajdu, et al., J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20, 204103 (2008).
V. Zavisova, M. Koneracká, M. Múčková, et al., J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1408 (2011).
D. L. Bica, L. Vekas, M. V. Avdeev, et al., J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 311, 17 (2007).
J. Halavaara, P. Tervahartiala, H. Isoniemi, and K. Hockerstedt, Acta Radiol. 43, 180 (2002).
S. Benderbous, C. Corot, P. Hacobs, and B. Bonnemain, Acad. Radiol. 3, 292 (1996).
A. A. Chernyshov, A. A. Veligzhanin, and Y. V. Zubavichus, Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. A 603, 95 (2009).
D. I. Svergun, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 25, 495 (1992).
P. V. Konarev, V. V. Volkov, A. V. Sokolova, et al., J. Appl. Crystallogr. 36, 1277 (2003).
G. K. Williamson and W. H. Hall, Acta Metall. 1, 22 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Shulenina, M.V. Avdeev, V.L. Aksenov, A.A. Veligzhanin, Ya.V. Zubavichus, A. Hajdu, E. Trombacz, 2012, published in Vestnik Moskovskogo Universiteta. Fizika, 2012, No. 2, pp. 38–43.
About this article
Cite this article
Shulenina, A.V., Avdeev, M.V., Aksenov, V.L. et al. A structural study of biocompatible magnetic nanofluid with synchrotron radiation-based X-ray scattering techniques. Moscow Univ. Phys. 67, 186–191 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0027134912020154
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0027134912020154