Abstract
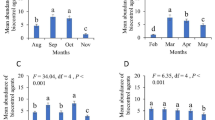
The Norway rat, Ratttus norvegicus, is a common agricultural pest and an important reservoir host of many zoonoses. A long-term field investigation on gamasid mites was made in 39 counties of Yunnan province, southwest China from 1990 to 2015. A total of 1448 Norway rats were captured, and 10,034 individuals of gamasid mites were collected from the body surface of the rats, which were identified as 42 species and 16 genera under 6 families. Based on some strategies of “data mining”, the present paper took advantage of the long-term accumulated original data and made an ecological analysis of gamasid mites on the Norway rat. The results showed that the infestation of gamasid mites on 1448 Norway rats was common with an overall prevalence (48.55%), mean abundance (6.93) and mean intensity (14.27). Of 42 species of gamasid mites, Laelaps nuttalli, Laelaps echidninus and Ornithonyssus bacoti were three dominant species, and they showed an aggregated distribution among different individuals of their rat host, R. norvegicus. There were much more species (39 species) of gamasid mites on the outdoor rats with a higher prevalence (65.12%), mean abundance (10.24) and mean intensity (15.72) than on the indoor rats (p < 0.001). The Norway rats in the lower altitude gradients showed a higher infestation prevalence and intensity of the mites, but lower species diversity. The adult rats had higher infestations (prevalence, mean abundance and mean intensity) of the mites than the juvenile rats. Most gamasid mites showed a predominantly male-biased sex ratio on Norway rats. The association coefficient was used to analyze the interspecific relationship between any two dominant mite species, and a positive association was found between L. nuttalli and L. echidninus. The curve tendency of species-sample relationship showed that the numbers of mite species still kept increasing without an eventual “platform” stage when the sampled rats reached 1200 individuals, and this implies a great heterogeneity of the mite community on the rat. Preston’s lognormal distribution model successfully fitted the theoretical curve of species abundance distribution of gamasid mites on R. norvegicus, which illustrated the distribution of the dominant, common and rare species of the mites.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amo L, Lopez P, Martin J (2005) Prevalence and intensity of haemogregarine blood parasites and their mite vectors in the common wall lizard, Podarcis muralis. Parasitol Res 96(6):378–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-005-1354-2
Archer CE, Schoeman MC, Appleton CC, Mukaratirwa S, Hope KJ, Matthews GB (2018) Predictors of Trypanosoma lewisi in Rattus norvegicus from Durban, South Africa. J Parasitol 104(3):187–195. https://doi.org/10.1645/17-92
Bhuyan PJ, Nath AJ (2016) Record of tropical rat mite, Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Mesostigmata: Macronyssidae) from domestic and peridomestic rodents (Rattus rattus) in Nilgiris, Tamil Nadu, India. J Arthropod Borne Dis 10(1):98–101
Cevidanes A, Altet L, Chirife AD, Proboste T, Millan J (2017) Drivers of Bartonella infection in micromammals and their fleas in a Mediterranean peri-urban area. Vet Microbiol 203:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.03.023
Cevidanes A, Proboste T, Chirife AD, Millan J (2016) Differences in the ectoparasite fauna between micromammals captured in natural and adjacent residential areas are better explained by sex and season than by type of habitat. Parasitol Res 115(6):2203–2211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-4962-0
Combs M, Puckett EE, Richardson J, Mims D, South JM (2018) Spatial population genomics of the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus) in New York City. Mol Ecol 27(1):83–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.14437
Deng GF, Wang DQ, Gu YM, Meng YC (1993) Economic insect fauna of China. Fasc 40, Acari: Dermanyssoidea. Science press, Beijing. [in Chinese]
Dong WG, Guo XG, Men XY, Qian TJ, Wu D (2008) Diversity of gamasid mites on small mammals in the surrounding areas of Erhai Lake in Yunnan. China. Acta Entomol Sin 51(11):1177–1186. https://doi.org/10.16380/j.kcxb.2008.11.014
Eslami A, Yousefi A, Dowling APG (2018) Prevalence of ectoparasites in black rat (Rattus rattus) from mangrove forests of Qeshm Island, Iran. Comp Clin Pathol 27(6):1583–1586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2777-3
Goswami S, Chakraborty S, Ghosh S, Chakrabarti A, Chakraborty B (2018) A review on application of data mining techniques to combat natural disasters. Ain Shams Eng J 9(3):365–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2016.01.012
Guo XG, Dong WG, Men XY, Qian TJ, Wu D, Ren TG, Qin F, Song WY, Yang ZH, Fletcher QE (2016) Species abundance distribution of ectoparasites on Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) from a localized area in Southwest China. J Arthropod Borne Dis 10(2):192–200
Guo XG, Qian TJ, Meng XY, Dong WG, Shi WX, Wu D (2006) Preliminary analysis of chigger communities associated with house rats (Rattus flavipectus) from six counties in Yunnan. China. Syst Appl Acarol 11(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.11.1.2
Guo XG, Speakman JR, Dong WG, Men XY, Qian TJ, Wu D, Qin F, Song WY (2013) Ectoparasitic insects and mites on Yunnan red-backed voles (Eothenomys miletus) from a localized area in Southwest China. Parasitol Res 112(10):3543–3549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3537-6
Guo TY, Xu RM (2001) Study on interspecies associations among the ectoparasites from the rodents in Dongling mountain in Beijing. Chin J Vector Biol Control 12(3):182–185. [in Chinese]
Himsworth CG, Bidulka J, Parsons KL, Feng AYT, Tang P, Jardine CM, Kerr T, Mak S, Robinson J, Patrick DM (2013) Ecology of Leptospira interrogans in Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) in an inner-city neighborhood of Vancouver, Canada. PLoS Neglect Trop Dis 7(6):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002270
Huang LQ, Guo XG, Ren TG, Wang QH, Wu D, Yan Y (2009a) Study on population ecology of Ornithonyssus bacoti in Yunnan, China. Chin J Vector Biol Control 20(6):550–552 [in Chinese]
Huang LQ, Guo XG, Wu D, Zhou DH (2010) Distribution and ecological niches of gamasid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) on small mammals in Southwest China. Psyche: J Entomol 2010:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/934508
Huang LQ, Guo XG (2010) Research advance in the vector gamasid mites and animal hosts of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Chin J Vector Biol Control 21(3):271–274 [in Chinese]
Huang LQ, Guo XG, Speakman JR, Dong WG (2013) Analysis of gamasid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) associated with the Asian house rat, Rattus tanezumi (Rodentia: Muridae) in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Parasitol Res 112(5):1967–1972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3354-y
Huang LQ, Guo XG, Wu D, Wang QH (2009b) Community structure and spatial distribution of gamasid mites associated with small mammals in Yunnan. China. Acta Entomol sin 52(12):1328–1337. https://doi.org/10.16380/j.kcxb.2009.12.016
Kataranovski M, Mirkov I, Belij S, Popov A, Petrovic Z, Gaci Z, Kataranovski D (2011) Intestinal helminths infection of rats (Ratus norvegicus) in the Belgrade area (Serbia): the effect of sex, age and habitat. Parasite 18(2):189–196
Kavakiotis I, Tsave O, Salifoglou A, Maglaveras N, Vlahavas I, Chouvarda I (2017) Machine learning and data mining methods in diabetes research. Comput Struct Biotec 15:104–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2016.12.005
Khokhlova IS, Dlugosz EM, Krasnov BR (2015) Experimental evidence of negative interspecific interactions among imago fleas: flea and host identities matter. Parasitol Res 115(3):937–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4818-z
Kia EB, Moghddas-Sani H, Hassanpoor H, Vatandoost H, Zahabiun F, Akhavan AA, Hanafi-Bojd AA, Telmadarraiy Z (2009) Ectoparasites of rodents captured in Bandar Abbas, southern Iran. J Arthropod Borne Dis 3(2):44–49
Krasnov BR, Matthee S (2010) Spatial variation in gender-biased parasitism: host-related, parasite-related and environment-related effects. Parasitology 137(10):1527–1536. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182010000454
Krasnov BR, Vinarski MV, Korallo-Vinarskaya NP, Mouillot D, Poulin R (2009) Inferring associations among parasitic gamasid mites from census data. Oecologia 160(1):175–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-009-1278-0
Larrive AD, Hammed A, Hodroge A, Berny P, Benoît E, Lattard V, Cosson JF (2019) Population genetics and genotyping as tools for planning rat management programmes. J Pest Sci 92(2):691–705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-018-1043-4
Li Y, Zhang L, Lv Y, Li HL (2017) Advances in research on common zoonotic parasites carried by rodent in China. J Pathog Biol 12(11):1119–1121 [in Chinese]
Liu L, Liu ZX, Du CH, Hong M, Wu AG, Song ZZ, Gao ZH (2014) Geographical distribution of host animals of plague in residential areas in Yunnan Province. Chin J Endemiol 33(5):517–521. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4255.2014.05.012
Luo LP, Guo XG, Qian TJ, Wu D, Meng XY, Dong WG (2006) Species investigation on ectoparasitic gamasid mites on Rattus flavipectus from 25 counties in Yunnan of China. Chin J Vector Biol Control 17(5):395–398 [in Chinese]
Luo LP, Guo XG, Qian TJ, Wu D, Meng XY, Dong WG (2007) Distribution of gamasid mites on small mammals in Yunnan Province, China. Insect Sci 14(1):71–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7917.2007.00128.x
Manu M, Onete M, Băncilă RI (2018) The effect of heavy metals on mite communities (Acari: Gamasina) from urban parks-Bucharest, Romania. Environ Eng Manag J 17(9):2071–2081
Matthews TJ, Whittaker RJ (2015) On the species abundance distribution in applied ecology and biodiversity management. J Appl Ecol 52(2):443–454 https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12380
Morales G, Pino LA (1987) Parasitología Cuantitativa. Fundación Fondo Editorial, Acta Científca Venezolana, Caracas
Orlova MV, Kazakov DV, Orlov OL, Mishchenko VA, Zhigalin AV (2017) The first data on the infestation of the parti-coloured bat, Vespertilio murinus (Chiroptera, Vespertilionidae), with gamasid mites, Steatonyssus spinosus (Mesostigmata, Gamasina, Macronyssidae). Russ J Theriol 16(1):66–73. https://doi.org/10.15298/rusjtheriol.16.1.06
Pan LJ, Guan WL, Li YH (2018) Population structure and spatial distribution pattern of endangered species rosa praelucens. Subtrop Plant Sci 47(3):229–234. [in Chinese]
Pan ZW, Deng GF (1980) Economic insect fauna of China. Fasc 17 Acariformes, Gamasina. Science press, Beijing. [in Chinese]
Peng PY, Guo XG, Jin DC, Dong WG, Qian TJ, Qin F, Yang ZH (2017) Species abundance distribution and ecological niches of chigger mites on small mammals in Yunnan province, Southwest China. Biologia 72(9):1031–1040. https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2017-0119
Peng PY, Guo XG, Song WY, Hou P et al (2015a) Analysis of ectoparasites infestation on Eothenomys miletus in 39 counties of three provinces in Southwest China. Mod Prevent Med 42(16):3016–3021. [in Chinese]
Peng PY, Guo XG, Song WY, Hou P, Zou YJ, Fan R, He XS (2015b) Analysis of ectoparasites (chigger mites, gamasid mites, fleas and sucking lice) of the Yunnan red-backed vole (Eothenomys miletus) sampled throughout its range in Southwest China. Med Vet Entomol 29(4):403–415. https://doi.org/10.1111/mve.12134
Peng PY, Guo XG, Song WY, Hou P, Zou YJ, Fan R (2016) Ectoparasitic chigger mites on large oriental vole (Eothenomys miletus) across southwest, China. Parasitol Res 115(2):623–632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4780-9
Pramestuti N, Umniyati SR, Mulyaningsih B, Widiastuti D, Raharjo J (2018) Evidence of Rickettsia typhi in rat fleas of various habitat and the potential transmission of murine typhus in banjarnegara, Central Java, Indonesia. Indian J Public Health Res Dev 9(8):1548–1554. https://doi.org/10.5958/0976-5506.2018.00952.x
Rahelinirina S, Rajerison M, Telfer S, Savin C, Carniel E, Duplantier JM (2017) The Asian house shrew Suncus murinus as a reservoir and source of human outbreaks of plague in Madagascar. PLoS Neglect Trop Dis 11(11):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006072
Samuel PP, Kamarasu K, Govindarajan R, Selvam A, Victor Jerald Leo S, Arunachalam N (2017) Preliminary investigation on the prevalence of scrub typhus vectors in Krishnagiri district, Tamil Nadu, India. J Adv Zool 38(2):128–132
Shimalov VV (2017) Helminth infections of the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus Berkenhout, 1769) in the biocenoses of South-West Belarus. J Parasit Dis 41(2):599–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-016-0844-8
Storm JJ, Ritzi CM (2008) Ectoparasites of small mammals in western Iowa. Northeast Nat 15(2):283–292
Tang Y, Yuan W, Rui L, Wu WW, Lin D, Chen LB (2019) Analysis of hospitalization cost prediction model of chronic disease based on data mining algorithm. J Mod Med Health 35(4):481–485. https://doi.org/10.3969/jiss.1009-5519.2019.04.001
Touati L, Figuerola J, Alfarhan AH, Samraoui B (2015) Distribution patterns of ectoparasites of glossy Ibis (Plegadis falcinellus) chicks. Zool Ecol 25(1):46–53. https://doi.org/. https://doi.org/10.1080/21658005.2015.1005447
Wang RL, Wen G, Liu Y, Luo JD, Li Q, Wang MT, Lin S (2019) Spatial distribution pattern of kiwifruit canker disease on ‘Xuxiang’ in field. Chin Agr Sci Bull 35(4):88–92. [in Chinese]
Wang XQ, Cao XY, Liu HL, Wu XL, Pu DQ, Li YJ, Fang C (2018) Spatial distribution of mixed spider populations in pepper fields. J Southern Agr 49(11):2204–2209. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.11.13
Wei L, Wang XW, Wang CM, He HX (2010) A survey of ectoparasites from wild rodents and Anourosorex squamipes in Sichuan Province, South-West China. J Ecol Nat Environ 2(8):160–166
Wu QM, Sun XY, Huang X, Yao ML, Chen C, Huang XF, Li Y, Chen RC, Yang YM, Sui Y (2017) Species diversity and abundance of wintering waterbird community in Duchang nature reserve in Jiangxi. Life Sci Res 21(5):417–423 [in Chinese] https://doi.org/10.16605/j.cnki.1007-7847.2017.05.008
Zhan YZ, Guo XG, Speakman JR, Zuo XH, Wu D, Wang QH, Yang ZH (2013) Abundances and host relationships of chigger mites in Yunnan Province, China. Med Vet Entomol 27(2):194–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2915.2012.01053.x
Zhang SY, Wu D, Guo XG, Men XY (2007) Community of fleas on Eothenomys miletus in Yunnan province. Chin J Vector Biol Control 18(6):440–442. [in Chinese]
Zhang SY, Wu D, Guo XG, Men XY, Gong ZD, Zhang LY, Wang ZK (2008) Preliminary research on ectoparasitic fleas and their species-plot relation with Apodemus chevrieri in 19 Counties and Towns in Yunnan. China. J Pathog Biol 3(5):383–386 [in Chinese] https://doi.org/10.13350/j.cjpb.2008.05.015
Zhang XM, Liu XJ, Yang ZJ (2006) Studies on the spatial distribution pattern of Lygus lucortum Meyer-Dur’s over winter eggs in jujube trees. Chin J Eco-Agr 14(3):157–159. [in Chinese]
Zhao ZM, Guo YQ (1990) Principle and methods of community ecology. Publishing House of Scientific and Technical Documentation Chongqing. [in Chinese]
Zomer RJ, Xu JC, Wang MC, Trabucco A, Li ZQ (2015) Projected impact of climate change on the effectiveness of the existing protected area network for biodiversity conservation within Yunnan Province, China. Biol Conserv 184:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2015.01.031
Acknowledgments
Up till now more than 60 people have joined this study, including field investigation, collection of gamasid mites and other ectoparasites, specimen making and identification of the mites. Here we’d like to express our sincere thanks to following people who have made special contributions to the field investigation and laboratory work: Qiao-Hua Wang, Yong Zhang, Cong-Hua Gao, Nan Zhao, Jian-Chang He, Guo-Li Li, Yan-Liu Li, Xue-Song He, Yun-Ji Zou, De-Cai Ouyang, Shuang-Lin Wang, some colleagues and college students. The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81672055) to Xian-Guo Guo, the Academician Workstation for Academician Jian-Guo Xu and the Innovation Team of Vector Biology, Dali University (No. ZKLX2019104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The sampling of the Norway rats was officially permitted by the local authority of wildlife service in Dali Prefecture, Yunnan Province, China. The use of animals (Norway rats) for research was also officially approved at the Institute of Pathogens and Vectors, Dali University.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript, and manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Guo, XG., Fan, R. et al. Ecological analysis of gamasid mites on the body surface of Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Biologia 75, 1325–1336 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00383-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00383-z