Abstract
When the solar irradiance propagates between the outer magnetospheric regions and the ionosphere, dynamic processes of the magnetosphere-ionosphere-thermosphere system are affected at the lower end of their paths by the interaction of radiation with the neutral troposphere. The main target of this work is to investigate the relationship between the diurnal magnetic field variations resulting from solar activities and the variation in the troposphere temperature. Meteorological and geomagnetic data acquired from different observatories located in Egypt, Portugal and Slovakia in a long-term and daily-term scales were analyzed.
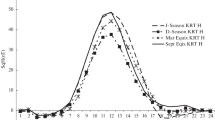
The long-term results show that there is a close relationship between the diurnal Sq magnetic field variations and the tropospheric temperature. The rate of temperature increase at mid-latitude areas is higher than at high-latitude. During the period of investigation, it is found that the troposphere temperature has increased by about 0.033 °C/year at Helwan, Egypt, 0.03 °C/year at Coimbra, Portugal, and 0.028 °C/year in Hurbanovo/Stará Lesná, Slovakia. The Sq geomagnetic variations depend on the intensity of the electric currents generated by the effect of solar radiation in the ionosphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, D.N. (2000), Effects of the Sun on the Earth’s environment, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 62, 1669–1681, DOI: 10.1016/S1364-6826(00)00119-X.
Brown, G.M., and J.I. John (1979), Solar cycle influences in tropospheric circulation, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 41, 43–52, DOI: 10.1016/0021-9169(79)90045-X.
Bucha, V., and V. Bucha, Jr. (1998), Geomagnetic forcing of changes in climate and in the atmospheric circulation, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 60,2, 145–169, DOI: 10.1016/S1364-6826(97)00119-3.
Chapman, S., and J. Bartels (1940), Geomagnetism, Oxford Univ. Press, London.
Cliver, E.W., V. Boriakoff, and J. Feynman (1998), Solar variability and climate change: Geomagnetic aa index and global surface temperature, Geophys. Res. Lett. 25,7, 1035–1038, DOI: 10.1029/98GL00499.
Cubasch U., R. Voss, G.C. Hegerl, J. Waszkewitz, and T.J. Crowley (1997), Simulation of the influence of solar radiation variations on the global climate with an ocean-atmosphere general circulation model, Clim. Dyn. 13,11, 757–767, DOI: 10.1007/s003820050196.
Dickinson, R.E. (1975), Solar variability and the lower Atmosphere, Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 56,12, 1240–1248, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0477 (1975)056<1240:SVATLA>2.0.CO;2.
Donarummo, J., Jr., M. Ram, and M.R. Stolz (2002), Sun/dust correlations and volcanic interference, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29,9, 1361–1364, DOI: 10.1029/2002GL014858.
Eddy, J.A. (1976), The Maunder minimum, Science 192,4245, 1189–1202, DOI: 10.1126/science.192.4245.1189.
Fluteau, F., V. Courtillot, Y. Gallet, J. Le Mouel, and A. Genevey (2006), Does the Earth’s magnetic field influence climate?, Eos Trans. AGU 87,52, Fall Meet. Suppl. Abstract GP51B-02.
Haigh, J.D. (2003), The effects of solar variability on the Earth’s climate, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 361,1802, 95–111, DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2002.1111.
Haigh, J.D., and H. Lundstedt (2007), Influence of Solar Activity Report, ESTEC Contract no. 18453/04/NL/AR, 1.
Hartley, D.E., J.T. Villarin, R.X. Black, and C.A. Davis (1998), A new perspective on the dynamical link between the stratosphere and troposphere, Nature 391, 471–474, DOI: 10.1038/35112.
Houghton, J.T., B.A. Callander., and S.K. Varney (eds.) (1992), Climate Change. The Supplementary Report to the IPCC 1991 Scientific Assessment, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Hoyt, D.V., and K.H. Schatten (1997), The Role of the Sun in Climate Change, Oxford Univ. Press, New York.
Hurrell, J.W. (1996), Influence of variations in extratropical wintertime teleconnections on northern hemisphere temperature, Geophys. Res. Lett. 23,6, 665–668, DOI: 10.1029/96GL00459.
Keckhut, P., C. Cagnazzo, M.-L. Chanin, C. Claud, and A. Hauchecorne (2005), The 11-year solar-cycle effects on temperature in the upper-stratosphere and mesosphere. Part I: Assessment of observations, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 67,11, 940–947, DOI: 10.1016/j.jastp.2005.01.008.
Kelly, P.M. (1977), Solar influence on North Atlantic mean sea level pressure, Nature 269, 320–322, DOI: 10.1038/269320a0.
Kerr, R.A. (2006), The Sun’s churning innards foretell more solar storms, Science 311, 5766, 1357, DOI: 10.1126/science.311.5766.1357.
Kondratyev, K.Ya., and G.A. Nikolsky (1983), The solar constant and climate, Sol. Phys. 89,1, 215–222, DOI: 10.1007/BF00211964.
Parkhomov, V.A., A.V. Moldavanov, and B. Tsegmed (2006), On two different geomagnetic manifestations of solar flare November 4, 2003, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 68,12, 1370–1382, DOI: 10.1016/j.jastp.2006.05.002.
Ram, M., and M.R. Stolz (1999), Possible solar influences on the dust profile of the GISP2 Ice Core from central Greenland, Geophys. Res. Lett. 26,8, 1043–1046, DOI: 10.1029/1999GL900199.
Reid, G.C. (1987), Influence of solar variability on global sea surface temperatures, Nature 329,6135, 142–143, DOI: 10.1038/329142a0.
Sharma, M. (2002), Variations in solar magnetic activity during the last 200 000 years: is there a Sun-climate connection, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 199, 459–472, DOI: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00516-2.
Svensmark, H., and E. Friis-Christensen (1997), Variation of cosmic ray flux and global cloud coverage - a missing link in solar-climate relationships, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 59,11, 1225–1232, DOI: 10.1016/S1364-6826(97)00001-1.
Thompson, D.W.J., M.P. Baldwin, and S. Solomon (2005), Stratosphere-troposphere coupling in the Southern Hemisphere, J. Atmos. Sci. 62,3, 708–715.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabeh, T., Carvalho, J., Khalil, A. et al. Climate changes associated with high-amplitude Sq geomagnetic variations. Acta Geophys. 59, 1044–1056 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-011-0029-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-011-0029-x