Abstract
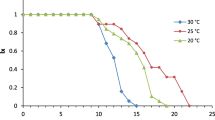
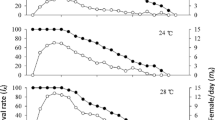
Aphids are a good model to study insect reaction to habitat change. Temperature is one of the main factors that influences insects. This paper examines the influence of temperature on developmental stages, fecundity, survival rate and demographic parameters of Cinara tujafilina (Hemiptera: Aphidoidea, Lachnidae), connected with decorative plants of the Cupressaceae family. C. tujafilina was reared in a laboratory on T. orientalis at five constant temperatures of 10, 15, 20, 25 and 28°C, 70% humidity and 14L:10D. The pre-reproduction stage varied from 7 at 25°C to 19 days at 10°C. Developmental threshold was assigned at 3.5°C. The longest reproduction stage for the aphids developing was recorded at 25°C, namely 33 days, while the shortest, at the temperature of 10°C, lasted 8 days. At 25°C this species is characterised by the shortest pre-reproduction stage, the highest fecundity, the highest survival rate and the highest demographic parameters, particularly rm (0.17). The results suggest that the optimal temperature for the species is 25°C, and indicate that climatic change will favourably influence its development and increase its role as a pest of decorative plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robinet C., Roques A., Direct impacts of recent climate warming on insect populations, Integr. Zool., 2010, 5, 132–142
Dixon A.F.G., Aphid Ecology, An optimization Approach (Second edn), Chapman & Hall, Glasgow and London, 1998
Hulle M., d’Acier A.C., Bankhead-Dronnet S., Harrington R., Aphids in the face of global changes, C. R. Biologies, 2010, 333, 497–503
Harrington R., Bale J.S., Tatchel G.M., Aphids in a Changing Climate, In: Insects in a Changing Environment Ed by Harrington R, Stork NE, Academic Press, 1995
Harrington R., Clark S., Welham S., Verrier P., Denholm C., Rounsevell M., et al., In: E. Owain (Ed.), Environmental change, life cycle traits and aphid phenology, 7th International Symposium on Aphids (2–7 October 2005, Fremantle, Australia), 2005
Harrington R., Clarc S., Welham S.J., Verrier P., Denholm C., Hulle M., et al., Environmental change and the phenology of European aphids, Global Change Biol., 2007, 13, 1550–1564
Danks H.V., The elements of seasonal adaptations in insects, Can. Entomol., 2007, 139, 1–44
Hulle M., Harrington R., Eouzan M., Pickup J., Turpeau E., In: E. Owain (Ed.), Aphid biodiversity changes in western Europe over the recent decades, 7th International Symposium on Aphids (2–7 October 2005, Fremantle, Australia), 2005
Zhou X., Harrington R., Woiwod I., Perry J.N., Bale J., Clark S.J., Effects of temperature on aphid phenology, Global Change Biol., 1995, 1, 303–313
Rakauskas R., Recent changes in aphid (Hemiptera, Sternorrhyncha: Aphididae) fauna of Lithuania: an effect of global warming? Ekologija, 2004, 1, 1–4
Simon J.C., Carrel E., Hebert P., Dedryver C.A., Bonhomme J., Gallic J.F., Genetic diversity and mode of reproduction in French populations of the aphid Rhopalosiphum padi. Heredity, 1996, 76: 305–313
Margaritopoulos J.T., Tsitsipis J.A., Goudoudaki S., Blackman R.L., Life cycle variation of Myzus persicae (Hemiptera:Aphididae) in Greece, Bull. Entomol.Res., 2002, 92, 309–319
Vorburger C., Lancaster M., Sunnucks P., Environmentally related patterns of reproductive modes in the aphid Myzus persicae and the predominance of two superclones in Victoria, Australia. Mol. Ecol., 2003, 12, 3493–3504
Ruszkowska M., Across the transformation life cycle of Rhopalosiphum padi (L.) (Homoptera:Aphidoidea): coevolution with temperature, Rozprawy Naukowe Instytutu Ochrony Roślin, 2007, 15, 1–60
Holopainen J.K., Kainulainen P., Reproductive capacity of the grey pine aphid and allocation response of Scots pine seedlings across temperature gradients: a test of hypotheses predicting outcomes of global warming, Can. J. For. Res., 2004, 34, 94–102
Yamamura K., Kiritari K., A simple method to estimate the potential increase in the number of generations under global warming in temperate zones, Appl. Entomol. Zool., 1998, 33, 289–298
Durak R., Soika G., Socha M., An occurrence and some elements of ecology of Cinara tujafilina (Del Guercio, 1909) (Hemiptera, Aphidinea) in Poland, J. Plant Prot. Res., 2006, 46, 269–273
Blackman R.L., Eastop V.F., Aphids on the World’s Trees: An identification and Information Guide, CAB International & The Natural History Museum, London, 1994
Colombo M., Parisini M., Nuovi acquisizioni sulla biliogia e sul controllo di Cinara (Del Guercio) (Aphidodea, Lachnidae), Boll. Zool. Agr. Bachic., 1984, 18, 191–194
Kairo T.M., Murphy S., Temperature and plant nutrient effects on the development, survival and reproduction of Cinara sp. Nov., an invasive pest of cypress trees in Africa, Entomol. Exp. App., 1999, 92, 147–156
Watson G.W., Voegetlin S.T., Murphy S.T., Foottit R.G., Biogeography of the Cinara cupressi complex (Hemiptera, Aphididae) on Cupressaceae, with description of a pest species introduced into Africa, Bull. Entomol. Res., 1999, 89, 271–283
Furuta K., Annual alternating population size of the thuja aphid, Cinara tujafilina (Del Guercio), and the impacts of syrphids and disease, J. Appl. Ent., 1988, 105, 344–354
Birch L.C., The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population, J. Anim. Ecol., 1948, 17, 15–26
Wyatt I.J., White P.F., Simple estimation of intrinsic rates for aphids and tetranychid mites, J. App. Ecol., 1977, 14, 757–766
Collins C.M., Leather S.R., Effect of temperature on fecundity and development of the Giant Willow Aphid, Tuberolachnus salignus (Sternorrhyncha: Aphididae), Eur. J. Entomol., 2001, 98, 177–182
Tang Y.O., Lapointe S.L., Brown L.G., Hunter W.B., Effects of host plant and temperature on the biology of Toxoptera citricida (Homoptera: Aphididae), Environ. Entomol., 1999, 28, 895–900
Mehrparvar M., Hatami B., Effect of temperature on some biological parameters of an Iranian population of the Rose aphid, Macrosiphum rosae (Hemiptera: Aphididae), Eur. J. Entomol., 2007, 104, 631–634
Satar S., Kersting U., Ulusoy M.R., Temperature dependent life history traits of Brevicoryne brassicae (L.) (Hom., Aphididae) on white cabbage, Turk. J. Agric. For., 2005, 29, 341–346
Auad A.M., Alves S.O., Carvalho C.A., Silva D.M., Resende T.T., Verissimo B.A., The impact of temperature on biological aspects and life table of Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae) fed with signal grass, Florida Entomol., 2009, 92, 569–577
Zhou X., Carter N., Effects of temperature, feeding position and crop growth stage on the population dynamics of the rose grain aphid, Metopolophium dirhodum (Hemiptera: Aphididae), Ann. Appl. Biol., 1992, 121, 27–37
Conti B.F., Bueno V.H., Sampaio M.V., Sidney L.A., Reproduction and fertility life table of three aphid species (Macrosiphini) at different temperatures, Rev. Bras. Entomol., 2010, 54, 654–660
Nimbalkar R.K., Shinde S.S., Wadikar M.S., Tawar D.S., Muley S.P., Effect of constant temperature on development and reproduction of the cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii) (Glover) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on Gossypium hirsutum in laboratory conditions, J. Ecobiotechnology, 2010, 2, 29–34
McCornack B.P., Ragsdale D.W., Venette R., Demography of Soybean Aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) at Summer Temperatures, J. Econ. Entomol., 2004, 97, 854–861
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Durak, R., Borowiak-Sobkowiak, B. Influence of temperature on the biological parameters of the anholocyclic species Cinara tujafilina (Hemiptera: Aphidoidea). cent.eur.j.biol. 8, 570–577 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-013-0161-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-013-0161-x