Abstract
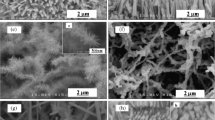
Two series of polycrystalline zinc oxide (ZnO) layers, from Zn or ZnO targets, were grown on silicon (1 1 1) substrates by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) at ambient oxygen pressure levels, stepwise increased from 1 to 35 Pa. For ablation of targets, a pulsed Nd:YAG laser was used. The structural and morphological properties of the layers were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). The SEM images of ZnO layers in SE mode show a uniform granular structure and modified surface morphology, depending on oxygen pressure. The mean grain size in height and lateral directions decreases with an increase of oxygen pressure from 1 to 5 Pa, while a subsequent rise of oxygen pressure from 5 to 35 Pa will cause an increase in the grain size. The AFM measurement revealed that the surface structures of zinc oxide layers grown from different targets were similar, and the layers formed at an ambient oxygen pressure of 5 Pa exhibited the smallest values of calculated roughness and granularity. SIMS depth profiling analyses confirmed that the ZnO composition was homogenous across the layer, up to the abrupt change of chemical composition at the interface between the ZnO layer and the Si substrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Ramamoorthy et al., Curr. Appl. Phys. 6, 103 (2006)
J.-H. Lim et al., Adv. Mater. 18, 2720 (2006)
G. Tobin et al., Physica B 340-342, 245 (2003)
S. J. Pearton, D. P. Norton, K. Ip, Y. W. Heo, T. Steiner, Superlattice. Microst. 34, 3 (2003)
A. Kobayashi, Y. Shirakura, K. Miyamura, J. Ohta, H. Fuioka, J. Cryst. Growth 305, 70 (2007)
A. E. Suliman, Y. Tang, L. Xu, Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C. 91, 1658 (2007)
N. W. Emanetoglu, C. Gorla, Y. Liu, S. Liang, Y. Lu, Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2, 247 (1999)
M. Jung, J. Lee, S. Park, H. Kim, J. Chang, J. Cryst. Growth 283, 384 (2005)
H. Miyashita, T. Satoh, T. Hirate, Superlattice. Microst. 39, 67 (2006)
A. El-Shaer, A. Ch. Mofor, A. Bakin, M. Kreye, A. Waag, Superlattice. Microst. 38, 265 (2005)
N. M. Sbrockey, S. Ganesan, III-Vs Review 17, 23 (2004)
S. S. Kim, B.-T. Lee, Thin Solid Films 446, 307 (2004)
Z. G. Zhang et al., Physica E 39, 253 (2007)
Y. Y. Villanueva, D.-R. Liu, P. T. Cheng, Thin Solid Films 501, 366 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
HaÅ¡ko, D., Bruncko, J., Vincze, A. et al. Comparative study of ZnO layers prepared by PLD from different targets at various oxygen pressure levels. centr.eur.j.phys. 7, 345–349 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11534-009-0047-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11534-009-0047-3