Abstract
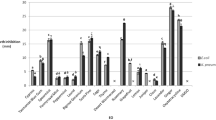
The antibacterial effect of essential oils (EOs) derived from Citrus lemon, Juniperus communis, Origanum majorana, and Salvia sclarea, was investigated either alone or in combination, on 2 food related bacteria (Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli). The influence of food ingredients — hydrolyzed proteins originating from animal and plant (meat extract and soy peptone) and sucrose — on the antibacterial effect of EOs was also tested. The most effective antibacterial activities were obtained with marjoram and clary sage oil, alone and in combination. High concentration of meat extract protected the bacteria from the growth inhibiting effect of marjoram oil, while soy peptone had no such effect. Sucrose intensified the lag phase lengthening by marjoram oil in a dose-independent manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burt S., Essential oils: antibacterial activity and potential applications in foods — a review, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 2004, 94, 223–253
Bagamboula C.F., Uyttendaele M., Debvere J., Inhibitory effect of thyme and basil essential oils, carvacrol, thymol, estragol, linalool and p-cymene towards Shigella sonnei and S. flexneri, Food Microbiol., 2004, 21, 33–42
de Souza E.L., de Barros J.C., da Concecao M.L., Neto N.J.G., da Costa A.C.V., Combined application of Origanum vulgare L. essential oil and acetic acid for controlling the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in foods, Braz. J. Microbiol., 2009, 40, 387–393
Devlieghere F., Vermeulen A., Debevere J., Chitosan: antimicrobial activity, interactions with food components and applicability as a coating on fruit and vegetables, Food Microbiol., 2009, 21, 703–714
Mytle N., Anderson G.L., Doyle M.P., Smith M.A., Antimicrobial activity of clove (Syzgium aromaticum) oil in inhibiting Listeria monocytogenes on chicken frankfurters, Food Control, 2006, 17, 102–107
Gill A.O., Delaquis P., Russo P., Holley R.A., Evaluation of antilisterial action of cilantro oil on vacuum packed ham, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 2002, 73, 83–92
Smith-Palmer A., Stewart J., Fyfe L., The potential application of plant essential oils as natural food preservatives in soft cheese, Food Microbiol., 2001, 18, 463–470
Tassou C., Drosinos E.H., Nychas G.-J.E., Effects of essential oil from mint (Mentha piperita) on Salmonella enteritidis and Listeria monocytogenes in model food systems at 4°C and 10°C, J. Appl. Bacteriol., 1995, 78, 593–600
Moreno A.B., del Pozo A.M., Borja M., San Segudo B., Activity of the antifungal protein from Aspergillus giganteus against Botrytis cinerea, Phytopathology, 2003, 93, 1344–1353
Gutierrez J., Barry-Ryan C., Bourke P., The antimicrobial efficacy of plant essential oil combinations and interactions with food ingredients, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 2008, 124, 91–97
Dorman H.J.D., Deans S.G., Antimicrobial agents from plants: antibacterial activity of plant volatile oils, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2000, 88, 308–316
Hammer K.A., Carson C.F., Riley T.V., Antimicrobial activity of essential oils and other plant extracts, J. Appl. Microbiol., 1999, 86, 985–990
Pol I.E., Mastwijk H.C., Slump R.A., Popa M.E., Smid E.J., Influence of food matrix on inactivation of Bacillus cereus by combinations of nisin, pulsed electric field treatment, and carvacrol, J. Food Protect., 2001, 64, 1012–1018
Gutierrez J., Barry-Ryan C., Bourke P., Antimicrobial activity of plant essential oils using food model media: Efficacy, synergistic potential and interactions with food components, Food Microbiol., 2009, 26, 142–150
Atrea I., Papavergou A., Amvrosiadis I., Savvaidis I.N., Combined effect of vacuum-packaging and oregano essential oil on the shelf-life of Mediterranean octopus (Octopus vulgaris) from the Aegean Sea stored at 4oC, Food Microbiol., 2009, 26, 166–172
Min B.J., Oh J.-H., Antimicrobial activity of catfish gelatin coating containing origanum (Thymus capitatus) oil against Gram-negative bacteria, J. Food Sci., 2009, 74, 143–148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tserennadmid, R., Takó, M., Galgóczy, L. et al. Antibacterial effect of essential oils and interaction with food components. cent.eur.j.biol. 5, 641–648 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-010-0058-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-010-0058-5