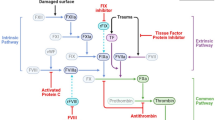
Abstract
▴ Human C1-esterase inhibitor concentrate (C1-INH concentrate) is derived from human plasma and is indicated for the treatment of acute episodes of hereditary angioedema.
▴ Intravenous C1-INH concentrate provided rapid symptom relief in patients with acute abdominal or facial episodes associated with type I or II hereditary angioedema, according to the results of the randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled IMPACT-1 trial. The median time to the onset of symptom relief was significantly shorter with C1-INH concentrate 20 U/kg than with placebo (0.5 vs 1.5 hours). A subsequent noncomparative extension trial (IMPACT-2) showed the ongoing efficacy of ‘on-demand’ treatment with C1-INH concentrate; overall, the onset of symptom relief occurred in a median 30 minutes.
▴ Several additional studies demonstrated the efficacy of intravenous C1-INH concentrate in patients with laryngeal edema, skin swellings, or abdominal episodes associated with type I or II hereditary angioedema.
▴ Self-administered home therapy with intravenous C1-INH concentrate significantly improved health-related quality of life in patients with hereditary angioedema. Dermatology Life Quality Index and Short Form 36-item Health Survey scores were significantly improved from baseline by self-administered home therapy with C1-INH concentrate.
▴ Intravenous C1-INH concentrate was well tolerated in patients with hereditary angioedema, with no confirmed cases of viral transmission.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowen T, Cicardi M, Bork K, et al. Hereditary angioedema: a current state-of-the-art review, VII: Canadian Hungarian 2007 international consensus algorithm for the diagnosis, therapy, and management of hereditary angioedema. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2008 Jan; 100(1 Suppl. 2): S30–40
Davis III AE. New treatments addressing the pathophysiology of hereditary angioedema. Clin Molecul Allerg 2008 Apr 14; 6: 2
Bork K. Pasteurized C1 inhibitor concentrate in hereditary angioedema: pharmacology, safety, efficacy and future directions. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2008; 4(1): 13–20
Longhurst HJ. Emergency treatment of acute attacks in hereditary angioedema due to C1 inhibitors deficiency: what is the evidence? Int J Clin Pract 2005 May; 59(5): 594–9
Cicardi M, Zingale LC. The deficiency of C1 inhibitor and its treatment. Immunobiology 2007; 212(4-5): 325–31
Zuraw BL. Clinical practice: hereditary angioedema. N Engl J Med 2008 Sep 4; 359(10): 1027–36
Cugno M, Cicardi M, Bottasso B, et al. Activation of the coagulation cascade in C1-inhibitor deficiencies. Blood 1997 May 1; 89(9): 3213–8
Davis III AE. The pathophysiology of hereditary angioedema. Clin Immunol 2005 Jan; 114(1): 3–9
CSL Behring. Berinert (C1-esterase inhibitor, human): UK summary of product characteristics [online]. Available from URL: http://emc.medicines.org.uk/medicine/21650/SPC/Berinert/ [Accessed 2009 Aug 27]
Groner A, Nowak T, Schäfer W. An integrated approach to effective pathogen reduction for a plasma-derived C1 inhibitor concentrate [poster]. 52nd Annual Meeting of the Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis Research; 2008 Feb 20–23; Wiesbaden
De Serres J, Gröner A, Lindner J. Safety and efficacy of pasteurized C1 inhibitor concentrate (Berinert® P) in hereditary angioedema: a review. Transfus Apher Sci 2003 Dec; 29(3): 247–54
Bernstein JA. Hereditary angioedema: a current state-of-the-art review, VIII: current status of emerging therapies. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2008 Jan; 100(1 Suppl. 2): S41–6
Gompels MM, Lock RJ, Abinun M, et al. C1 inhibitor deficiency: consensus document. Clin Exp Immunol 2005 Mar; 139(3): 379–94
Martinez-Saguer I, Rusicke E, Aygören-Pürsün E, et al. Pharmacokinetic analysis of human plasma-derived pasteurized C1-inhibitor concentrate in adults and children with hereditary angioedema: a prospective study. Transfusion (Paris). Epub 2009 Sep 24
Beinrohr L, Harmat V, Dobó J, et al. C1 inhibitor serpin domain structure reveals the likely mechanism of heparin potentiation and conformational disease. J Biol Chem 2007 Jul 20; 282(29): 21100–9
Craig TJ, Levy RJ, Wasserman RL, et al. Efficacy of human C1 esterase inhibitor concentrate compared to placebo in acute hereditary angioedema attacks. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009 Oct; 124(4): 801–8
Craig TJ, Wasserman RL, Levy R, et al. C1-esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) -standard of care for the treatment of acute attacks in hereditary angioedema (HAE): initial results of an ongoing, prospective, open-label study of North America (I.M.P.A.C.T.2) [poster]. 64th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Asthma, Allergy, and Immunology; 2008 Mar 14–18; Philadelphia (PA)
Bork K, Barnstedt S-E. Treatment of 193 episodes of laryngeal edema with C1 inhibitor concentrate in patients with hereditary angioedema. Arch Intern Med 2001 Mar 12; 161: 714–8
Bork K, Staubach P, Hardt J. Treatment of skin swellings with C1-inhibitor concentrate in patients with hereditary angio-oedema. Allergy 2008 Jun; 63(6): 751–7
Bork K, Meng G, Staubach P, et al. Treatment with C1 inhibitor concentrate in abdominal pain attacks of patients with hereditary angioedema. Transfusion 2005 Nov; 45(11): 1774–84
Farkas H, Jakab L, Temesszentandrási G, et al. Hereditary angioedema: a decade of human C1-inhibitor concentrate therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007 Oct; 120(4): 941–7
Kreuz W, Martinez-Saguer I, Aygören-Pürsün E, et al. C1-inhibitorconcentrate for individual replacement therapy in patients with severe hereditary angioedema refractory to danazol prophylaxis. Transfusion 2009 Sep; 49(9): 1987–95
Bygum A, Andersen KE, Mikkelsen CS. Self-administration of intravenous C1-inhibitor therapy for hereditary angioedema and associated quality of life benefits. Eur J Dermatol 2009 Mar–Apr; 19(2): 147–51
Longhurst HJ, O'Grady C. Home therapy for HAE: the Barts experience [abstract]. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004 Sep; 114(3 Suppl.): S99–100
Rusicke E, Martinez-Saguer I, Aygören-Pürsün E, et al. Home treatment in patients with hereditary angioedema (HAE) [abstract no. 700]. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006 Feb; 117(2 Suppl. 1): S180
Longhurst HJ, Carr S, Khair K. C1-inhibitor concentrate home therapy for hereditary angioedema: a viable, effective treatment option. Clin Exp Immunol 2007 Jan; 147(1): 11–7
Bork K, Hardt J. Hereditary angioedema: increased number of attacks after frequent treatments with C1 inhibitor concentrate. Am J Med 2009 Aug; 122(8): 780–3
CSL Behring. Berinert® (C1 esterase inhibitor [human]) [online]. Available from URL: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/BloodBloodProducts/ApprovedProducts/LicensedProductsBLAs/FractionatedPlasma Products/UCM186268.pdf [Accessed 2009 Oct 13]
Acknowledgments and Disclosures
The manuscript was reviewed by: M. Cicardi, Universitià degli Studi di Milan, Dipartimento di Scienze Cliniche “Luigi Sacco”, Ospedale Luigi Sacco, Milan, Italy; H. Farkas, 3rd Department of Internal Medicine, Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary.
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keating, G.M. Human C1-Esterase Inhibitor Concentrate (Berinert®). BioDrugs 23, 399–406 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2165/11201100-000000000-00000
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/11201100-000000000-00000