Abstract
Objective
Zanamivir is eliminated almost exclusively by renal excretion. This study evaluated the effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of intravenous zanamivir.
Design
This open-label study compared individuals with mild/moderate or severe renal impairment, as defined by creatinine clearance (CLcr), with healthy participants.
Study participants
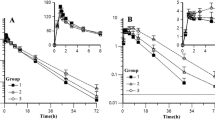
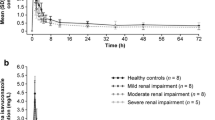
There were 17 participants (9 men and 8 women), of whom 7 had normal renal function (CLcr >70 ml/min), 5 had mild/moderate renal impairment (CLcr 25 to 70 ml/min) and 5 had severe renal impairment (CLcr <25 ml/min).
Interventions
Single 4mg doses of zanamivir were administered intravenously to healthy participants and those with mild/moderate renal impairment; participants with severe renal impairment received 2mg. Zanamivir concentrations were determined in blood and urine. Safety was evaluated by monitoring adverse events, vital signs and laboratory parameters.
Results
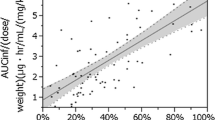
Zanamivir was well tolerated both in participants with renal impairment and in healthy volunteers. There were no clinically significant changes attributable to zanamivir treatment. Renal dysfunction had marked effects on the pharmacokinetics of zanamivir. Although no statistically significant differences were detected between either renal impairment group and the normal renal function group for the maximum serum concentration (Cmax) or the time this occurred (tmax), a strong relationship was detected between CLcr and total body clearance (CL), renal clearance (CLr) and the terminal phase elimination rate constant (λcz). Each 2-fold increase in CLcr produced average increases of 100, 121 and 85% in CL, CLr and λz, respectively. The area under the serum concentration-time curve from zero to infinity (AUC∞) was on average increased 2-fold in individuals with mild/moderate renal impairment (4mg dose) and 3.5-fold in those with severe impairment (2mg dose) compared with healthy individuals (4mg dose).
Conclusions
The proposed total daily dosage of zanamivir by oral inhalation is 20mg. Given the tolerability (observed in a separate study to be reported in this supplement) after daily intravenous dosages of 1200mg, and the limited systemic absorption after oral inhalation, the increased drug exposure in patients with severe renal failure is not considered clinically significant. Furthermore, the local concentrations in the lung following oral inhaled delivery are essential for efficacy. Therefore, for orally inhaled zanamivir, no dosage adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Von Itzstein M, Wu W-Y, Kok GB, et al. Rational design of potent sialidase based inhibitors of influenza virus replication. Nature 1993: 363: 418–23.
Whittington A, Bethell R. Recent developments in the antiviral therapy of influenza. Expert Opin Ther Pat 1995; 5: 793–803.
Woods JM, Bethell RC, Coates JAV, et al. 4-Guanidino-2,4-dideoxy-2,3-dehydro-N-acetylneuraminic acid is a highly effective inhibitor both of the sialidase (neuraminidase) and of growth of a wide range of influenza A and B viruses in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1993; 37: 1473–9.
Cass LMR, Efthymiopoulos C, Bye A. Pharmacokinetics of zanamivir after intravenous, oral, inhaled or intranasal administration to healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacokinet 1999; 36 Suppl. 1: 1–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cass, L.M.R., Efthymiopoulos, C., Marsh, J. et al. Effect of Renal Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics of Intravenous Zanamivir. Clin Pharmacokinet 36 (Suppl 1), 13–19 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199936001-00002
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199936001-00002