Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of tea polyphenols on cardiac function in rats with diabetic cardiomyopathy, and the mechanism by which tea polyphenols regulate autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Methods
Sixty Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into six groups: a normal control group (NC), an obesity group (OB), a diabetic cardiomyopathy group (DCM), a tea polyphenol group (TP), an obesity tea polyphenol treatment group (OB-TP), and a diabetic cardiomyopathy tea polyphenol treatment group (DCM-TP). After successful modeling, serum glucose, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels were determined; cardiac structure and function were inspected by ultrasonic cardiography; myocardial pathology was examined by staining with hematoxylin-eosin; transmission electron microscopy was used to observe the morphology and quantity of autophagosomes; and expression levels of autophagy-related proteins LC3-II, SQSTM1/p62, and Beclin-1 were determined by Western blotting.
Results
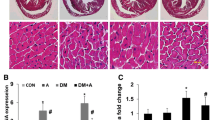
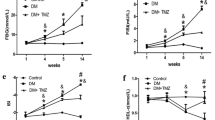
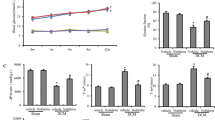
Compared to the NC group, the OB group had normal blood glucose and a high level of blood lipids; both blood glucose and lipids were increased in the DCM group; ultrasonic cardiograms showed that the fraction shortening was reduced in the DCM group. However, these were improved significantly in the DCM-TP group. Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed disordered cardiomyocytes and hypertrophy in the DCM group; however, no differences were found among the remaining groups. Transmission electron microscopy revealed that the numbers of autophagosomes in the DCM and OB-TP groups were obviously increased compared to the NC and OB groups; the number of autophagosomes in the DCM-TP group was reduced. Western blotting showed that the expression of LC3-II/I and Beclin-1 increased obviously, whereas the expression of SQSTM1/p62 was decreased in the DCM and OB-TP groups (P<0.05).
Conclusions
Tea polyphenols had an effect on diabetic cardiomyopathy in rat cardiac function and may alter the levels of autophagy to improve glucose and lipid metabolism in diabetes.
中文概要
目的
探究茶多酚对自噬的调控及对糖尿病心肌病大鼠 心功能的影响。
创新点
本研究提示了糖尿病可诱导心肌自噬水平增高, 而茶多酚可抑制这一现象;相反,高脂血症可抑 制心肌自噬,而茶多酚却能诱导被抑制的自噬。
方法
各组大鼠造模成功后测定血中的血糖、血脂水平; 心超检测大鼠心脏结构及功能变化;苏木精-伊 红(H&E)染色观察心肌结构及病理改变;透射 电镜观察自噬体的形态和数量;蛋白质印迹法 (Western blotting)检测自噬相关蛋白LC3-II、 SQSTM1/p62 及Beclin-1 的表达水平。
结论
茶多酚对糖尿病心肌病大鼠心功能具有保护作 用,机制可能通过调节自噬水平改善糖尿病心肌 糖脂代谢紊乱有关。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen C, Yang S, Li H, et al., 2017. Mir30c is involved in diabetic cardiomyopathy through regulation of cardiac autophagy via BECN1. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 7:127–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.03.005
Chung YR, Park SJ, Moon KY, et al., 2017. Diabetic retinopathy is associated with diastolic dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 16(1):82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-017-0566-y
Ding ML, Ma H, Man YG, et al., 2017. Protective effects of a green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, against sevoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis involve regulation of CREB/BDNF/TrkB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathways in neonatal mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 95(12):1396–1405. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2016-0333
Ding S, Jiang J, Yu P, 2017. Green tea polyphenol treatment attenuates atherosclerosis in high-fat diet-fed apolipoprotein E-knockout mice via alleviating dyslipidemia and upregulating autophagy. PLoS ONE, 12(8):e0181666. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181666
Efeyan A, Comb WC, Sabatini DM, et al., 2015. Nutrientsensing mechanisms and pathways. Nature, 517:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14190
Fahie K, Zachara NE, 2016. Molecular functions of glycoconjugates in autophagy. J Mol Bol, 428(16):3305–3324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.06.011
Fan DM, Fan K, Yu CP, et al., 2017. Tea polyphenols dominate the short-term tea (Camellia sinensis) leaf litter decomposition. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 18(2):99–108. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600044
Gu W, Lin Y, Gou X, et al., 2017a. Tea polyphenol inhibits autophagy to sensitize epirubicin-induced apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells. Neoplasma, 64(05):674–680. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2017_504
Gu W, Yin H, Liu Y, et al., 2017b. The mechanism underlying the effects of tea polyphenol on epirubicin-induced autophagy and apoptosis in T24 bladder cancer cells. Chin J Cell Mol Immunol, 33(6):772–777 (in Chinese).
Jaishy B, Abel ED, 2016. Lipids, lysosomes, and autophagy. J Lipid Res, 57(9):1619–1635. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R067520
Kanamori H, Takemura G, Goto K, 2015. Autophagic adaptations in diabetic cardiomyopathy differ between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Autophagy, 11(7):1146–1160. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1051295
Kubli DA, Gustafsson ÅB, 2015. Unbreak my heart: targeting mitochondrial autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Ann Surg Oncol, 22(17):1527–1544. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2015.6322
Lai D, Gao J, Bi X, et al., 2017. The Rho kinase inhibitor, fasudil, ameliorates diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction by improving calcium clearance and actin remodeling. J Mol Med, 95(2):155–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1469-1
Li HL, Li ZJ, Wei ZS, et al., 2015. Long-term effects of oral tea polyphenols and Lactobacillus brevis M8 on biochemical parameters, digestive enzymes, and cytokines expression in broilers. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 16(12):1019–1026. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1500160
Lin C, Zhang M, Zhang Y, et al., 2017. Helix B surface peptide attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy via AMPK-dependent autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 482(4):665–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.091
Liu SM, Ou SY, Huang HH, 2017. Green tea polyphenols induce cell death in breast cancer MCF-7 cells through induction of cell cycle arrest and mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 18(2):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600022
Nazio F, Cecconi F, 2017. Autophagy up and down by outsmarting the incredible ULK. Autophagy, 13(5):967–968. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2017.1285473
Ruiz M, Coderre L, Allen BG, et al., 2017. Protecting the heart through MK2 modulation, toward a role in diabetic cardiomyopathy and lipid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta, 39(17):30241–30247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.07.015
Shin HR, Kim H, Kim KI, 2016. Epigenetic and transcriptional regulation of autophagy. Autophagy, 12(11):2248–2249. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1214780
Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, et al., 2009. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature, 458(7242):1131–1135. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07976
Su HM, Feng LN, Zheng XD, et al., 2016. Myricetin protects against diet-induced obesity and ameliorates oxidative stress in C57BL/6 mice. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 17(6):437–446. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600074
Sun XH, Yin MS, Mu YL, 2016. Alterations of mTOR pathway and autophagy in early type 2 diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. Chin J Pathol, 45(10):707–710 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2016.10.008
Trivedi PC, Bartlett JJ, Perez LJ, et al., 2016. Glucolipotoxicity diminishes cardiomyocyte TFEB and inhibits lysosomal autophagy during obesity and diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1861(12):1893–1910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.09.004
Velázquez AP, Graef M, 2016. Autophagy regulation depends on ER homeostasis controlled by lipid droplets. Autophagy, 12(8):1409–1410. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1190074
Wang M, Zhang WB, Zhu JH, 2009. Breviscapine ameliorates hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes induced by high glucose in diabetic rats via the PKC signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 30(8):1081–1091. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.95
Wieczór R, Wieczór AM, Gadomska G, et al., 2016. Overweight and obesity versus concentrations of VEGF-A, sVEGFR-1, and sVEGFR-2 in plasma of patients with lower limb chronic ischemia. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 17(11):842–849. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600009
Xie X, Yi W, Zhang P, 2017. Green tea polyphenols, mimicking the effects of dietary restriction, ameliorate highfat diet-induced kidney injury via regulating autophagy flux. Nutrients, 9(5):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050497
Yanagi S, Matsumura K, Marui A, et al., 2011. Oral pretreatment with a green tea polyphenol for cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in an isolated rat heart model. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 141(2):511–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.04.016
Yang Y, Rong X, Lv X, et al., 2017. Inhibition of mevalonate pathway prevents ischemia-induced cardiac dysfunction in rats via RhoA-independent signaling pathway. Cardiovasc Ther, 35(5):e12285. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-5922.12285
Yu HT, Zhen J, Pang B, et al., 2015. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates oxidative stress and myocardial apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 16(5):344–354. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1400204
Zhang L, Ding WY, Wang ZH, et al., 2016. Early administration of trimetazidine attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats by alleviating fibrosis, reducing apoptosis and enhancing autophagy. J Transl Med, 14(1):109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-016-0849-1
Zhang PW, Tian C, Xu FY, et al., 2016. Green tea polyphenols alleviate autophagy inhibition induced by high glucose in endothelial cells. Biomed Environ Sci, 29(7):524–528. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2016.069
Zhao P, Kuai J, Gao J, et al., 2017. Delta opioid receptor agonist attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury by regulating autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 492(1):140–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.029
Zhuo C, Jiang R, Lin X, et al., 2017. LncRNA H19 inhibits autophagy by epigenetically silencing of DIRAS3 in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Oncotarget, 8(1):1429–1437. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13637
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Ms. Qi WANG and Xiao-xia LIN, the lab administrator in Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University (Hangzhou, China) for their help. Most of research was performed in the Biomedical Research Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Scientific and Technological Projects for Medicine and Health of Zhejiang Province (No. 2015128660) and the Major Research and Development Projects for the Zhejiang Science and Technology Agency (No. 2017C03034), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Chen, Y., Huang, Sw. et al. Regulation of autophagy by tea polyphenols in diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 19, 333–341 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1700415
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1700415