Abstract
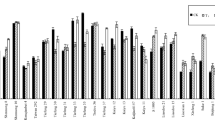
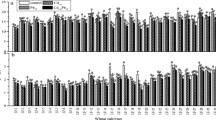
The selection and breeding of pollution-safe cultivars (PSCs) is a practicable and cost-effective approach to minimize the influx of heavy metal to the human food chain. In this study, both pot-culture and field experiments were conducted to identify and screen out cadmium pollution-safe cultivars (Cd-PSCs) from 50 pakchoi (Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis) cultivars for food safety. When treated with 1.0 or 2.5 mg/kg Cd, most of the pakchoi cultivars (>70%) showed greater or similar shoot biomass when compared with the control. This result indicates that pakchoi has a considerable tolerance to soil Cd stress. Cd concentrations in the shoot varied significantly (P<0.05) between cultivars: in two Cd treatments (1.0 and 2.5 mg/kg), the average values were 0.074 and 0.175 mg/kg fresh weight (FW), respectively. Cd concentrations in the shoots of 14 pakchoi cultivars were lower than 0.05 mg/kg FW. In pot-culture experiments, both enrichment factors (EFs) and translocation factors (TFs) of six pakchoi cultivars were lower than 1.0. The field studies further confirmed that the Hangzhouyoudonger, Aijiaoheiye 333, and Zaoshenghuajing cultivars are Cd-PSCs, and are therefore suitable for growth in low Cd-contaminated soils (≤1.2 mg/kg) without any risk to food safety.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway, B.J., 1995. Heavy Metals in Soils. Blackie Academic & Professional, London, p.38–57.
Arao, T., Ae, N., Sugiyama, M., Takahashi, M., 2003. Genotypic differences in cadmium uptake and distribution in soybeans. Plant Soil, 251(2):247–253. [doi:10.1023/A:1023079819086]
Arduini, I., Ercoli, L., Mariotti, M., Masoni, A., 2006. Response of miscanthus to toxic cadmium applications during the period of maximum growth. Environ. Exp. Bot., 55(1–2):29–40. [doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.09.009]
Baker, A.J.M., Whiting, S.N., 2002. In search of the holy grail—a further step in understanding metal hyperaccumulation? New Phytol., 155(1):1–4. [doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00449_1.x]
Chaney, R.L., Malik, M., Li, Y.M., Brown, S.L., Brewer, E.P., Angle, J.S., Baker, A.J.M., 1997. Phytoremediation of soil metals. Curr. Opin. Biotech., 8(3):279–284. [doi:10.1016/S0958-1669(97)80004-3]
Chapman, P.M., 2002. Ecological risk assessment (ERA) and hormesis. Sci. Total Environ., 288(1–2):131–140. [doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01120-2]
Chen, F., Dong, J., Wang, F., Wu, F.B., Zhang, G.P., Li, G.M., Chen, Z.F., Chen, J.X., Wei, K., 2007. Identification of barley genotypes with low grain Cd accumulation and its interaction with four microelements. Chemosphere, 67(10):2082–2088. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.10.014]
Clarke, J.M., McCaig, T.N., DePauw, R.M., Knox, R.E., Clarke, F.R., Fernandez, M.R., 2005. Strongfield durum wheat. Can. J. Plant Sci., 85(3):651–654. [doi:10.4141/P04-119]
Clarke, J.M., McCaig, T.N., DePauw, R.M., Knox, R.E., Clarke, F.R., Fernandez, M.R., 2006. Registration of ’strongfield’ durum wheat. Crop Sci., 46(5):2306–2307. [doi:10.2135/cropsci2005.12.0454]
Das, P., Samantaray, S., Rout, G.R., 1997. Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: a review. Environ. Pollut., 98(1):29–36. [doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(97)00110-3]
Dunbar, K.R., McLaughlin, M.J., Reid, R.J., 2003. The uptake and partitioning of cadmium in two cultivars of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Exp. Bot., 54(381):349–354.
Grant, C.A., Clarke, J.M., Duguid, S., Chaney, R.L., 2008. Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation. Sci. Total Environ., 390(2–3): 301–310. [doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.10.038]
Guo, X.F., Wei, Z.B., Wu, Q.T., Qiu, J.R., Zhou, J.L., 2011. Cadmium and zinc accumulation in maizegrain as affected by cultivars and chemical fixation amendments. Pedosphere, 21(5):650–656. [doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(11) 60167-7]
Harrison, H.A., 1986. Carrot response to sludge application and bed type. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci., 11(2):211–215.
Harrison, H.A., Staub, J.E., 1986. Effects of sludge, bed, and genotype on cucumber growth and elemental concentration of fruit and peel. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci., 11(2): 205–211.
He, J.Y., Zhu, C., Ren, Y.F., Yan, Y.P., Jiang, D., 2006. Genotypic variation in grain cadmium concentration of lowland rice. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci., 169(5):711–716. [doi:10.1002/jpln.200525101]
Kaminek, M., 1992. Progress in cytokinin research. Trends Biotechnol., 10:159–164. [doi:10.1016/0167-7799(92)90204-9]
Kurz, H., Schulz, R., Romheld, V., 1999. Selection of cultivars to reduce the concentration of cadmium and thallium in food and fodder plants. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci., 162(3):323–328. [doi:10.1002/(SICI)1522-2624(199906) 162:3<323::AID-JPLN323>3.0.CO;2-M]
Li, T.Q., Yang, X.E., Lu, L.L., Islam, E., He, Z.L., 2009. Effects of zinc and cadmium interactions on root morphology and metal translocation in a hyperaccumulating species under hydroponic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater., 169(1–3):734–741. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.004]
Li, Y.M., Chaney, R.L., Schneiter, A.A., Miller, J.F., Elias, E.M., Hammond, J.J., 1997. Screening for low grain cadmium phenotypes in sunflower, durum wheat and flax. Euphytica, 94(1):23–30. [doi:10.1023/A:10029 96405463]
Liu, J.G., Liang, J.S., Li, K.Q., Zhang, Z.J., Yu, B.Y., Lu, X.L., Yang, J.C., Zhu, Q.S., 2003a. Correlations between cadmium and mineral nutrients in absorption and accumulation in various genotypes of rice under cadmium stress. Chemosphere, 52(9):1467–1473. [doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00484-3]
Liu, J.G., Li, K.Q., Xu, J.K., Liang, J.S., Lu, X.L., Yang, J.C., Zhu, Q.S., 2003b. Interaction of Cd and five mineral nutrients for uptake and accumulation in different rice cultivars and genotypes. Field Crop Res., 83(3):271–281. [doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(03)00077-7]
Liu, J.G., Qian, M., Cai, G.L., Yang, J.C., Zhu, Q.S., 2007. Uptake and translocation of Cd in different rice cultivars and the relation with Cd accumulation in rice grain. J. Hazard. Mater., 143(1–2):443–447. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.09.057]
Liu, W.T., Zhou, Q.X., Sun, Y.B., Liu, R., 2009. Identification of Chinese cabbage genotypes with low cadmium accumulation for food safety. Environ. Pollut., 157(6): 1961–1967. [doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.01.005]
Liu, W.T., Zhou, Q.X., An, J., Sun, Y.B., Liu, R., 2010. Variations in cadmium accumulation among Chinese cabbage cultivars and screening for Cd-safe cultivars. J. Hazard. Mater., 173(1–3):737–743. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.147]
Lu, R.K., 1999. Analytical Methods for Soils and Agricultural Chemistry. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
McGrath, S.P., Zhao, F.J., 2003. Phytoextraction of metals and metalloids from contaminated soils. Curr. Opin. Biotech., 14(3):277–282. [doi:10.1016/S0958-1669(03)00060-0]
Miller, J.F., Green, C.E., Li, Y.M., Chaney, R.L., 2006. Registration of three low cadmium (HA 448, HA 449, and RHA 450) confection sunflower genetic stocks. Crop Sci., 46(1):489–490. [doi:10.2135/cropsci2005.04-0012]
MHC (Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China), 2005. GB 2762-2005: Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods. MHC, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Nyitrai, P., Bóka, K., Gáspár, L., Sárvári, É., Keresztes, Á., 2004. Rejuvenation of ageing bean leaves under the effect of low-dose stressors. Plant Biol., 6(6):708–714. [doi:10.1055/s-2004-830385]
Ryan, J.A., Pahren, H.R., Lucas, J.B., 1982. Controlling cadmium in the human chain: a review and rationale based on health effects. Environ. Res., 28(2):251–302. [doi:10.1016/0013-9351(82)90128-1]
Singh, S., Eapen, S., D’souza, S.F., 2006. Cadmium accumulation and its influence on lipid peroxidation and antioxidative system in an aquatic plant, Bacopa monnieri L. Chemosphere, 62(2):233–246. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.017]
Stolt, P., Asp, H., Hultin, S., 2006. Genetic variation in wheat cadmium accumulation on soils with different cadmium concentrations. J. Agron. Crop Sci., 192(3):201–208. [doi:10.1111/j.1439-037X.2006.00202.x]
Thomas, G.M., Harrison, H.C., 1991. Genetic line effects on parameters influencing cadmium concentration in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). J. Plant Nutr., 14(9):953–962. [doi:10.1080/01904169109364255]
Yu, H., Wang, J.L., Fang, W., Yuan, J.G., Yang, Z.Y., 2006. Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars of rice. Sci. Total Environ., 370(2–3):302–309. [doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.06.013]
Zeng, F.R., Mao, Y., Cheng, W.D., Wu, F.B., Zhang, G.P., 2008. Genotypic and environmental variation in chromium, cadmium and lead concentrations in rice. Environ. Pollut., 153(2):309–314. [doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.08.022]
Zhang, G.P., Fukami, M., Sekimoto, H., 2002. Influence of cadmium on mineral concentrations and yield components in wheat genotypes differing in Cd tolerance at seedling stage. Field Crops Res., 77(2–3):93–98. [doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(02)00061-8]
Zhou, Q.X., Song, Y.F., 2004. Principles, Methods of Contaminated Soil Remediation. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Zhu, Y., Yu, H., Wang, J.L., Fang, W., Yuan, J.G., Yang, Z.Y., 2007. Heavy metal accumulation of 24 asparagus bean cultivars grown in soil contaminated with Cd alone and with multiple metals (Cd, Pb, and Zn). J. Agric. Food Chem., 55(3):1045–1052. [doi:10.1021/jf062971p]
Zhu, Y.G., Chen, S.B., Yang, J.C., 2004. Effects of soil amendments on lead uptake by two vegetable crops from a lead-contaminated soil from Anhui, China. Environ. Int. 30(3):351–356. [doi:10.1016/j.envint.2003.07.001]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National High-Tech R & D Program (863) of China (No. 2009AA06Z316), the Science and Technology Commission of Zhejiang Province (No. 2008C33047), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Li, Tq., Han, X. et al. Cadmium accumulation in different pakchoi cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 13, 494–502 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1100356
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1100356