Abstract
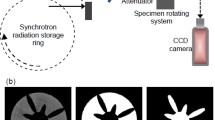
Based on the high flux synchrotron X-ray of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF), high precision 3D digital models of diesel nozzle tips have been established by X-ray micro-tomography technology, which reveal the internal surfaces and structures of orifices. To analyze the machining precision and characteristics of orifice processing methods, an approach is presented based on the parameters of the internal structures of nozzle orifices, including the nozzle diameter, the orifice inner surface waviness, the eccentricity distance and the angle between orifices. Using this approach, two kinds of nozzle orifice processing methods, computerized numerical control drilling and electric discharge machining, have been studied and compared. The results show that this approach enables a simple, direct, and comprehensive contrastive analysis of nozzle orifice processing methods. When processing a single orifice, the electric discharge machining method has obvious advantages. However, when there are multiple orifices, the error levels of the two methods are similar in relation to the symmetry of distribution of the orifices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delphine, L., Samuel, L., Grégory, B., Benoît, J., 2007. Metrology of Steel Micro-Nozzles Using X-ray Microtomography. DIR, Lyon, France.
Diver, C., Atkinson, J., Helml, H.J., Li, L., 2004. Micro-EDM drilling of tapered holes for industrial applications. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 149(1–3): 296–303. [doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2003.10.064]
Gao, Y., Huang, W.D., Gao, Y., Gong, H.F., Hu, Z.J., Li, L.G., 2010. The Study of Spray Nozzle Orifice Manufacture Consistency. APC Joint Annual Meeting, Yichang, Hubei, China (in Chinese).
Jung, D., Wang, W.L., Knafl, A., Jacobs, J., Hu, S.J., Assanis, D.N., 2008. Experimental investigation of abrasive flow machining effects on injector nozzle geometries, engine performance and emissions in a DI diesel engine. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 9(1): 9–15. [doi:10.1007/s12239-008-0002-0]
Kao, C.C., Shih, A.J., 2007. Form measurements of micro-holes. Measurement Science and Technology, 18:3603–3611. [doi:10.1088/0957-0233/18/11/045]
Kim, B., Masuzawa, T., Bourouina, T., 1999. The vibroscanning method for the measurement of micro-hole profiles. Measurement Science and Technology, 10(8):697–705. [doi:10.1088/0957-0233/10/8/304]
Kostas, J., Honnerya, D., Soriaa, J., 2009. Time resolved measurements of the initial stages of fuel spray penetration. Fuel, 88(11):2225–2237. [doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2009.05.013]
Li, X.H., Yu, H.X., He, J.H., 2010. The introduction of SSRF. Modern Physics, 22(3):14–19 (in Chinese).
Li, Z.L., Wu, Z.J., Gao, Y., Deng, J., Hu, Z.J., Li, L.G., Xiao, T.Q., Fu, Y.N., Chen, R.C., 2011. Measurement method for diesel nozzle internal geometry and size using high-energy synchrotron radiation X-ray. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 41(1): 128–132 (in Chinese).
Macián, V., Bermúdez, V., Payri, R., Gimeno, J., 2003. New technique for the determination of the internal geometry of diesel nozzle with the use of the silicone methodology. Experimental Techniques, 27(2):39–43.
Payri, R., Salvador, F.J., Gimeno, J., Zapata, L.D., 2008. Diesel nozzle geometry influence on spray liquid-phase fuel penetration in evaporative conditions. Fuel, 87(7): 1165–1176. [doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2007.05.058]
Payri, R., Salvador, F.J., Gimeno, J., de la Morena, J., 2009. Effects of nozzle geometry on direct injection diesel engine combustion process. Applied Thermal Engineering, 29(10):2051–2060. [doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2008.10.009]
Peiner, E., Balke, M., Doering, L., 2009. Form measurement inside fuel injector nozzle spray holes. Microelectronic Engineering, 86(4–6):984–986. [doi:10.1016/j.mee.2008.12.016]
Ren, Z.D., Huang, Q.Y., 2008. Discuss of spray nozzle orifices processing technology and applications. Automobile Industries, 14:50–55 (in Chinese).
Som, S., Ramirez, A.I., Longman, D.E., Aggarwal, S.K., 2011. Effect of nozzle orifice geometry on spray, combustion, and emission characteristics under diesel engine conditions. Fuel, 90(3):1267–1276. [doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2010.10.048]
Wang, W.L., Hu, S.J., 2004. Geometry and surface characterization of micro-holes in fuel injector nozzles. Nanotechnology and Precision Engineering, 1:65–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 50946052, 51076118 and 51006075), the New Century Excellent Talents (No. NCET-10-0605), the Shanghai Rising-Star Program (No. 11QH1402500), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 200802471052)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Zj., Li, Zl., Huang, Wd. et al. Comparisons of nozzle orifice processing methods using synchrotron X-ray micro-tomography. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 13, 182–188 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1100252
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1100252