Abstract
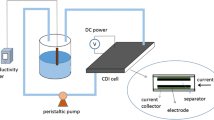
The application of membrane capacitive deionisation was investigated for treating model water samples and real waste waters from the textile industry. For the pre-treatment of waste waters, nanofiltration was integrated in order to prevent scaling and fouling of membranes and electrodes during membrane capacitive deionisation. Different conditions were applied when treating water samples with membrane capacitive deionisation with the aim of optimising conditions for high desalination efficiency and, consequently, for conductivity reduction. The conductivity of waste waters with high salt concentrations was reduced to the required value, below 1.5 mS cm−1. The desalination rates achieved as much as 95 %, depending on the initial conductivity and the different ions present in the water samples. In addition, chemometric characterisation of the samples was performed in order to determine the existence of significant correlations between the monitored parameters: the presence of various ions (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, Br−, F−, SO42−, NO3−, desalination and water recovery, the duration of each phase and the flow of the solution during each phase. A model for desalination rate prediction was designed using multiple linear regression. It was established that the model values accorded well with the experimental values — the differences between model and experimental values were less than 1 %.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari, A., Remigy, J. C., & Aptel, P. (2002). Treatment of textile dye effluent using a polyamide-based nanofiltration membrane. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 41, 601–609. DOI: 10.1016/s0255-2701(01)00181-7.
Babu, B. R., Parande, A. K., Raghu, S., & Prem Kumar, T. (2007). Cotton textile processing: Waste generation and effluent treatment. Journal of Cotton Science, 11, 141–153.
Biesheuvel, P. (2009). Thermodynamic cycle analysis for capacitive deionization. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 332, 258–264. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2008.12.018.
Broséus, R., Cigana, R., Barbeau, B., Daines-Martinez, C., & Suty, H. (2009). Removal of total dissolved solids, nitrates and ammonium ions from drinking water using charge-barrier capacitive deionisation. Desalination, 249, 217–223. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2008.12.048.
Dermentzis, K., & Ouzounis, K. (2008). Continuous capacitive deionization—electrodialysis reversal through electrostatic shielding for desalination and deionization of water. Electrochimica Acta, 53, 7123–7130. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2008.05.026.
Isabel, E., & Schafer, A. (2010). Sustainable water for the future: Water recycling, reuse, desalination. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier.
Joarder, M. A. M., Raihan, F., Alam, J. B., & Hasanuzzaman, S. (2008). Regression analysis of ground water quality data of Sunamganj district, Bangladesh. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2, 291–296.
Kim, Y. J., & Choi, J. H. (2010). Enhanced desalination efficiency in capacitive deionization with an ion-selective membrane. Separation and Purification Technology, 71, 70–75. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2009.10.026.
Košmelj, K., & Breskvar Žaucer, L. (2006). Metode za razvrščanje enot v skupine; osnove in primer. Acta Agriculturae Slovenica, 87, 229–310. (in Slovenian)
Ledakowicz, S., Solecka, M., & Zylla, R. (2001). Biodegradation, decolourisation and detoxification of textile wastewater enhanced by advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Biotechnology, 89, 175–184. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-1656(01)00296-6.
Li, H. B., Zou, L., Pan, L. K., & Sun, Z. (2010). Using graphene nano-flakes as electrodes to remove ferric ions by capacitive deionization. Separation and Purification Technology, 75, 8–14. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2010.07.003.
Majcen Le Marechal, A., Križanec, B., Vajnhandl, S., & Volmajer Valh, J. (2012). Textile finishing industry as an important source of organic pollutants. In V. T. Puzyn, & A. Mostragg-Szlichtyng (Eds.), Organic pollutants ten years after the Stockholm convention — environmental and analytical update (pp. 30–54). Rijeka, Croatia: InTech.
Marmagne, O., & Coste, C. (1996). Color removal from textile plant effluents. American Dyestuff Reporter, 4, 15–27.
Massart, D. (1997). Handbook of chemometrics and qualimetrics: Part A. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier.
Meier, P., & Zünd, R. (2000). Statistical methods in analytical chemistry (2nd ed.). New York, NY, USA: Wiley.
Meriç, S., Lofrano, G., & Belgiorno, V. (2005). Treatment of reactive dyes and textile finishing wastewater using Fenton’s oxidation for reuse. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 23, 248–258.
Miller, J., & Miller, J. (2005). Statistics and chemometrics for analytical chemistry (5th ed.). Edinburgh, UK: Pearson.
Patel, H., & Vashi, R. T. (2010). Treatment of textile wastewater by adsorption and coagulation. E-Journal of Chemistry, 7, 1468–1476.
Perkowski, J., Kos, L., & Ledakowicz, S. (1996). Application of ozone in textile wastewater treatment. Ozone: Science & Engineering: The Journal of the International Ozone Association, 18, 73–85. DOI: 10.1080/01919519608547342.
Pohar, M., Blas, M., & Turk, S. (2004). Comparison of logistic regression and linear discriminant analysis: A simulation study. Metodološki Zvezki, 1, 143–161.
Robinson, T., McMullan, G., Marchant, R., & Nigam, P. (2001). Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: A critical rewiev on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresource Technology, 77, 247–255. DOI: 10.1016/s0960-8524(00)00080-8.
Subramani, A., Badruzzaman, M., Oppenheimer, J., & Jacangelo, J. G. (2011). Energy minimization strategies and renewable energy utilization for desalination: A review. Water Research, 45, 1907–1920. DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.12.032.
Van Limpt, B. (2010). Performance relations in capacitive deionization systems. Wageningen, The Netherlands: Wageningen University.
Varmuza, K., & Filzmoser, P. (2008). Introduction to multivariate statistical analysis in chemometrics. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press.
Yang, C. M., Choi, W. H., Na, B. K., Cho, B. W., & Cho, W. I. (2005). Capacitive deionization of NaCl solution with carbon aerogel—silicagel composite electrodes. Desalination, 174, 125–133. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2004.09.006.
Yang, J., Zou, L., Song, H. H., & Hao, Z. P. (2011). Development of novel MnO2/nanoporous carbon composite electrodes in capacitive deionization technology. Desalination, 276, 199–206. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.03.044.
Zupan, J. (2009). Kemometrija in obdelava eksperimentalnih podatkov (1st ed.). Ljubljana, Slovenia: Inštitut Nove Revije, Zavod za Humanistiko in Kemijski Inštitut Ljubljana. (in Slovenian)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biro, M., Vončina, D.B. Innovative approach to treating waste waters by a membrane capacitive deionisation system. Chem. Pap. 70, 576–584 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0239
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0239