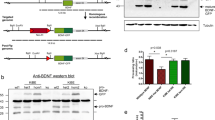
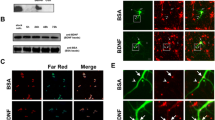
Abstract
The neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a regulatory factor of several, partially contrasting, aspects of the biology of neural cells, including survival, growth, differentiation, and cell death. Regulation of the local availability of BDNF at distinct subcellular domains such as the cell soma, dendrites, axons, and spines appears to be the key to conferring spatial and temporal specificity of the different effects elicited by this neurotrophin. This article reviews recent findings in the context of epileptogenesis and visual cortex maturation that showed that different BDNF messenger RNA (mRNA) transcripts are localized at different subcellular locations in hippocampal and cortical neurons. It also reviews findings demonstrating that strong depolarizing stimuli, both in vitro and in vivo, elicit accumulation of BDNF mRNA and protein in the distal dendrites through a signaling pathway involving the activation of the N-methyl-d-aspartate and tyrosine kinase B receptors and an intracellular increase in Ca2+ concentration. Finally, this article proposes that the regulation of the delivery of BDNF mRNA and protein to the different subcellular domains—particularly the dendritic compartment—may represent a fundamental aspect of the processes of cellular and synaptic morphological rearrangements underlying epileptogenesis and postnatal development of the visual cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barde Y. A., Edgar D., and Thoenen H. (1982) Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1, 549–553.
Leibrock J., Lottspeich F., Hohn A., et al. (1989) Molecular cloning and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature 341, 149–152.
Bibel M. and Barde Y. A. (2000) Neurotrophins: key regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous system. Genes Dev. 14, 2919–2937.
Huang E. J. and Reichardt L. F. (2003) Trk receptors: roles in neuronal signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 609–642.
Casaccia-Bonnefil P., Gu C., and Chao M. V. (1999) Neurotrophins in cell survival/death decisions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 468, 275–282.
Lu B. (2003) Pro-region of neurotrophins: role in synaptic modulation. Neuron. 39, 735–738.
Schuman E. (1999) Neurotrophin regulation of synaptic transmission. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 9, 105–109.
Tanaka T., Saito H., and Matsuki N. (1997) Inhibition of GABAA synaptic responses by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 17, 2959–2966.
Kaplan D. R. and Miller F. D. (2000) Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 10, 381–391.
Thoenen H. (2000) Neurotrophins and activity-dependent plasticity. Prog. Brain Res. 128, 183–191.
Patapoutian A. and Reichardt L. F. (2001) Trk receptors: mediators of neurotrophin action. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11, 272–280.
Heerssen H. M. and Segal R. A. (2002) Location, location, location: a spatial view of neurotrophin signal transduction. Trends Neurosci. 25, 160–165.
Palacios I. M. and St Johnston D. (2001) Getting the message across: the intracellular localization of mRNAs in higher eukaryotes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 17, 569–614.
Steward O. (1997) mRNA localization in neurons: a multipurpose mechanism? Neuron 18, 9–12.
Steward O. and Schuman E. M. (2001) Protein synthesis at synaptic sites on dendrites. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 299–325.
Tiedge H., Bloom F. E., and Richter D. (1999) RNA, whither goest thou? Science 283, 186, 187.
Tiedge H. and Brosius J. (1996) Translational machinery in dendrites of hippocampal neurons in culture. J. Neurosci. 16, 7171–7181.
Torre E. R. and Steward O. (1996) Protein synthesis within dendrites: glycosylation of newly synthesized proteins in dendrites of hippocampal neurons in culture. J. Neurosci. 16, 5967–5978.
Steward O. and Reeves T. M. (1988) Protein-synthetic machinery beneath postsynaptic sites on CNS neurons: association between polyribosomes and other organelles at the synaptic site. J. Neurosci. 8, 176–184.
Gardiol A., Racca C., and Triller A. (1999) Dendritic and postsynaptic protein synthetic machinery. J. Neurosci. 19, 168–179.
Kuhl D. and Skehel P. (1998) Dendritic localization of mRNAs. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 8, 600–606.
Mohr E. (1999) Subcellular RNA compartmentalization. Prog. Neurobiol. 57, 507–525.
Eberwine J., Belt B., Kacharmina J. E., and Miyashiro K. (2002) Analysis of subcellularly localized mRNAs using in situ hybridization, mRNA amplification, and expression profiling. Neurochem Res. 27, 1065–1077.
Kang H. and Schuman E. M. (1996) A requirement for local protein synthesis in neurotrophin-induced hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Science 273, 1402–1406.
Van de Bor V. and Davis I. (2004) mRNA localization gets more complex. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16, 300–307.
Wells D. G., Richter J. D., and Fallon J. R. (2000) Molecular mechanisms for activity-regulated protein synthesis in the synapto-dendritic compartment. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 10, 132–137.
Kindler S. and Monshausen M. (2002) Candidate RNA-binding proteins regulating extrasomatic mRNA targeting and translation in mammalian neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 25, 149–165.
van Eeden F. and St Johnston D. (1999) The polarisation of the anterior-posterior and dorsal-ventral axes during Drosophila oogenesis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 9, 396–404.
Kiebler M. A., Hemraj I., Verkade P., et al. (1999) The mammalian staufen protein localizes to the somatodendritic domain of cultured hippocampal neurons: implications for its involvement in mRNA transport. J. Neurosci. 19, 288–297.
Kohrmann M., Luo M., Kaether C., DesGroseillers L., Dotti C. G., and Kiebler M. A. (2001) Microtubule-dependent recruitment of Staufen-green fluorescent protein into large RNA-containing granules and subsequent dendritic transport in living hippocampal neurons. Mol. Biol. Cell 10, 2945–2953.
Tang S. J. and Schuman E. M. (2002) Protein synthesis in the dendrite. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 357, 521–529.
Davis L., Banker G. A., and Steward O. (1987) Selective dendritic transport of RNA in hippocampal neurons in culture. Nature 330, 477–479.
Severt W. L., Biber T. U., Wu X., Hecht N. B., DeLorenzo R. J., and Jakoi E. R. (1999) The suppression of testis-brain RNA binding protein and kinesin heavy chain disrupts mRNA sorting in dendrities. J. Cell Sci. 112, 3691–3702.
Hoek K. S., Kidd G. J., Carson J. H., and Smith R. (1998) hnRNP A2 selectively binds the cytoplasmic transport sequence of myelin basic protein mRNA. Biochemistry 37, 7021–7029.
Mazroui R., Huot M. E., Tremblay S., Filion C., Labelle Y., and Khandjian E. W. (2002) Trapping of messenger RNA by Fragile X Mental Retardation protein into cytoplasmic granules induces translation repression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 3007–3017.
Shan J. Munro T. P., Barbarese E., Carson J. H., and Smith R. (2003) A molecular mechanism for mRNA trafficking in neuronal dendrites. J. Neurosci. 23, 8859–8866.
Anderson K. D., Merhege M. A., Morin M., Bolognani F., and Perrone-Bizzozero N. I. (2003) Increased expression and localization of the RNA-binding protein HuD and GAP-43 mRNA to cytoplasmic granules in DRG neurons during nerve regeneration. Exp. Neurol. 183, 100–108.
Tiruchinapalli D. M., Oleynikov Y., Kelic S., et al. (2003) Activity-dependent trafficking and dynamic localization of zipcode binding protein 1 and beta-actin mRNA in dendrites and spines of hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 23, 3251–3261.
Macchi P., Kroening S., Palacios I. M., et al. (2003) Barentsz, a new component of the Staufen-containing ribonucleoprotein particles in mammalian cells, interacts with Staufen in an RNA-dependent manner. J. Neurosci. 23, 5778–5788.
Barbarese E., Koppel D. E., Deutscher M. P., et al. (1995) Protein translation components are colocalized in granules in oligodendrocytes. J. Cell Sci. 108, 2781–2790.
Carson J. H., Kwon S., and Barbarese E. (1998) RNA trafficking in myelinating cells. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 8, 607–612.
Krichevsky A. M. and Kosik K. S. (2001) Neuronal RNA granules: a link between RNA localization and stimulation-dependent translation. Neuron 32, 683–696.
Kanai Y., Dohmae N., and Hirokawa N. (2004) Kinesin transports RNA: isolation and characterization of an RNA-transporting granule. Neuron 43, 513–525.
Tongiorgi E., Righi M., and Cattaneo A. (1997) Activity-dependent dendritic targeting of BDNF and TrkB mRNAs in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 17, 9492–9505.
Righi M., Tongiorgi E., and Cattaneo A. (2000) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) induces dendritic targeting of BDNF and tyrosine kinase B mRNAs in hippocampal neurons through a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-dependent pathway. J. Neurosci. 20, 3165–3174.
Tongiorgi E., Armellin M., Giulianini P. G., et al. (2004) BDNF mRNA and protein are targeted to discrete dendritic laminae by events that trigger epileptogenesis. J. Neurosci. 24, 6842–6852.
Job C. and Eberwine J. (2001) Identification of sites for exponential translation in living dendrites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 13,037–13,042.
Tongiorgi E., Armellin M., and Cattaneo A. (2000) Differential somato-dendritic localization of TrkA, TrkB, TrkC and p75 mRNAs in vivo. Neuroreport 11, 3265–3268.
McNamara J. O. (1999) Emerging insights into the genesis of epilepsy. Nature 399 (Suppl), A15-A22.
Mody I. (1999) Synaptic plasticity in kindling. Adv. Neurol. 79, 631–643.
Brooks-Kayal A. R., Shumate M. D., Jin H., Rikhter T. Y., and Coulter D. A. (1998) Selective changes in single cell GABA(A) receptor subunit expression and function in temporal lobe epilepsy. Nat. Med. 4, 1166–1172.
Ernfors P., Bengzon J., Kokaia Z., Persson H., and Lindvall O. (1991) Increased levels of messenger RNAs for neurotrophic factors in the brain during kindling epileptogenesis. Neuron 7, 165–176.
Isackson P. J., Huntsman M. M., Murray K. D., and Gall C. M. (1991) BDNF mRNA expression is increased in adult rat forebrain after limbic seizures: temporal patterns of induction distinct from NGF. Neuron 6, 937–948.
Bengzon J., Kokaia Z., Ernfors P., et al. (1993) Regulation of neurotrophin and trkA, trkB and trkC tyrosine kinase receptor messenger RNA expression in kindling. Neuroscience 53, 433–446.
Simonato, M., Molteni R., Bregola G., et al. (1998) Different patterns of induction of FGF-2, FGF-1 and BDNF mRNAs during kindling epielptogenesis in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 955–963.
Murray K. D., Isackson P. J., Eskin T. A., et al. (2000) Altered mRNA expression for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and type II calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in the hippocampus of patients with intractable temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Comp. Neurol. 418, 411–422.
Huang Y., Doherty J. J., and Dingledine R. (2002) Altered histone acetylation at glutamate receptor 2 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor genes is an early event triggered by status epilepticus. J. Neurosci. 22, 8422–8428.
Binder D. K., Routbort M. J., and McNamara J. O. (1999) Immunohistochemical evidence of seizure-induced activation of trk receptors in the mossy fiber pathway of adult rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 19, 4616–4626.
Kokaia M., Ernfors P., Kokaia Z., Elmer E., Jaenisch R., and Lindvall O. (1995) Suppressed epileptogenesis in BDNF mutant mice. Exp. Neurol. 133, 215–224.
Binder D. K., Routbort M., Ryan T. E., Yancopoulos D. G., and McNamara J. O. (1999b) Selective inhibition of kindling development by intraventricular administration of TrkB receptor body. J. Neurosci. 19, 1424–1436.
Lahteinen S., Pitkanen A., Saarelainen T., Nissinen J., Koponen E., and Castren E. (2002) Decreased BDNF signalling in transgenic mice reduces epileptogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 15, 721–734.
Croll S. D., Suri C., Compton D. L., et al. (1999) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor transgenic mice exhibit passive avoidance deficits, increased seizure severity and in vitro hyper-excitability in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Neuroscience 93, 1491–1506.
Xu B., Michalski B., Racine R. J., and Fahnestock M. (2004) The effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) administration on kindling induction, Trk expression and seizure-related morphological changes. Neuroscience 126, 521–531.
He X. P., Kotloski R., Nef S., Luikart B. W., Parada L. F., and McNamara J. O. (2004) Conditional deletion of TrkB but not BDNF prevents epileptogenesis in the kindling model. Neuron 43, 31–42.
Schinder A. F. and Poo M. (2000) The neurotrophin hypothesis for synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 23, 639–645.
Korte M., Minichiello L., Klein R., and Bonhoeffer T. 2000) Shc-binding site in the TrkB receptor is not required for hippocampal long-term potentiation. Neuropharmacology 39, 717–724.
He X. P., Minichiello L., Klein R., and McNamara, J. O. (2002) Immunohistochemical evidence dence of seizure-induced activation of trkB receptors in the mossy fiber pathway of adult mouse hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 22, 7502–7508.
Zhou X. F. and Rush R. A. (1996) Endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor is anterogradely transported in primary sensory neurons. Neuroscience 74, 945–953.
Conner J. M., Lauterborn J. C., Yan Q., Gall C. M., and Varon S. (1997) Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein and mRNA in the normal adult rat CNS: evidence for anterograde axonal transport. J. Neurosci. 17, 2295–2313.
Smith M. A., Zhang L. X., Lyons W. E., and Mamounas L. A. (1997) Anterograde transport of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal mossy fibers. Neuroreport 8, 1829–1834.
Fawcett J. P., Bamji S. X., Causing C. G., et al. (1998) Functional evidence that BDNF is an anterograde neuronal trophic factor in the CNS. J. Neurosci. 18, 2808–2821.
Elmer E., Kokaia Z., Kokaia M., Carnahan J., Nawa H., and Lindvall O. (1998) Dynamic changes of brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein levels in the rat forebrain after single and recurring kindling-induced seizures. Neuroscience 83, 351–362.
Altar C. A. and Di Stefano P. S. (1998) Neurotrophin trafficking by anterograde transport. Trends Neurosci. 21, 433–437.
Simonato M., Bregola G., Armellin M., et al. (2002) Dendritic targeting of mRNAs for plasticity genes in experimental models of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 43(Suppl), 153–158.
Merlio J. P., Ernfors P., Kokaia Z., et al. (1993) Increased production of the TrkB protein tyrosine kinase receptor after brain insults. Neuron 10, 151–64.
Wetmore C., Olson L., and Bean A. J. (1994) Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression and release from hippocampal neurons is mediated by non-NMDA type glutamate receptors. J. Neurosci. 14, 1688–1700.
Zafra F., Hengerer B., Leibrock J., Thoenen H., and Lindholm D. (1990) Activity dependent regulation of BDNF and NGF mRNAs in the rat hippocampus is mediated by non-NMDA glutamate receptors. EMBO J. 9, 3545–3550.
McNamara J. O., Russell R. D., Rigsbee L., and Bonhaus D. W. (1988) Anticonvulsant and antiepileptogenic actions of MK-801 in the kindling and electroshock models. Neuropharmacology 27, 563–568.
Ormandy G. C., Jope R. S., and Snead O. C. 3rd (1989) Anticonvulsant actions of MK-801 on the lithium-pilocarpine model of status epilepticus in rats. Exp. Neurol. 106, 172–180.
Rice A. C. and DeLorenzo R. J. (1998) NMDA receptor activation during status epilepticus is required for the development of epilepsy. Brain Res. 782, 240–247.
Vezzani A., Ravizza T., Moneta D., et al. (1999) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor immunore-activity in the limbic system of rats after acute seizures and during spontaneous convulsions: temporal evolution of changes as compared to Neuropeptide Y. Neuroscience 90, 1445–1461.
Kryl D., Yacoubian T., Haapasalo A., Castren E., Lo D., and Barker P. A. (1999) Subcellular localization of full-length and truncated Trk receptor isoforms in polarized neurons and epithelial cells. J. Neurosci. 19, 5823–5833.
Goutan E., Marti E., and Ferrer I. (1998) BDNF, and full length and truncated TrkB expression in the hippocampus of the rat following kainic acid excitotoxic damage. Evidence of complex time-dependent and cell-specific responses. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 59, 154–164.
Drake C. T., Milner T. A., and Patterson S. L. (1999) Ultrastructural localization of full-length trkB immunoreactivity in rat hippocampus suggests multiple roles in modulating activity-dependent synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 19, 8009–8026.
Bhattacharyya A., Watson F. L., Bradlee T. A., Pomeroy S. L, Stiles C. D., and Segal R. A. (1997) Trk receptors function as rapid retrograde signal carriers in the adult nervous system. J. Neurosci. 17, 7007–7016.
Lessmann V. and Heumann R. (1998) Modulation of unitary glutamatergic synapses by neurotrophin-4/5 or brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal microcultures: presynaptic enhancement depends on pre-estab lished paired-pulse facilitation. Neuroscience 86, 399–413.
Schinder A. F., Berninger B., and Poo M. (2000) Postsynaptic target specificity of neurotrophin-induced presynaptic potentiation. Neuron 25, 151–163.
Wardle R. A. and Poo M. M. (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulation of GABA ergic synapses by postsynaptic regulation of chloride transport. J. Neurosci. 23, 8722–8732.
Kang H. and Schuman E. M. (1995a) Long-lasting neurotrophin-induced enhancement of synaptic transmission in the adult hippocampus. Science 267, 1658–1662.
Kang H. and Schuman E. M. (1995b) Neurotrophin-induced modulation of synaptic transmission in the adult hippocampus. J. Physiol. Paris 89, 11–22.
Kang H., Welcher A. A., Shelton D., and Schuman E. M. (1997) Neurotrophins and time: different roles for TrkB signaling in hippocampal long-term potentiation. Neuron 19, 653–664.
Messaoudi E., Bardsen K., Srebro B., and Bramham C. R. (1998) Acute intrahippocampal infusion of BDNF induces lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the rat dentate gyrus. J. Neurophysiol. 79, 496–499.
Tanaka T., Saito H., and Matsuki N. (1997) Inhibition of GABAA synaptic responses by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 17, 2959–2966.
Frerking M., Malenka R. C., and Nicoll R. A. (1998) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) modulates inhibitory, but not excitatory, transmission in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 80, 3383–3386.
Figurov A., Pozzo-Miller L. D., Olafsson P., Wang T., and Lu B. (1996) Regulation of synaptic responses to high-frequency stimulation and LTP by neurotrophins in the hippocampus. Nature 381, 706–709.
Gottschalk W., Pozzo-Miller L. D., Figurov A., and Lu B. (1998) Presynaptic modulation of synaptic transmission and plasticity by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the developing hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 18, 6830–6839.
Patterson S. L., Abel T., Deuel T. A., Martin K. C., Rose J. C., and Kandel E. R. (1996) Recombinant BDNF rescues deficits in basal synaptic transmission and hippocampal LTP in BDNF knockout mice. Neuron 16, 1137–1145.
Berninger B., Schinder A. F., and Poo M. M. (1999) Synaptic reliability correlates with reduced susceptibility to synaptic potentiation by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Learn Mem. 6, 232–242.
Kafitz K. W., Rose C. R., Thoenen H., and Konnerth A. (1999) Neurotrophin-evoked rapid excitation through TrkB receptors. Nature 401, 918–921.
Lohof A. M., Ip N. Y., and Poo M. M. (1993) Potentiation of developing neuromuscular synapses by the neurotrophins NT-3 and BDNF. Nature 363, 350–353.
Takei N., Sasaoka K., Inoue K., Takahashi M., Endo Y., and Hatanaka H. (1997) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases the stimulation-evoked release of glutamate and the levels of exocytosis-associated proteins in cultured cortical neurons from embryonic rats. J. Neurochem. 68, 370–375.
Takei N., Numakawa T., Kozaki S., et al. (1998) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces rapid and transient release of glutamate through the non-exocytotic pathway from cortical neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 27,620–27,624.
Li Y. X., Zhang Y., Lester H. A., Schuman E. M., and Davidson N. (1998) Enhancement of neurotransmitter release induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 18, 10,231–10,240.
Levine E. S., Crozier R. A., Black I. B., and Plummer M. R. (1998) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates hippocampal synaptic transmission by increasing N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 10,235–10,239.
Suen P. C., Wu K., Levine E. S., et al. (1997) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor rapidly enhances phosphorylation of the postsynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 8191–8195.
Brunig I., Penschuck S., Berninger B., Benson J., and Fritschy J. M. (2001) BDNF reduces miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents by rapid downregulation of GABA(A) receptor surface expression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 13, 1320–1328.
Scharfman H. E. (1997) Hyperexcitability in combined entorhinal/hippocampal slices of adult rat after exposure to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Neurophysiol. 78, 1082–1095.
Scharfman H. E., Goodman J. H., and Sollas A. L. (1999) Actions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in slices from rats with spontaneous seizures and mossy fiber sprouting in the dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 19, 5619–5631.
Binder D. K., Croll S. D., Gall C. M., and Scharfman H. E. (2001) BDNF and epilepsy: too much of a good thing? Trends Neurosci. 24, 47–53.
King G. L., Dingledine R., Giacchino J. L., and McNamara J. O. (1985) Abnormal neuronal excitability in hippocampal slices from kindled rats. J. Neurophysiol. 54, 1295–1304.
Egan M. F., Kojima M., Callicott J. H., et al. (2003) The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 112, 257–269.
Chen Z. Y., Patel P. D., Sant G., et al. (2004) Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Met66) alters the intracellular trafficking and activity-dependent secretion of wild-type BDNF in neurosecretory cells and cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 24, 4401–4411.
Kanemoto K., Kawasaki J., Tarao Y., et al. (2003) Association of partial epilepsy with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene polymorphisms. Epilepsy Res. 53, 255–258.
Chou I. C., Tsai C. H., Lee C. C., Lin S. S., and Tsai F. J. (2004) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Val66Met polymorphisms in febrile seizures. Epilepsy Res. 60, 27–29.
Liu Q. R., Walther D., Drgon T., et al. (2005) Human brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) genes, splicing patterns and assessments of associations with substance abuse and Parkinson's disease. Am. J. Med. Gen. Part B (Neuropsych. Gen.) 134, 93–103.
Pinkstaff J. K., Chappell S. A., Mauro V. P., Edelman G. M., and Krushel L. A. (2001) Internal initiation of translation of five dendritically localized neuronal mRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 2770–2775.
Zaitsev E. and Lu B. (2003) CAP-independent translation of BDNF: IRES activity of two BDNF RNA transcripts. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 334.5.
Wiesel T. N. and Hubel D. H. (1963) Single cell responses in striate cortex of kittens deprived of vision in one eye. J. Neurophysiol. 26, 1003–1017.
Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N., and LeVay S. (1977) Plasticity of ocular dominance columns in monkey striate cortex. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 278, 377–409.
Shatz C. J. and Stryker M. P. (1978) Ocular dominance in layer IV of the cat's visual cortex and the effects of monocular deprivation. J. Physiol. 281, 267–283.
Kohara K., Kitamura A., Adachi N., et al. (2003) Inhibitory but not excitatory cortical neurons require presynaptic brain-derived neurotrophic factor for dendritic development, as revealed by chimera cell culture. J. Neurosci. 23, 6123–6131.
Jin X., Hu H., Mathers P. H., and Agmon A. (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediates activity-dependent dendritic growth in nonpyramidal neocortical interneurons in developing organotypic cultures. J. Neurosci. 23, 5662–5673.
McAllister A. K., Katz L. C., and Lo D. C. (1996) Neurotrophin regulation of cortical dendritic growth requires activity. Neuron 17, 1057–1064.
Horch H. W., Kruttgen A., Portbury S. D., and Katz L. C. (1999) Destabilization of cortical dendrites and spines by BDNF. Neuron 23, 353–364.
Sermasi E., Tropea D., and Domenici L. (1999) A new form of synaptic plasticity is transiently expressed in the developing rat visual cortex: a modulatory role for visual experience and BDNF. Neuroscience 91, 163–173.
Cabelli R. J., Hohn A., and Shatz C. J. (1995) Inhibition of ocular dominance column formation by infusion of NT-4/5 or BDNF. Science 267, 1662–1666.
Hata Y., Ohshima M., Ichisaka S., Wakita M., Fukuda M., and Tsumoto T. (2000) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor expands ocular dominance columns in visual cortex in monocularly deprived and nondeprived kittens but does not in adult cats. J. Neurosci. 20, RC57.
Lodovichi C., Berardi N., Pizzorusso T., and Maffei L. (2000) Effects of neurotrophins on cortical plasticity: same or different?. J. Neurosci. 20, 2155–2165.
Huang Z. J., Kirkwood A., Pizzorusso T., et al. (1999). BDNF regulates the maturation of inhibition and the critical period of plasticity in mouse visual cortex. Cell 98, 739–755.
Gianfranceschi L., Siciliano R., Walls J., et al. (2003) Visual cortex is rescued from the effects of dark rearing by overexpression of BDNF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 100, 12,486–12,491.
Carmignoto G., Pizzorusso T., Tia S., and Vicini S. (1997) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor potentiate excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat visual cortex. J. Physiol. 498, 153–164.
Akaneya Y., Tsumoto T., Kinoshita S., and Hatanaka H. (1997) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances long-term potentiation in rat visual cortex. J. Neurosci. 17, 6707–6716.
Sermasi E., Margotti E., Cattaneo A., and Domenici L. (2000) TrkB signalling controls LTP but not LTD in the developing rat visual cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 1411–1419.
Kinoshita S., Yasuda H., Taniguchi N., Katoh-Semba R., Hatanaka H., and Tsumoto (1999) T. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Prevents Low-Frequency Inputs from Inducing Long-Term Depression in the Developing Visual Cortex. J. Neurosci. 19, 2122–2130.
Jiang B., Akaneya Y., Hata Y., and Tsumoto T. (2003) Long-term depression is not induced by low-frequency stimulation in rat visual cortex in vivo: a possible preventing role of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Neurosci. 23, 3761–3770.
Capsoni, S., Tongiorgi E., Cattaneo A., and Domenici L. (1999) Dark rearing blocks the developmental down-regulation of brain-drived neurotrophic factor messenger RNA expression in layers IV and V of the rat visual cortex. Neuroscience 88, 393–403.
Capsoni S., Tongiorgi E., Cattaneo A., and Domenici L. (1999) Differential regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA cellular expression in the adult rat visual cortex. Neuroscience 93, 1033–1040.
Pattabiraman P. P., Tropea D., Chiaruttini C., Tongiorgi E., Cattaneo A., and Domenici L. (2005) Neuronal activity regulates the developmental expression and subcellular localization of cortical BDNF mRNA isoforms in vivo Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 28, 556–570.
Tropea D., Capsoni S., Tongiorgi E., Giannotta S., Cattaneo A., and Domenici L. (2001) Mis-match between BDNF mRNA and protein expression in the developing visual cortex. Role of visual experience. Eur. J. Neurosci. 13, 709–721.
Wu L., Wells D., Tay J., Medis, D., et al. (1998) CPEB-mediated cytoplasmic polyadenylation and the regulation of experience-dependent translation of alpha-CaMKII mRNA at synapses. Neuron 21, 1129–1139.
Timmusk T., Palm K., Metsis M., et al. (1993) Multiple promoters direct tissue-specific expression of the rat BDNF gene. Neuron 10, 475–489.
Metsis M., Timmusk, T., Arenas E., and Persson H. (1993) Differential usage of multiple brain-derived neurotrophic factor promoters in the rat brain following neuronal activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90, 8802–8806.
Kokaia Z., Metsis M., Kokaia M., et al. (1994) Brain insults in rats induce increased expression of the BDNF gene through differential use of multiple promoters. Eur. J. Neurosci. 6, 587–596.
Timmusk T., Belluardo N., Persson H., and Metsis M. (1994) Analysis of transcriptional initiation and translatability of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNAs in the rat brain. Neuroscience 60, 287–291.
Hendry S. H., Jones E. G., DeFelipe J., Schmechel D., Brandon C., and Emson P. C. (1984) Neuropeptide-containing neurons of the cerebral cortex are also GABAergic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 6526–6530.
Gonchar Y. and Burkhalter A. (1997) Three distinct families of GABAergic neurons in rat visual cortex. Cereb. Cortex 7, 347–358.
Gupta A., Wang Y., and Markram H. (2000) Organizing principles for a diversity of GABAergic interneurons and synapses in the neocortex. Science 287, 273–278
Cellerino A., Maffei L., and Domenici L. (1996) The distribution of brain derived neurotrophic factor and its receptor trkB in parvalbumin containing neurons of the rat visual cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 6, 100–108.
Schmidt-Kastner R., Wetmore C., and Olson L. (1996) Comparative study of brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger RNA and protein at the cellular level suggests multiple roles in hippocampus, striatum and cortex. Neuroscience 74, 161–183.
Horch H. W. and Katz L. C. (2002) BDNF release from single cells elicits local dendritic growth in nearby neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 1177–1184.
Righi M., Tongiorgi E., and Cattaneo A. (2000) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) induces dendritic targeting of BDNF and tyrosine kinase B mRNAs in hippocampal neurons through a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-dependent pathway. J. Neurosci. 20, 3165–3174.
Kang H. J. and Schuman E. M. (1996) A requirement for local protein synthesis in neurotrophin-induced hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Science 273, 1402–1406.
Aakalu G., Smith W. B., Nguyen N., Jiang C., and Schuman E. M. (2001) Dynamic visualization of local protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 30, 489–502.
Takei N., Inamura N., Kawamura M., et al. (2004) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces mammalian target of rapamycin dependent local activation of translation machinery and protein synthesis in neuronal dendrites. J. Neurosci. 24, 9760–9769.
Smart F. M., Edelman G. M., and Vanderklish P. W. (2003) BDNF induces translocation of initiation factor 4E to mRNA granules: evidence for a role of synaptic microfilaments and integrins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 14,403–14,408.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tongiorgi, E., Domenici, L. & Simonato, M. What is the biological significance of BDNF mRNA targeting in the dendrites?. Mol Neurobiol 33, 17–32 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:33:1:017
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:33:1:017