Abstract
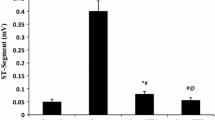
In rats, high doses of isoproterenol (Iso) have caused acute myocardial lesions and increased serum levels of cardiac troponin T (cTnT). We determined whether low doses of lso also cause cardiac alterations and whether monitoring cTnT levels could detect this injury. Rats received 8 to 500 μg/kg lso and were followed for 3 to 48 h. Lesion severity was scored from 0 to 5. Within 3 h, mean cTnT was elevated in all 29 rats receiving 8, 16, 32, or 64 μg/kg lso (0.20 to 0.28 ng/mL), but minimal lesions occurred in only two animals. However, by 6 h, cardiac lesions and increases in serum cTnT (mean=0.21 to 0.23 ng/mL) were observed in all 14 rats receiving 32 or 64 μg/kg lso. Doses of 125, 250, or 500 μg/kg lso caused more significant increases in cTnT levels and marked myocardial lesions that reached a peak 3 to 6 h after dosing. The magnitude of the lesions and cTnT levels declined between 12 and 48 h post treatment. Thus, a range of low lso doses can cause myocardial lesions, and serum cTnT levels can be monitored to detect the onset and progression of this type of acute cardiac injury in rats; however, careful attention to dosing and sampling times is critical to interpretation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chappel, C. I., Rona, G., Balazs, T., et al. (1959). Severe myocardial necrosis produced by isoproterenol, in the rat. Arch., Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 122:123–128.
Rona, G., Chappel, C. I., Balazs, T., et al. (1959). An infarct-like myocardial lesion and other toxic manifestations produced by isoproterenol in the rat. Arch. Pathol. 67: 448–453.
Rona, G., Kahn, D. S., and Chappel, C. I. (1963). Studies on the infarct-like myocardial necrosis produced by isoproterenol. A review. Rev. Can. Biol. 22:241–255.
Davies, M. J. (1977). The pathology of mycardial ischaemia. J. Clin. Pathol. Suppl. (R. Coll. Pathol.) 11:45–52.
Mair, J. (1997). Progress in myocardial damage detection: new biochemical markers for clinicians. Cri. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 34:1–66.
Katus, H.A., Remppis, A., Neuman, F. J., et al. (1991). Diagnostic efficiency of troponin T measurements in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 83:902–912.
Adams, J. E. III, Bodor, G. S., Davila-Roman, V. G., et al. (1993). Cardiac troponin I. A marker with high specificity for cardiac, injury. Circulation 88:101–106.
O'Brien, P. J., Daweron, G. W., Beck, M. L., et al. (1997). Troponin T is a sensitive, specific biomarker of cardiac injury in laboratory animals. Lab. Animal Sci. 147:486–495.
O'Brien, P. J., Landt, Y., and Ladenson, J. H. (1997). Differential reactivity of cardiac and skeletal muscle from various species in a cardiac troponin I immunoassay. Clin Chem. 43:2333–2338.
O'Brien, P. J., Dameron, G. W., Beck, M. L., et al. (1998). Differential reactivity of cardiac and skeletal muscle from various species in two generations of cardiac troponin-T immunoassays. Res. Vet. Sci. 65:135–137.
Bleuel, H., Deschl, U., Bertsch, T., et al. (1995). Diagnostic efficiency of troponin T measurements in rats with experimental myocardial damage. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 47: 121–127.
Bertsch, T., Bleuel, H., Aufenanger, J., et al. (1997). Comparison of cardiac troponin T and cardiac troponin I concentrations in peripheral blood during orciprenaline induced tachycardia in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 49:467–468.
Bertsch, T., Bleuel, H., Deschl, U., et al. (1999). A new sensitive cardiac troponin T rapid test (TROPT) for the detection of experimental acute damage in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 51:565–569.
Bertinchant, J. P., Robert, E., Polge, A., et al. (2000). Comparison of the diagnostic value of cardiac troponin I and T determinations for detecting early myocardial damage and the relationship with histological findings after isoproterenol-induced cardiac injury. Clin. Chimica Acta 298: 13–28.
Bartsch, V. W., Roesch, E., Hebold, G., et al. (1974). Einbeitrag zur differenzi erang zwischein echter und scheinbarer, β-rezeptoren blockade am herzen. Arzneim-Forsch (Drug Res.) 24:303–308.
Mueller-Bardorf, M., Hallermayer, K., Schroder, A., et al. (1997). Improved troponin T ELISA specific for cardiac troponin T isoform: assay development and analytical and clinical validation. Clin. Chem. 43:458–466.
Noronha-Dutra, A. A., Steen, E. M., and Woolf, N. (1984). The early changes induced by isoproterenol in the endocardium and adjacent myocardium. Am. J. Pathol. 114: 231–239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herman, E., Zhang, J., Knapton, A. et al. Serum cardiac troponin T as a biomarker for acute myocardial injury induced by low doses of isoproterenol in rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol 6, 211–221 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/CT:6:3:211
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CT:6:3:211