Abstract
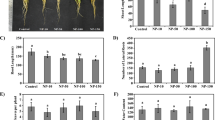
Previous research showed that nano-TiO2 could significantly promote photosynthesis and greatly improve growth of spinach, but, we also speculated that an increase of spinach growth by nano-TiO2 treatment might be closely related to the change of nitrogen metabolism. The effects of nano-anatase TiO2 on the nitrogen metabolism of growing spinach were studied by treating them with nano-anatase TiO2. The results showed that, nano-anatase TiO2 treatment could obviously increase the activities of nitrate reductase, glutamate dehydrogenase, glutamine synthase, and glutamic-pyruvic transaminase during the growing stage. Nano-anatase TiO2 treatment could also promote spinach to absorb nitrate, accelerate, inorganic nitrogen (such as NO t-3 −N and NH +4 −N) to be translated into organic nitrogen (such as protein and chlorophyll), and enhance the fresh weight and dry weights.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. H. Crabtree, A new type of hydrogen bond, Science 282, 200–2001 (1998).
L. Zheng, F. S. Hong, S. P. Lu, and C. Liu, Effect of nano-TiO2 on strength of naturally aged seeds and growth of spinach, Biol. Trace Element Res. 104(1), 82–93 (2005).
F. S. Hong, P. Yang, F. Q. Gao, et al.., Effect of nano-anatase TiO2 on spectral characterization of photosystem II particles from spinach, Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 21(2), 196–200 (2005).
F. S. Hong, F. Yang, C. et al.., Influences of nano-TiO2 on the chloroplast ageing of spinach under light, Biol. Trace Element Res. 104(3), 249–260 (2005).
F. S. Hong, J. Zhou, C. Liu, et al.., Effect of nano-TiO2 on photochemical reaction of chloroplasts of spinach, Biol. Trace Element Res. 105, 269–280 (2005).
B. B. Buchanan, W. Gruissen, and R. L. Johones, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants, Science Press, Beijing, pp. 786–824 (2002).
W. H. Wu. Plant Physiology, Science Press, Beijing, pp. 128–165, 105–108 (2003), (in Chinese).
L. N. Ji, J. J. Huang, and T. H. Mo, Bioinoganic Chemistry: Introduction, Zhongshan University Press, Guangzhou, pp. 119–149 (2001) (in Chinese).
P. Yang, and F. Gao. Bioinorganic Chemistry: Theory, Science Press, Beijing, pp. 186–189 (2002), (in Chinese).
C. M. Lu, C. Y. Zhang, J. Q. Wen, and G. R. Wu, Research of the effect of nanometer materials on germination and growth enhancement of Glycine Max and its mechanism, Soybean Sci. 21(3), 168–171 (2002) (in Chinese).
A. M. Limani, C. Rouillon, G. Glevarec, A. Gallais, and B. Hirel, Genetic and physiological analysis of germination efficiency in maize in relation to nitrogen metabolism reveals the importance of cytosolic glutamine synthetase, Plant Physiol. 130(4), 1860–1870 (2002).
H. M. Lam, K. T. Coschigano, and I. C. Oliverira, The molecular genetics of nitrogen assimilation into amino acids in higher plants, Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 47, 569 (1996).
C. M. Ribaudo, D. P. Rondanini, J. A. Gura, and A. A. Fraschina, Response of Zea mays to the inoculation with Azospirillum on nitrogen metabolism under greenhouse conditions, Biol. Plant 44(4), 631–634 (2001).
Shanghai Plant Physiology Society ed., Experimental Guideof Modern Plant Physiology, Science Press, Beijing, pp. 154–156 (1999) (in Chinese).
D. I. Arnon, Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24, 1–15 (1949).
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr, and R. J. Randall, Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent, J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Hong, F., You, W. et al. Influence of nano-anatase TiO2 on the nitrogen metabolism of growing spinach. Biol Trace Elem Res 110, 179–190 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:110:2:179
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:110:2:179