Abstract
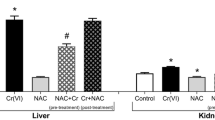
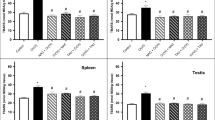
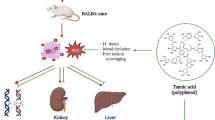
The kidney has been regarded as a critical organ of toxicity induced by acute exposure to hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] compounds. Reactive intermediates and free radicals generated during reduction process might be responsible for Cr(VI) toxicity. In this study, the effects of pretreatment or posttreatment of taurine on Cr(VI)-induced oxidative stress and chromium accumulation in kidney tissue of Swiss albino mice were investigated. Single intraperitoneal (ip) potassium dichromate treatment (20 mgCr/kg), as Cr(VI) compound, significantly elevated the level of lipid peroxidation as compared with the control group (p<0.05). This was accompanied by significant decreases in nonprotein sulfhydryls (NPSH) level, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) enzyme activities as well as a significant chromium accumulation (p<0.05). Taurine administration (1 g/kg, ip) before or after Cr(VI) exposure resulted in reduction of lipid peroxidation levels and improvement in SOD enzyme activity (p<0.05). On the other hand, administration of the antioxidant before Cr(VI) exposure restored the NPSH level and CAT enzyme activity and also reduced tissue chromium levels (p<0.05), whereas postreatment had only slight effects on these parameters. In view of the results, taurine seems to exert some beneficial effects against Cr(VI)-induced oxidative stress and chromium accumulation in mice kidney tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO, Chromium, Environmental Health Criteria Series: 61, WHO, Geneva (1988).
M. Costa, Toxicity and carcinogenicity of Cr(VI) in animal models and humans, Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 27, 431–442 (1997).
R. Codd, C. T. Dillon, A. Levina, and P. A. Lay, Studies on the genotoxicity of chromium: from test tube to the cell, Coord. Chem. Rev. 216–217, 537–582 (2001).
Y. L. Huang, C. Y. Chen, J. Y. Sheu, I. C. Chuang, J. H. Pan, and T. H. Lin, Lipid peroxidation in workers exposed to hexavalent chromium, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 56, 235–247 (1999).
S. N. Mattagajasingh, and H. P. Misra, Alterations in the prooxidant and antioxidant status of human leukemic T-lymphocyte MOLT4 cells treated with potassium chromate, Mol. Cell. Biochem. 142, 61–70 (1995).
D. Bagchi, S. J. Stohs, B. W. Downs, M. Bagchi, and H. G. Preuss, Cytotoxicity and oxidative mechanisms of different forms of chromium, Toxicology 180, 5–22 (2002).
S. De Flora, and K. E. Wetterhahn, Mechanisms of chromium metabolism and genotoxicity. Life Chem. Rep. 7, 169–244 (1989).
K. J. Liu, and X. Shi, In vivo reduction of chromium (VI) and its related free radical gen eration, Mol. Cell. Biochem. 222, 41–47 (2001).
X. Shi, A. Chiu, C. T. Chen, B. Halliwell, V., Castranova, and V. Vallyathan, Reduction of chromium (VI) and its relationship to carcinogenesis, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2, 87–104 (1999).
I. R. Walpole, K. Johnston, R. Clarkson, G. Wilson, and G. Bower, Acute chromium poisoning in a 2 year old child, Aust. Paediatr. J. 21, 65–67 (1985).
C. A. Michie, M. Hayhurst, G. J. Knobel, J. M. Stokol, and B. Hensley, Poisoning with a traditional remedy containing potassium dichromate, Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 10, 129–131 (1991).
P. Sanz, S. Nogue, P. Munne, R. Torra, and F. Marques, Acute potassium dichromate poisoning. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 10, 228–229 (1991).
K. L. Meert, J. Ellis, R. Aronow, and E. Perrin, Acute ammonium dichromate poisoning, Ann. Emerg. Med. 24, 748–750 (1994).
Z. Kolacinski, P. Kostrzewski, S. Kruszewska, G. Razniewska, and J. Mielczarska, Acute potassium dichromate poisoning: a toxicokinetic case study, J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 37, 785–791 (1999).
Y. Loubieres, A. De Lassence, M. Bernier, et al., Acute, fatal, oral chromic acid poisoning, J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 37, 333–336 (1999).
R. A. Goyer, and T. W. Clarkson, Toxic effects of metals, in Casarett and Doull's Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons, 6th ed., C. D. Klaassen, ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, pp. 811–867 (2001).
A. P. Evan, and W. G. Dail, The effects of sodium chromate on the proximal tubules of the rat kidney. Fine structural damage and lysozymuria, Lab. Invest 30, 704–715 (1974).
Y. Hojo, and Y. Satomi, In vivo nephrotoxicity induced in mice by chromium (VI), involvement of glutathione and chromium(V), Biol. Trace Element Res. 31, 21–31 (1991).
R. Laborda, J. Diaz-Mayans, and A. Nunez, Nephrotoxic and hepatotoxic effects of chromium compounds in rats, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 36, 332–336 (1986).
X. Wang, Q. Qin, X. Xu, et al., Chromium-induced early changes in renal function among ferrochromium-producing workers, Toxicology 90, 93–101 (1994).
C. S. Liu, H. W. Kuo, J. S. Lai, and T. I. Lin, Urinary N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase as an indicator of renal dysfunction in electroplating workers, Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 71, 348–352 (1998).
R. P. Wedeen, S. Haque, I. Udasin, P. C. D'Haese, M. Elseviers, and M. E. De Broe Absence of tubular proteinuria following environmental exposure to chromium, Arch. Environ. Health 51, 321–323 (1996).
S. Langard, and T. Norseth, Chromium, in Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, Volume II: Specific Metals, 2nd ed., L. Friberg, G. F. Nordberg, and V. B. Vouk, eds., Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 185–210 (1986).
D. G. Barceloux, Chromium, Clin. Toxicol. 37 173–194 (1999).
R. J. Huxtable, and L. A. Sebring, Towards a unifying theory for the actions of taurine, Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 7, 481–485 (1986).
H. P. Redmond, P. P. Stapleton, P. Neary, and D. Bouchier-Hayes, Immunonutrition: the role of taurine, Nutrition 14, 599–604 (1998).
H. Ha, M. R. Yu, and K. H. Kim, Melatonin and taurine reduce early glomerulopathy in diabetic rats, Free Radical Biol. Med. 26, 944–950 (1999).
A. Erdem, N. U. Gundogan, A. Usubutun, et al., The protective effect of taurine against gentamicin-induced acute tubular necrosis in rats, Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 15, 1175–1182 (2000).
H. Gürer, H. Özgüne s, E. Saygin, and N. Ercal, Antioxidant effect of taurine against lead-induced oxidative stress, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 41, 397–402 (2001).
E. Waters, J. H. Wang, H. P. Redmond, Q. D. Wu, E. Kay, and D. Bouchier-Hayes, Role of taurine in preventing acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury in the rat, Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 280, G1274-G1279 (2001).
B. Eppler, and R. Dawson, Jr. Cytoprotective role of taurine in a renal epithelial cell culture model, Biochem. Pharmacol., 63, 1051–1060 (2002).
S. Ueno, N. Susa, Y. Furukawa, and M. Sugiyama, Formation of paramagnetic chromium in liver of mice treated with dichromate(VI). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 135, 165–171 (1995).
J. Azuma, T. Hamaguchi, H. Ohta, et al., Calcium overload-induced mycardial damage caused by isoproterenol and by adriamycin: possible role of taurine in its prevention. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 217, 167–179, (1987).
T. Hamaguchi, J. Azuma, N. Awata, et al., Reduction of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice by taurine, Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 59, 21–30 (1988).
K. Korang, L. Milakofsky, T. A. Hare, J. M. Hofford, and W. H. Vogel, Levels of taurine, amino acids and related compounds in plasma, vena cava, aorta and heart of rats after taurine administration, Pharmacology 52, 263–270 (1996).
H. Ohkawa, N. Ohishi, and K. Yagi, Assay for lipid peroxides by thiobarbituric acid reaction, Anal. Biochem. 95, 351–358 (1979).
J. Rungby, and E. Ernst, Experimentally induced lipid peroxidation after exposure to chromium, mercury or silver: Interactions with carbon tetrachloride, Pharmacol. Toxicol. 70, 205–207 (1992).
J. Sedlak, and R. H. Lindsay, Estimation of total protein-bound and non-protein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman's reagent, Anal. Biochem. 25, 192–205 (1968).
J. D. Crapo, J. M. McCord, and I. Fridovich, Preparation and assay of superoxide dismutases, Methods Enzymol. 53, 382–393 (1978).
H. Aebi. Catalase in vitro Methods Enzymol. 105, 121–126 (1984).
E. C. Phifer, Determination of chromium and molybdenum in medical foods by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry, J. AOAC Int. 78, 1497–1501 (1995).
M. A. Sipowicz, L. M. Anderson, W. E. Utermahlen, Jr., H. J. Issaq, and K. S. Kasprzak, Uptake and tissue distribution of chromium (III) in mice after a single intraperitoneal or subcutaneous administration, Toxicol. Lett. 93, 9–14 (1997).
S. J. Stohs, and D. Bagchi, Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions, Free Radical Biol. Med. 18, 321–336 (1995).
T. Sengupta, D. Chattopadhyay, N. Ghosh, G. Maulik, and G. C. Chatterjee, Impact of chromium on lipoperoxidative processes and subsequent operation of the glutathione cycle in rat renal system, Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 29, 287–290 (1992).
Y. Hojo, A. Okado, S. Kawazoe, and T. Mizutani, Direct evidence for in vivo hydroxyl radical generation in blood of mice after acute chromium (VI) intake. Electron spin resonance spin-trapping investigation, Biol. Trace Element Res. 76, 75–84 (2000).
J. P. Kehrer, The Haber-Weiss reaction and mechanisms of toxicity, Toxicology 149, 43–50 (2000).
B. Halliwell, Reactive oxygen species in living systems: source, biochemistry, and role in human disease, Am. J. Med. 91 (Suppl. 3C), 14S-22S (1991).
J. M. C. Gutteridge, Lipid peroxidation and antioxidants as biomarkers of tissue damage, Clin. Chem. 41, 1819–1828 (1995).
A. Meister, Glutathione metabolism, Methods Enzymol. 251, 3–7 (1995).
C. K. Sen, Nutritional biochemistry of cellular glutathione, Nutr. Biochem. 8, 660–672 (1997).
H. J. Wiegand, H. Ottenwalder, and H. M. Bolt, The reduction of chromium (VI) to chromium (III) by glutathione: an intracellular redox pathway in the metabolism of the carcinogen chromate, Toxicology 33, 341–348 (1984).
OEHHA, Public Health Goal for Chromium in Drinking Water, Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, California Environmental Protection Agency (1999). http://www.oehha.ca.gov/water/phg/pdf/chrom_f.pdf
M. Gunaratnam, M. Pohlscheidt, and M. H. Grant, Pretreatment of rats with the inducing agents phenobarbitone and 3-methylcholantrene ameliorates the toxicity of chromium (VI) in hepatocytes, Toxicology In Vitro 16, 509–516 (2002).
A. M. Standeven, and K. E. Wetterhahn, Possible role of glutathione in chromium(VI) metabolism and toxicity in rats, Pharmacol. Toxicol. 68, 469–476 (1991).
D. Y. Cupo, and K. E. Wetterhahn, Modification of Cr(VI)-induced DNA damage by glutathione and cytochromes P-450 in chicken embryo hepatocytes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 6755–6759 (1985).
R. D. Snyder, Role of active oxygen species in metal-induced DNA strand breakage in human diploid fibroblasts, Mutat. Res. 193, 237–246 (1988).
C. Michiels, M. Raes, O. Toussaint, and J. Remacle, Importance of Se-glutathione peroxidase, catalase and Cu/Zn-SOD for cell survival against oxidative stress, Free Radical Biol. Med. 17, 235–248 (1994).
R. Shainkin-Kestenbaum, C. Caruso, and G. M. Berlyne, Effect of chromium on oxygen free radical metabolism, inhibition of superoxide dismutase and enhancement of 6-hydroxydopamine oxidation, J. Trace Elements Electrolytes Health Dis. 5, 197–201 (1991).
Y. H. Koh, S. J. Yoon, and J. W. Park, Inactivation of copper, zinc superoxide dismutase by the lipid peroxidation products malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 32, 440–444 (1999).
U. Korallus, C. Harzdorf, and J. Lewalter, Experimental bases for ascorbic acid therapy of poisoning by hexavalent chromium compounds, Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 53, 247–256 (1984).
E. Ginter, D. Chorvatovicova, and A. Kosinova, Vitamin C lowers mutagenic and toxic effects of hexavalent chromium in guinea pigs, Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 59, 161–166 (1989).
M. Sugiyama, Effects of vitamins on chromium (VI)-induced damage, Environ. Health Perspect. 92, 63–70 (1991).
N. Susa, S. Ueno, Y. Furukawa, J. Ueda, and M. Sugiyama, Potent protective effect of melatonin on chromium (VI)-induced DNA single-strand breaks, cytotoxicity, and lipid peroxidation in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 144, 377–384 (1997).
S. K. Dey, P. Nayak, and S. Roy, Chromium-induced membrane damage: protective role of ascorbic acid, J. Environ. Sci. 13, 272–275 (2001).
S. K. Dey, P. Nayak, and S. Roy, Alpha-tocopherol supplementation on chromium toxicity: a study on rat liver and kidney cell membrane, J. Environ. Sci. 15, 356–359 (2003).
S. H. Hansen, The role of taurine in diabetes and the development of diabetic complications. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 17, 330–346 (2001).
A. S. Ebrahim, and D. Sakthisekaran, Effect of vitamin E and taurine treatment on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense in perchloroethylene-induced cytotoxicity in mice. Nutr. Biochem. 8, 270–274 (1997).
D. Appenroth, K. Winnefeld, H. Schröter, and M. Rost, The ambiguous effect of ascorbic acid on chromate induced proteinuria in rats. Arch. Toxicol. 68, 138–141 (1994).
B. Halliwell, and J. M. C. Cutteridge, Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 3rd ed., Oxford University Press, New York, (2000).
R. W. Grunewald, and R. K. H. Kinne, Osmoregulation in the mammalian kidney: the role of organic osmolytes, J. Exp. Zool. 283, 708–724 (1999).
M. Ogasawara, T. Nakamura, I. Koyama, M. Nemoto, and T. Yoshida, Reactivity of taurine with aldehydes and its physiological role, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol, 359, 71–78 (1994).
O. I. Aruoma, B. Halliwell, B. M. Hoey, and J. Butler, The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their metabolic precursors, Biochem. J. 256, 251–255 (1988).
X. Shi, D. C. Flynn, D. W. Porter, S. S. Leonard, V. Vallyathan, V. Castranova, Efficacy of taurine based compounds as hydroxyl radical scavengers in silica induced peroxidation, Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 27, 365–374 (1997).
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Hexavalent chromium (colorimetric), Method 7196A (1992).
J. E. Sutherland, A. Zhitkovich, T. Kluz, and M. Costa, Rats retain chromium in tissues following chronic ingestion of drinking water containing hexavalent chromium, Biol. Trace Element Res. 74, 41–54 (2000).
J. Chmielnicka, E. Swietlicka, and M. Nasiadek, Essential elements as early indicators of hexavalent chromium nephrotoxicity, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety Environ. Res. B 53, 20–26 (2002).
D. F. Hwang, L. C. Wang, and H. M. Cheng, Effects of taurine on toxicity of copper in rats, Food Chem. Toxicol. 36, 239–244 (1998).
D. F. Hwang, and L. C. Wang, Effect of taurine on toxicity of cadmium in rats. Toxicology 167, 173–180 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boşgelmez, I.I., Güvendik, G. Effects of taurine on oxidative stress parameters and chromium levels altered by acute hexavalent chromium exposure in Mice Kidney tissue. Biol Trace Elem Res 102, 209–225 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:102:1-3:209
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:102:1-3:209