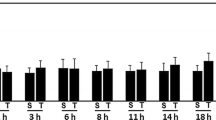
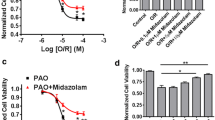
Abstract
Extracellular hypertonicity can induce the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). Of these, both extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) and the stress-activated kinase p38 have been implicated in neuronal cell survival. Resuscitation with hypertonic saline decreases secondary brain injury after trauma, as well as neuronal damage, after ischemia. Since hypertonicity has been shown to support somatic cell survival, we investigated if hypertonicity can also prevent neuronal cell death via MAPK signaling. Death of postnatal rat corticospinal motoneurons (CSMNs) was induced by serum deprivation, and survival in both isotonic and hypertonic media was assessed after 20 h. Addition of NaCl (4–250 mM) to isotonic medium significantly and dose dependently protected CSMN in enriched cultures, increasing cell survival by up to 70% over that in isotonic medium. This response was not restricted to NaCl; addition of KCl, choline chloride, and sucrose had similar effects on cell survival. In addition, hypertonicity supported the survival of pure CSMN populations, albeit with lower potency. In cortical cell suspensions, hypertonic NaCl (20–100 mM) increased basal phosphorylation of p38 and ERK. The activation of both MAPKs, which was induced by 40 mM NaCl, was transient. Cultivation of CSMNs in media containing the specific p38 inhibitor SB203580 abolished the protective effect of hypertonic NaCl, indicating a central role for p38. We therefore conclude that hypertonicity can prevent neuronal cell death via MAPK signaling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloyez R. S., Bamji S. X., Pozniak C. D., Toma J. G., Atwal J., Kaplan D. R., and Miller F. D. (1998) p53 is essential for developmental neuron death as regulatated by the TrkA and p75 neurotrophin receptor. J. Cell Biol. 143, 1691–1703.
Anderson C. N. G. and Tolkovsky A. M. (1999) A role for MAPK/ERK in sympathetic neuron survival: protection against a p53-dependent, JNK-independent induction of apoptosis by cytosine arabinoside. J. Neurosci. 19, 664–673.
Birkenkamp K. U., Dokter W. H. A., Esselink M. T, Jonk L. J. C., Kruijer W., and Vellenga E. (1999) A dual function for p38 MAP kinase in hematopoietic cells: involvement in apoptosis and cell activation. Leukemia 13, 1037–1045.
Chan W. H., Yu J. S., and Yang S. D. (1999) PAK2 is cleaved and activated during hyperosmotic shock-induced apoptosis via a caspase-dependent mechanism: Evidence for the involvement of oxidative stress. J. Cell. Physiol. 178, 397–408.
Creedon D. J., Johnson E. M., and Lawrence J. C. (1996) Mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent pathways mediate the effects of nerve growth factor and cAMP on neuronal survival. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 20,713–20,718.
Duzgun S. A., Rasque H., Kito H., Azuma N., Li W., Basson M.D., Gahtan V., et al. (2000) Mitogen-activated protein phosphorylation in endothelial cells exposed to hyperosmolar conditions. J. Biol. Biochem. 76, 567–571.
English J. D. and Sweatt J. D. (1996) Activation of p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase in hippocampal long term potentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 24,329–24,332.
Finkbeiner S., Tavazoie S. F., Maloratsky A., Jacobs K. M., Harris K. M., and Greenberg M. E. (1997) CREB: a major mediator of neuronal neurotrophin responses. Neuron 19, 1031–1047.
GunnMoore F.J. and Tavare J. M. (1998) Apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells induced by serum withdrawal, glutamate or beta-amyloid, is independent of Jun kinase or p38 mitogen activated protein kinase activation. Neurosci. Lett. 250, 53–56.
Hamaguchi S. and Ogata H. (1995) Does hypertonic saline have preventive effects against delayed neuronal death in gerbil hippocampus? Shock 3, 280–283.
Härtl R., Ghajar J., Hochleuthner H., and Maruitz W. (1997) Hypertonic/hyperoncotic saline reliably reduces ICP in severely head-injured patients with intracranial hypertension. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. (Wien) 70, 126–129.
Horn P., Munch E., Vajkoczy P., Herrmann P., Quintel M., Schilling L., et al. (1999) Hypertonic saline solution for control of elevated intracranial pressure in patients with exhausted response to mannitol and barbiturates. Neurol. Res. 21, 758–764.
Horstmann S., Kahle P.J., and Borasio G. D. (1998) Inhibitors of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase promote neuronal survival in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 52, 483–490.
Imura T., Shimohama S., Kageyama T., and Kimura J. (1999) Selective induction of glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 by hypertonic stress in C6 glioma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 265, 240–245.
Iwasaki S., Iguchi M., Watanabe K., Hoshino R., Tsujimoto M., and Kohno M. (1999) Specific activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway and induction of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells by bone morphogenetic protein-2. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 26,503–26,510.
Jiang Y., Chen C. H., Li Z. J., Guo W., Gegner J. A., Lin S. C., and Han J. H. (1996) Characterization of the structure and function of a new mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38-beta). J. Biol. Chem. 271, 17,920–17,926.
Junger H. and Junger W. G. (1998) CNTF and GDNF but not NT-4 support corticospinal motoneuron growth via direct mechanisms. Neuroreport 9, 3749–3754.
Junger H. and Varon S. (1997) Neurotrophin-4 (NT-4) and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) promote survival of corticospinal motoneurons of neonatal rats in vitro. Brain Res. 762, 56–60.
Junger W. G., Coimbra R., Liu F. C., Herdon-Remelius C., Junger W., Junger H., et al. (1997) Hypertonic saline resuscitation: a tool to modulate immune function in trauma patients? Shock 8, 235–241.
Kankaanranta H., De Souza P. M., Barnes P. J., Salmon M., Giembycz M. A., and Lindsay M. A. (1999) SB 203580, an inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, enhances constitutive apoptosis of cytokine-deprived human eosinophils. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 290, 621–628.
Kummer J. L., Rao P. K., and Heidenreich K. A. (1997) Apoptosis induced by withdrawal of trophic factors is mediated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 33, 20,490–20,494.
Lee J. C., Laydon J. T., McDonnell P. C., Gallagher T. F., Kumar S., Green D., et al. (1994) A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature 372, 739–746.
Luh E. H., Shackford S. R., Shatos M. A., and Pietropaoli J. A. (1996) The effects of hyperosmolarity on the viability and function of endothelial cells. J. Surg. Res. 60, 122–128.
Mao Z. X., Bonni A., Xia F., Nadal-Vicens M., and Greenberg M. E. (1999) Neuronal activity-dependent cell survival mediated by transcription factor MEF2. Science 286, 785–790.
Mattox K. L., Maningas P. A., Moore E. E., Mateer J. R., Marx J. A., Aprahamian C., et al. (1990) Prehospital hypertonic saline/dextran infusion for post-traumatic hypotension. The U.S.A. Multicenter Trial. Ann. Surg. 213, 482–491.
Mazzoni I. E., Saïd F. A., Aloyz R., Miller F. D., and Kaplan D. (1999) Ras regulates sympathetic neuron survival by suppressing the p53-mediated cell death pathway. J. Neurosci. 19, 9716–9727.
Morooka T. and Nishida E. (1998) Requirement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase for neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 24,285–24,288.
Nemoto S., Xiang J. L., Huang S., and Lin A. N. (1998) Induction of apoptosis by SB202190 through inhibition of p38 beta mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 16,415–16,420.
Neuhofer W., Müller E., Burger-Kentischer A., Fraek M. L., Thurau K., and Beck F. X. (1999) Inhibition of NaCl-induced heat shock protein 72 expression renders MDCK cells susceptible to high urea concentrations. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 437, 611–616.
Perron J. C. and Bixby J. L. (1999) Distinct neurite outgrowth signaling pathways converge on ERK activation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 13, 362–378.
Roulston A., Reinhard C., Amiri P., and Williams L. T. (1998) Early activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 kinase regulate cell survival in response to tumor necrosis factor alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 10,232–10,239.
Schmid R. S., Graff R. D., Schaller M. D., Chen S. Z., Schachner M., Hemperly J. J., and Maness P. F. (1999) NCAM stimulates the RAS-MAPK pathway and CREB phosphorylation in neuronal cells. J. Neurobiol. 38, 542–558.
Sheikh-Hamad D., DiMari J., Suki W. N., Safirstein R., Watts B. A., III, and Rouse D. (1998) p38 kinase activity is essential for osmotic induction of mRNAs for HSP70 and transporter for organic solute betaine in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 1832–1837.
Simma B., Burger R., Falk M., Sacher P., and Fanconi S. (1998) A prospective, randomized, and controlled study of fluid management in children with severe head injury: Lactated Ringer’s solution versus hypertonic saline. Crit. Care Med. 26, 1265–1270.
Smirnova I. V., Citron B. A., Arnold P. M., Zhang S. X., and Festoff B. W. (1998) Characterization of apoptosis in a motoneuron cell line. Spine 23, 151–158.
Soupart A. and Decaux G. (1996) Therapeutic recommendations for management of severe hyponatremia: current concepts on pathogenesis and prevention of neurologic complications. Clin. Nephrol. 46, 149–169.
Stanciu M., Wang Y., Kentor R., Burke N., Watkins S., Kress G., et al. (2000) Persistent activation of ERK contributes to glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity in a neuronal cell line and primary cortical neuron cultures. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 12,200–12,206.
Suzuki K., Ajito T., and Iwabuchi S. (1998) Effect of a 7.2% hypertonic saline solution infusion on arterial blood pressure serum sodium concentration and osomotic pressure in normovolemic heifers. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 60, 799–803.
Tombes R. M., Auer K. L., Mikkelsen R., Valerie K., Wymann M. P., Marshall C. J., et al. (1998) The mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade can either stimulate or inhibit DNA synthesis in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes depending upon whether its activation is acute/phasic or chronic. Biochem. J. 330, 1451–1460.
Ushio-Fukai M., Alexander R. W., Akers M., and Griendling K. K. (1998) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is a critical component of the redox-sensitive signaling pathways activated by angiotensin II—Role in vascular smooth muscle cell hypertrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 15,022–15,029.
Walton M. R. and Dragunow M. (2000) Is CREB a key to neuronal survival? Trends Neurosci. 23, 48–53.
Xia Z. G., Dickens M., Raingeaud J., Davis R. J., and Greenberg M. E. (1995) Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science 270, 1326–1331.
Zechner D., Craig R, Hanford D. S., McDonough P. M., Sabbadini R. A., and Glembotski C. C. (1998) MKK6 activates myocardial cell NF-kappa B and inhibits apoptosis in a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8232–8239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junger, H., Edelman, D.B. & Junger, W.G. Hypertonicity promotes survival of corticospinal motoneurons via mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 signaling. J Mol Neurosci 21, 111–120 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:21:2:111
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:21:2:111