Abstract
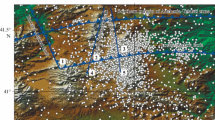
Based on the concept of “active blocks” and spatial distribution of historical earthquakes with surface ruptures as well as major and subordinate active faults. The Sichuan-Yunnan region can be divided into four first-order blocks. They are the Markam block (I), the Sichuan-Yunnan rhombic block (II), Baoshan-Pu’er block (III), and Mizhina-Ximeng block (IV). Cut by sub-ordinate NE-trending active faults, the Sichuan-Yunnan rhombic block (II) can be further divided into two sub-blocks: the northwestern Sichuan sub-block (ll1) and the middle Yunnan sub-block (ll2), while the Baoshan- Pu’er block (III) can be further divided into three sub-blocks: Baoshan sub-block (Ill1), Jinggu sub-block (lll2), and Mengla sub-block (lll3). A quantitative study of offset landforms is carried out and the basic types of active faults and their long-term slip rates along the major boundaries of active blocks of different orders in the Sichuan-Yunnan region are determined, through slip vector analysis, the motion states of the active blocks are clarified and the deformation coordination on the block margins is discussed. It is suggested that the tectonic motion of the blocks in this region is a complex or superimposition of three basic types of motions: southeastward sliding, ro-tating on vertical axis, and uplifting. The Markam block (I), the northwestern Sichuan sub-block (ll1), and middle Yunnan sub-block (ll2) have a southeastward horizontal sliding rate of 1-5 mm/a, clockwise rotating angular rate of 1.4-4°/Ma, and uplifting rate of about 1 mm/a. The Baoshan-Pu’er (III) and Mizhina-Ximeng (IV) blocks have also been extensively clockwise rotated. This pattern of motion is a strain response to the collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates and the localized deformation and differential slip on the block margins associated with the northward motion of the Indian Plate. Because a set of transverse thrusts between the blocks absorbs and transforms some components of eastward or southeastward sliding motion, the eastward escape or extrusion of the Tibetan Plateau is limited as “imbricated thrusting transformation-limited extrusion model”.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nur, A., Ron, H., Scotti, O., Kinematics and mechanics of tectonic block rotations, Geophysical Monograph: 49/IUGG Series 4, 1989, 31–46.
Ding Guoyu, Introduction to the Lithospheric Dynamics of China (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 1991, 600.
Scotti, O., Nur, A., Estevez, R., Distributed deformation and block rotation in three dimensions, J. Geophys. Res., 1991, 96 (B7): 12225–12243.
Nur, A., Ron, H., Beroza, G., The nature of the Landers-Mojave earthquake line, Science, 1993, 261: 201–203.
Ma Xingyuan, Explanatory Notes of the Lithospheric Dynamics Map of China and Adjacent Seas, Scale 1: 4000000 (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987, 1–53.
Xu, X. W., Cheng, G. L., Ma, X. Y. et al., Rotation model and dynamics of blocks in North China and its adjacent areas, Earth Science: J. China Univ. Geosci. (in Chinese), 1994, 19(2): 129–138.
Li Ping, Wang Liangmou, Discussion on the seismo-geological characteristics of the Yunnan-West Sichuan region, Scientia Geologica Sinica (in Chinese with English abstract), 1975 (4): 308–325.
Kan Rongju, Wang Shaoji, Huang Kun et al., Modern tectonic stress field and relative motion of intraplate block in Southwestern China, Seismology and Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1983, 5(2): 79–90.
Wang Liangmou, The mechanical study of formation mechanism for the Kangdian active tectonic zone and its intense seismicity, Seismogeology Committee of the Seismological Society of China, The Active Faults in China (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 1982, 242–250.
Ding Guoyu, Neotectonic deformation and recent intraplate motion of China continent, International Symposium on Tectonic Evolution and Dynamics of Continental Lithosphere Third National Conference on Tectonics, Collected Papers (II) (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1990, 73–85.
Deng Qidong, Xu Xiwei, Yu Guihua, Characteristics of regionalization of active faults in China and their genesis, in A Study on the Active Faults in China (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 1994, 1–14.
Lee, T. Y., Lawyer, L. A., Cenozoic reconstruction of southeast Asia, Tectonophysics, 1995, 85–138.
Xu, X. W., Deng, Q. D., Nonlinear characteristics of paleoseismicity in China, J. Geophys. Res., 1996, 101(B3): 6209–6231.
Xiang Hongfa, Guo Shunmin, Xu Xiwei et al., Division of South Sichuan-Yunnan region into active blocks and characteristics of present-day movement, Seismology and Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 2000, 22(3): 253–264.
Chen Guoxin, Zhou Rongjun, Huang Jinli et al., Tectonic deformation and strong earthquake rupture in Sichuan-Yunnan active tectonic region, in Neotectonics and Enviroment (ed. Lu Yanzhou) (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 2001, 185–198.
Tapponnier, P., Molnar, P., Slip-line field theory and large-scale continental tectonics,Nature, 1976, 264: 319–364.
Guo Shunmin, Xian Hongfa, Zhou Ruiqi et al., Longling-Lancang fault zone in southwest Yunnan, China-a newly generated rupture zone in continental crust (J), Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(4): 375–379.
Wu Qinafan, Zu Jinhua, Xie Yizhen et al., Basic characteristics of geothermal field in Yunnan Province, Seismology and Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1988, 10(4): 177–183.
Wang Ji-an, Xu Qing, Zhang Wenren et al., Terrestrial heat flow data and some geologic-geothermal problems in Yunnan Province, Seismology and Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1990, 12(4): 367–377.
Wang Jiyang, Huang Shaopeng, Compilation of terrestrial heat flow data in the China continent region, 2nd ed, Seismology and Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1990, 12(4): 351–366.
Allen, C. R., Zhuoli, L., Hong, Q. et al., Field study of a highly active fault zone: the Xianshuihe fault of southwestern China, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., 1991, 103: 1178–1199.
Zhao, G., Liu, W., Wei, H. et al., The Quaternary slip rate ad segmentation of the Xianshuihe active fault zone, in Proceedings of the PRC-USA Bilateral Symposium on the Xianshuihe Fault Zone, Chengdu, China, Oct. 1990, Beijing: Seismol Press, 1992, 41–57.
Ren Jinwei, Late Quaternary displacement and slip rate along Zemuhe fault in Sichuan, China Seismology and Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1994, 16(2): 146.
Song Fangmin, Wang Yipeng, Yu Weixian et al., Xiaojiang Active Fault Zone (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 1998, 237.
Seismological Bureau of Yunnan Province, The 1996 Lijiang Earthquake (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 1998, 1–188.
Guo Shunmin, Ji Fengju, Xiang Hongfa et al., The Honghe Active Fault Zone (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 2001, 1–172.
Shen Jun, Wang Yipeng, Ren Jinwei, The Quaternary right-lateral strike-slip movement along Deqin-Zhongdian-Daju fault zone in Yunnan, China, in Study on the Recent Deformation and Dynamics of the Lithosphere of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 2001, 106–122.
Tang Rongchang, Han Weibin et al., Acitive faults and earthquakes in Sichuan Province (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 1993, 1–368.
Guo Shunmin, Active Faults in Northwestern Yunnan (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 1990, 1–321.
Zhou Rongjun, Pu Xiaohong, He Yulin et al., Recent activity of Minjinang fault zone, uplift of Minshan block and their relation with seismicity of Sichuan, Seismology and Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 2000, 22(3): 285–294.
Zhou Rongjun, Li Yong, Densmore, A. L. et al., New evidence for tectonic deformation of the eastern Tibetan Plateau in late Quaternary, in Abstracts for 8th Anniversary of the Seismological Society of China (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 2000.
Seismological Bureau of Qinghai Province, Institute of Crustal Dynamics, China Seismological Bureau, East Kunlun Active Fault Zone (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismological Press, 1999, 1–186.
Pei Xiyu, Basic characteristics of segmentation of the late Quaternary Anninghe active fault, Sichuan Seismology (in Chinese), 1998, (4): 52–61.
Yo-ichiro Otofuji, Liu Yuyan, Mashiko Yokoyama et al., Tectonic deformation of the southwestern part of Yangtze craton inferred from paleomagnetism, EPSL, 1998, 156:47–60.
Anne, R., Reconstruction de la zone de collision Inde-Asie Etude centree sur l’Indochine, Ph. D. Thesis, Paris: Universite Paris 7, 1999, 1–230.
Wang, Q., Zhang, P., Jeffrey, T. et al., Present-day crustal deformation in China constrained by global positioning system measurements, Science, 2001, 294: 574–577.
Wang Qi, Zhang Peizhen, Feymueller, J. T. et al., Present-day crustal movement and tectonic deformation in China Continent, Science in China, Series D, 2002, 45(10): 865–874.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Wen, X., Zheng, R. et al. Pattern of latest tectonic motion and its dynamics for active blocks in Sichuan-Yunnan region, China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 46 (Suppl 2), 210–226 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1360/03dz0017
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03dz0017