Summary
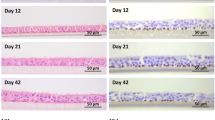
In the present study, culture conditions that promote the growth and differentiation of manatee respiratory tract epithelial cells toward a mucociliary phenotype were determined. Characterization of a manatee-specific cell line enables investigators to conduct in vitro testing where live-animal experimentation is not possible. Cell cultures were established from both explants and enzymatically dissociated cells that were isolated from manatee bronchial tissue. To modulate their differentiation, bronchial epithelial cells were grown on TranswellР collagen membranes either submerged or at an air-liquid interface. Growth on a collagen membrane at an air-liquid interface and medium supplemented with retinoic acid was required to promote a mucociliary phenotype. When cells were grown in submerged cultures without retinoic acid, they appeared more squamous and were not ciliated. Intracellular keratin proteins were detected in both submerged and interface cultures. Cultured manatee bronchial epithelial cells will facilitate future studies to investigate their potential role in pulmonary disease associated with brevetoxicosis after exposure to the red-tide organism, Karenia brevis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, K. B.; Cheng, P. W.; Kim, K. C. Characterization of guinea pig tracheal epithelial cells maintained in biphasic organotypic culture: cellular composition and biochemical analysis of released glycoconjugates. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2:145–154; 1990.
Bossart, G. D.; Baden, D. G.; Ewing, R. Y.; Roberts, B.; Wright, S. D. Brevetoxicosis in manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris) from the 1996 epizootic: gross, histologic, and immunohistochemical features. Toxicol. Pathol. 26:276–282; 1998.
Castleman, W. L.; Northrop, P. J.; McAllister, P. K. Replication of parainfluenza type-3 virus and bovine respiratory syncytial virus in isolated bovine type-II alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Vet. Res. 52:880–885; 1991.
Chopra, D. P.; Sullivan, J.; Wille, J. J.; Siddiqui, K. M. Propagation of differentiating normal human tracheobronchial epithelial cells in serum-free medium. J. Cell Physiol. 130:173–181; 1987.
de Jong, P. M.; Sterkenburg, M. A. J. A.; Kempenaar, J. A.; Kijkman, J. H.; Ponec, M. Serial culturing of human bronchial epithelial cells derived from biopsies. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 29A:379–387; 1993.
Elliget, K. A.; Lechner, J. F. Normal human bronchial epithelial cell cultures. In: Ian Freshney, R., ed. Culture of specialized cells; culture of epithelial cells. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1992:181–187.
Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission. Manatee necropsy report (MSW 0152). Report nr 0152. Marine Mammal Pathobiology Laboratory, Florida Marine Research Institute; 2001: 1p.
Harlow, E.; Lane, D. Cell staining. In: Harlow, E.; Lane, D., ed. Antibodies, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1988.
Jetten, A. M.; Shirley, J. E. Characterization of transglutaminase activity in rabbit tracheal epithelial cells. Regulation by retinoids. J. Biol. Chem. 261:15097–15101; 1986.
Kaartinen, L.; Nettesheim, P.; Adler, K. B.; Randell, S. H. Rat tracheal epithelial cell differentiation in vitro. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 29A:481–492; 1993.
Lechner, J. F.; Haugen, A.; Autrup, H.; McClendon, I. A.; Trump, B. F.; Harris, C. C. Clonal growth of epithelial cells from normal adult human bronchus. Cancer Res. 41:2294–2304; 1981.
Lechner, J. F.; Haugen, A.; McClendon, I. A.; Pettis, E. W. Clonal growth of normal adult human bronchial epithelial cells in a serum-free medium. In Vitro 18:633–642; 1982.
Lee, T. C.; Wu, R.; Brody, A. R.; Barrett, J. C.; Nettesheim, P. Growth and differentiation of hamster tracheal epithelial cells in culture. Exp. Lung Res. 6:27–45; 1984.
Mendelsohn, M. G.; Dilorenzo, T. P.; Abramson, A. L.; Steinberg, B. M. Retinoic acid regulates, in vitro, the two normal pathways of differentiation of human laryngeal keratinocytes. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 27A:137–141; 1991.
Moller, P. C.; Partridge, L. R.; Cox, R. A.; Pellegrini, V.; Ritchie, D. G. The development of ciliated and mucus cells from basal cells in hamster tracheal epithelial cell cultures. Tissue Cell. 21:195–198; 1989.
Niles, R.; Kim, K. C.; Hyman, B.; Christensen, T.; Wasano, K.; Brody, J. Characterization of extended primaryand secondary cultures of hamster tracheal epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 24:457–463; 1988.
Pfeifer, A.; Lechner, J. F.; Masui, T.; Reddel, R. R.; Mark, G. E.; Harris, C. C. Control of growth and squamous differentiation in normal human bronchial epithelial cells by chemical and biological modifiers and transferred genes. Environmental Health Perspect. 80:209–220; 1989.
Sweat, J. M.; Dunigan, D. D.; Wright, S. D.; Wright, S. D. Characterization of kidney epithelial cells from the Florida manatee, Trichechus manatus latirostris. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 37A:386–394; 2001.
Thacher, S. M.; Rice, R. H. Keratinocyte-specific transglutaminase of cultured human epidermal cells: relation to cross-linked envelope formation and terminal differentiation. Cell. 40:685–695; 1985.
Whitcutt, M. J.; Adler, K. B.; Wu, R. A biphasic chamber system for maintaining polarity of differentiation of cultured respiratory tract epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 24A:420–428; 1988.
Willey, J. C.; Laveck, M. A.; McClendon, I. A.; Lechner, J. F. Relationship of ornithine decarboxylase activity and cAMP metabolism to proliferation of normal human bronchial epithelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 124:207–212; 1985.
Wilson, A. P. Animal cell culture, 2nd ed. Oxford: IRL Press; 1992;263.
Wu, R.; Nolan, E.; Turner, C. Expression of tracheal differentiated functions in serum-free hormone-supplemented medium. J. Cell Physiol. 125:167–181; 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sweat, J.M., Johnson, C.M. & Gibbs, E.P.J. In vitro development and characterization of a manatee bronchial cell line. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 39, 249–256 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1290/1543-706X(2003)039<0249:IVDACO>2.0.CO;2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/1543-706X(2003)039<0249:IVDACO>2.0.CO;2