Abstract
Introduction
Accumulation of mucinous ascites causes significant morbidity for patients with unresectable pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP). The success of paracentesis for mucin evacuation is limited due to the presence of adhesions, disease burden, and the viscous nature of mucinous ascites. We sought to review our experience with laparoscopic evacuation of mucinous ascites for palliation of PMP.
Methods
Records were reviewed for patients who underwent laparoscopy for carcinomatosis secondary to appendix or colon cancer from July 2007 to January 2014. Of 123 patients, 10 were identified who underwent 17 laparoscopic procedures for palliative evacuation of mucinous ascites.
Results
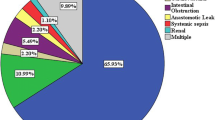
All patients had primary appendiceal cancers and all presented with symptomatic ascites causing abdominal distension and bloating. Pneumoperitoneum was established with a Veress needle or 5-mm optical viewing trocar in the majority of cases (n = 11). In the remaining six cases, an open technique was used and a 10-mm Hasson trocar was placed. There were no trocar-related complications. The median volume of mucin evacuated was 2.0 liters (range 1.7–8.0). All procedures were done as same-day surgeries; no patients required hospitalization. All patients reported symptomatic improvement following the procedure. One patient experienced a grade 1 complication of persistent drainage from one incision, which was managed in the outpatient setting. The median follow-up for all pts was 9.1 months. The median time to recurrent symptoms requiring repeat intervention was 5.3 months.
Conclusions
Laparoscopic evacuation of mucinous ascites for select patients with PMP is feasible and results in significant, durable symptom control with minimal morbidity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turaga KK, Pappas SG, Gamblin T. Importance of histologic subtype in the staging of appendiceal tumors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:1379–85.
Moran B, Baratti D, Yan TD, Kusamura S, Deraco M. Consensus statement on the loco-regional treatment of appendiceal mucinous neoplasms with peritoneal dissemination (pseudomyxoma peritonei). J Surg Oncol. 2008;98:277–82.
Kelly KJ, Nash GM. Peritoneal debulking/intraperitoneal chemotherapy-non-sarcoma. J Surg Oncol. 2014;109:14–22.
Chua TC, Moran BJ, Sugarbaker PH, et al. Early- and long-term outcome data of patients with pseudomyxoma peritonei from appendiceal origin treated by a strategy of cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2449–56.
Chua TC, Baker B, Yan TD, Zhao J, Morris DL. Palliative effects of an incomplete cytoreduction combined with perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol. 2010;33:568–71.
Glehen O, Mohamed F, Sugarbaker PH. Incomplete cytoreduction in 174 patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis from appendiceal malignancy. Ann Surg. 2004;240:278–85.
National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Version 4.0.: National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health; 29 May 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelly, K.J., Baumgartner, J.M. & Lowy, A.M. Laparoscopic Evacuation of Mucinous Ascites for Palliation of Pseudomyxoma Peritonei. Ann Surg Oncol 22, 1722–1725 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4118-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4118-3