Abstract
Background
Chemokines and their receptors are known to play important roles in the tumorigenesis of many malignancies. The chemokine CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 were suggested to be involved in cancer invasion and metastasis. The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate the prognostic impact of the expressions of CXCL12, CXCR4 and CXCR7 in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Methods
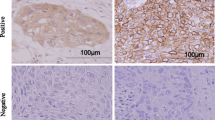
We used immunohistochemistry (IHC) and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to evaluate the expressions of CXCL12, CXCR4, and CXCR7 in ESCC patients’ tumor biopsy specimens obtained during preoperative endoscopy or surgery. These results were compared with the patients’ clinicopathological parameters and survival.
Results
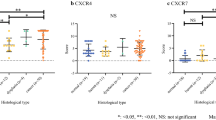
IHC was conducted for 172 patients. High expression of CXCR4 in the cytoplasm and nuclei and that of CXCR7 were associated with poor cause-specific survival (CSS) (P= .002 and .010, respectively). The specimens from 52 of the 172 patients were examined by RT-PCR and quantitative real-time PCR. The expression levels of messenger RNA (mRNA) of CXCR4 and CXCR7 were significantly increased in the tumors compared with normal esophageal mucosae (P < .0001). The expression level of mRNA of CXCR4 was associated with poor recurrence-free survival and CSS (P = .012 and .038, respectively).
Conclusions
CXCR4 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with ESCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990. Int J Cancer. 1999;83:18–29.
Ando N, Iizuka T, Ide H, et al. Surgery plus chemotherapy compared with surgery alone for localized squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus: a Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study-JCOG9204. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4592–6.
Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, et al. A randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for localized squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus (JCOG 9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:68–74.
Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Miyazaki Y, et al. Perioperative therapy for esophageal cancer. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62:531–40.
Yoshimura T, Matsushima K, Tanaka S, Robinson EA, Appella E, Oppenheim JJ, Leonard EJ. Purification of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor that has peptide sequence similarity to other host defense cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84:9233–7.
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, et al. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2001;410:50–6.
Lazennec G, Richmond A. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: new insights into cancer-related inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16:133–44.
Murphy PM, Baggiolini M, Charo IF, et al. International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:145–76.
Matsusue R, Kubo H, Hisamori S, et al. Hepatic stellate cells promote liver metastasis of colon cancer cells by the action of SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:2645–53.
Hu J, Deng X, Bian X, et al. The expression of functional chemokine receptor CXCR4 is associated with the metastatic potential of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:4658–65.
Scala S, Ottaiano A, Ascierto PA, et al. Expression of CXCR4 predicts poor prognosis in patients with malignant melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:1835–41.
Zhao H, Guo L, Zhao H, Zhao J, Weng H, Zhao B. CXCR4 over-expression and survival in cancer: a system review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2015;6:5022–40.
Burns JM, Summers BC, Wang Y, et al. A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2201–13.
Balabanian K, Lagane B, Infantino S, et al. The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals through the orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:35760–6.
Sun X, Cheng G, Hao M, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 chemokine axis and cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010;29:709–22.
Libert F, Parmentier M, Lefort A, Dumont JE, Vassart G. Complete nucleotide sequence of a putative G protein coupled receptor: RDC1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18:1917.
Miao Z, Luker KE, Summers BC, et al. CXCR7(RDC1) promotes breast and lung tumor growth in vivo and is expressed on tumor-associated vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:15735–40.
Hattermann K, Held-Feindt J, Lucius R, Muerkoster SS, Penfold ME, Schall TJ, Mentlein R. The chemokine receptor CXCR7 is highly expressed in human glioma cells and mediates antiapoptotic effects. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3299–308.
Wang J, Shiozawa Y, Wang J, et al. The role of CXCR7/RDC1 as a chemokine receptor for CXCL12/SDF-1 in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:4283–94.
Lu CL, Guo J, Gu J, Ge D, Hou YY, Lin ZW, Ding JY. CXCR4 heterogeneous expression in esophageal squamous cell cancer and stronger metastatic potential with CXCR4-positive cancer cells. Dis Esophagus. 2014;27:294–302.
Sasaki K, Natsugoe S, Ishigami S, et al. Expression of CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 correlates with lymph node metastasis in submucosal esophageal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2008;97:433–8.
Sasaki K, Nastugoe S, Ishigami S, et al. Expression of CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2009;21:65–71.
Yoshida T, Seike J, Miyoshi T, et al. A preoperative chemotherapy with weekly docetaxel plus low-dose cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil for stage II/III squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Esophagus. 2010;7:95–100.
The Japan Esophageal Society. Guidelines for the Clinical and Pathologic Studies on Carcinoma of the Esophagus. 10th ed. Tokyo: Kanehara; 2008.
Tachezy M, Zander H, Gebauer F, von Loga K, Pantel K, Izbicki JR, Bockhorn M. CXCR7 expression in esophageal cancer. J Transl Med. 2013;11:238.
Masuda T, Nakashima Y, Ando K, et al. Nuclear expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 indicate poorer prognosis in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:6397–403.
Wang L, Wang Z, Yang B, Yang Q, Wang L, Sun Y. CXCR4 nuclear localization follows binding of its ligand SDF-1 and occurs in metastatic but not primary renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2009;22:1333–9.
Kato M, Kitayama J, Kazama S and Nagawa H. Expression pattern of CXC chemokine receptor-4 is correlated with lymph node metastasis in human invasive ductal carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. 2003;5:R144–50.
Yoshitake N, Fukui H, Yamagishi H, et al. Expression of SDF-1 alpha and nuclear CXCR4 predicts lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:1682–9.
Wang N, Wu QL, Fang Y, et al. Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: pattern of expression and correlation with clinical outcome. J Transl Med. 2005;3:26.
Na IK, Scheibenbogen C, Adam C, et al. Nuclear expression of CXCR4 in tumor cells of non-small cell lung cancer is correlated with lymph node metastasis. Hum Pathol. 2008;39:1751–5.
Iwakiri S, Mino N, Takahashi T, et al. Higher expression of chemokine receptor CXCR7 is linked to early and metastatic recurrence in pathological stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2009;115:2580–93.
Rubin JB, Kung AL, Klein RS, et al. A small-molecule antagonist of CXCR4 inhibits intracranial growth of primary brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:13513–8.
Smith MC, Luker KE, Garbow JR, Prior JL, Jackson E, Piwnica-Worms D, Luker GD. CXCR4 regulates growth of both primary and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:8604–12.
Burger JA, Peled A. CXCR4 antagonists: targeting the microenvironment in leukemia and other cancers. Leukemia. 2009;23:43–52.
Beider K, Ribakovsky E, Abraham M, et al. Targeting the CD20 and CXCR4 pathways in non-Hodgkin lymphoma with rituximab and high-affinity CXCR4 antagonist BKT140. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:3495–507.
Devine SM, Flomenberg N, Vesole DH, et al. Rapid mobilization of CD34+ cells following administration of the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 to patients with multiple myeloma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1095–102.
Hartmann TN, Grabovsky V, Pasvolsky R, et al. A crosstalk between intracellular CXCR7 and CXCR4 involved in rapid CXCL12-triggered integrin activation but not in chemokine-triggered motility of human T lymphocytes and CD34+ cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2008;84:1130–40.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Toshio Yamaguchi for his help with the IHC analysis. This work was supported by a Grant-in Aid for Scientific Research (C), JSPS KAKENHI Grant No. 24591945.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goto, M., Yoshida, T., Yamamoto, Y. et al. CXCR4 Expression is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 24, 832–840 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4974-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4974-5