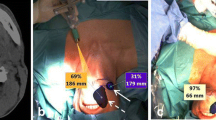
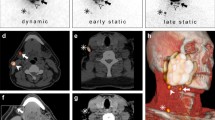
Abstract
Objective
Long-term results of sentinel node biopsy (SNB) in early (T1/T2) oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) in a single-institution experience.
Methods
Prospective consecutive cohort analysis of 79 patients (67% male, median age 60 years, age range 34–87 years) included between 2000 and 2006. Lymphatic mapping consisted of preoperative lymphoscintigraphy, single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT/CT), and intraoperative use of a handheld gamma probe. Endpoints of the study were neck control rate, overall (OS), disease-specific (DSS), and disease-free survival (DFS).
Results
Twenty-nine of 79 patients (37%) had positive sentinel nodes (SN). Six of 29 (21%) patients showed isolated tumor cells, 14/29 (48%) micrometastases, and 9/29 (31%) macrometastases. OS, DFS, and DSS at 5 years for the entire cohort were 80, 85, and 87%, for SN-negative patients were 88, 96, and 96%, and for SN-positive patients were 74, 73, and 77%, respectively. Only the difference in DSS achieved statistical significance. The neck control rate after 5 years was 96% in SN-negative and 74% in SN-positive patients. This difference was statistically significant.
Conclusions
SNB is a safe and accurate staging modality to select patients with clinically stage I/II OSCC with occult lymph node disease for elective neck dissection (END). The promising reported short-term results have been sustained by long-term follow-up. Patients with negative SN and no END achieve an excellent neck control rate which compares favorably with reports on primary END. The neck control rate in SN-negative patients is superior to that in SN-positive patients, which is reflected in superior DSS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stoeckli SJ. Sentinel node biopsy for oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(9):1539–51.
van den Brekel MW, van der Waal I, Meijer CJ, Freeman JL, Castelijns JA, Snow GB. The incidence of micrometastases in neck dissection specimens obtained from elective neck dissections. Laryngoscope. 1996;106(8):987–91.
Byers RM, Wolf PF, Ballantyne AJ. Rationale for elective modified neck dissection. Head Neck Surg. 1988;10(3):160–7.
de Boer M, van Deurzen CH, van Dijck JA, Borm GF, van Diest PJ, Adang EM, et al. Micrometastases or isolated tumor cells and the outcome of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(7):653–63.
Civantos FJ, Stoeckli SJ, Takes RP, Woolgar JA, de Bree R, Paleri V, et al. What is the role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in the management of oral cancer in 2010? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;267(6):839–44.
Stoeckli SJ, Pfaltz M, Steinert H, Schmid S. Histopathological features of occult metastasis detected by sentinel lymph node biopsy in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2002;112(1):111–5.
Stoeckli SJ, Steinert H, Pfaltz M, Schmid S. Sentinel lymph node evaluation in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;125(3):221–6.
Taylor RJ, Wahl RL, Sharma PK, Bradford CR, Terrell JE, Teknos TN, et al. Sentinel node localization in oral cavity and oropharynx squamous cell cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127(8):970–4.
Shoaib T, Soutar DS, MacDonald DG, Camilleri IG, Dunaway DJ, Gray HW, et al. The accuracy of head and neck carcinoma sentinel lymph node biopsy in the clinically N0 neck. Cancer. 2001;91(11):2077–83.
Civantos FJ, Gomez C, Duque C, Pedroso F, Goodwin WJ, Weed DT, et al. Sentinel node biopsy in oral cavity cancer: correlation with PET scan and immunohistochemistry. Head Neck. 2003;25(1):1–9.
Zitsch III RP, Todd DW, Renner GJ, Singh A. Intraoperative radiolymphoscintigraphy for detection of occult nodal metastasis in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;122(5):662–6.
Ross GL, Shoaib T, Soutar DS, MacDonald DG, Camilleri IG, Bessent RG, et al. The first international conference on sentinel node biopsy in mucosal head and neck cancer and adoption of a multicenter trial protocol. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9(4):406–10.
Alkureishi LW, Ross GL, Shoaib T, Soutar DS, Robertson AG, Thompson R, et al. Sentinel node biopsy in head and neck squamous cell cancer: 5-year follow-up of a European multicenter trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(9):2459–64.
Hermanek P, Hutter RV, Sobin LH, Wittekind C. International Union Against Cancer. Classification of isolated tumor cells and micrometastasis. Cancer. 1999;86(12):2668–73.
Kontio R, Leivo I, Leppanen E, Atula T. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma without clinically evident metastasis. Head Neck. 2004;26(1):16–21.
Khafif A, Schneebaum S, Fliss DM, Lerman H, Metser U, Ben-Yosef R, et al. Lymphoscintigraphy for sentinel node mapping using a hybrid single photon emission CT (SPECT)/CT system in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2006;28(10):874–9.
Haerle SK, Hany TF, Strobel K, Sidler D, Stoeckli SJ. Is there an additional value of SPECT/CT over planar lymphoscintigraphy for sentinel node mapping in oral/oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma? Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(11):3118–24.
Pitman KT, Johnson JT, Myers EN. Effectiveness of selective neck dissection for management of the clinically negative neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997;123(9):917–22.
Gourin CG, Conger BT, Porubsky ES, Sheils WC, Bilodeau PA, Coleman TA. The effect of occult nodal metastases on survival and regional control in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2008;118(7):1191–4.
Civantos FJ, Zitsch RP, Schuller DE, Agrawal A, Smith RB, Nason R, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy accurately stages the regional lymph nodes for T1-T2 oral squamous cell carcinomas: results of a prospective multi-institutional trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(8):1395–400.
Ross GL, Soutar DS, Gordon MacDonald D, Shoaib T, Camilleri I, Roberton AG, et al. Sentinel node biopsy in head and neck cancer: preliminary results of a multicenter trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004;11(7):690–6.
Kovacs AF, Stefenelli U, Seitz O, Middendorp M, Diener J, Sader R, et al. Positive sentinel lymph nodes are a negative prognostic factor for survival in T1-2 oral/oropharyngeal cancer-a long-term study on 103 patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(2):233–9.
Bilde A, von Buchwald C, Therkildsen MH, Mortensen J, Kirkegaard J, Charabi B, et al. Need for intensive histopathologic analysis to determine lymph node metastases when using sentinel node biopsy in oral cancer. Laryngoscope. 2008;118(3):408–14.
Goerkem M, Braun J, Stoeckli SJ. Evaluation of clinical and histomorphological parameters as potential predictors of occult metastases in sentinel lymph nodes of early squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(2):527–35.
Dunne AA, Kulkens C, Ramaswamy A, Folz BJ, Brandt D, Lippert BM, et al. Value of sentinel lymphonodectomy in head and neck cancer patients without evidence of lymphogenic metastatic disease. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2001;28(4):339–44.
Morton DL, Wen DR, Wong JH, Economou JS, Cagle LA, Storm FK, et al. Technical details of intraoperative lymphatic mapping for early stage melanoma. Arch Surg. 1992;127(4):392–9.
Ambrosch P, Brinck U. Detection of nodal micrometastases in head and neck cancer by serial sectioning and immunostaining. Oncology (Williston Park). 1996;10(8):1221–6; discussion 6, 9.
Kuriakose MA, Trivedi NP. Sentinel node biopsy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;17(2):100–10.
Bernier J, Domenge C, Ozsahin M, Matuszewska K, Lefebvre JL, Greiner RH, et al. Postoperative irradiation with or without concomitant chemotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(19):1945–52.
Cooper JS, Pajak TF, Forastiere AA, Jacobs J, Campbell BH, Saxman SB, et al. Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(19):1937–44.
Studer G, Zwahlen RA, Graetz KW, Davis BJ, Glanzmann C. IMRT in oral cavity cancer. Radiat Oncol. 2007;2:16.
Liao CT, Lin CY, Fan KH, Wang HM, Ng SH, Lee LY, et al. Identification of a high-risk group among patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma and pT1-2N0 disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010. [Epub ahead of print].
Cosmidis A, Rame JP, Dassonville O, Temam S, Massip F, Poissonnet G, et al. T1-T2 NO oropharyngeal cancers treated with surgery alone. A GETTEC study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2004;261(5):276–81.
Wolfensberger M, Zbaeren P, Dulguerov P, Muller W, Arnoux A, Schmid S. Surgical treatment of early oral carcinoma-results of a prospective controlled multicenter study. Head Neck. 2001;23(7):525–30.
Yuen AP, Wei WI, Wong YM, Tang KC. Elective neck dissection versus observation in the treatment of early oral tongue carcinoma. Head Neck. 1997;19(7):583–8.
Yuen AP, Ho CM, Chow TL, Tang LC, Cheung WY, Ng RW, et al. Prospective randomized study of selective neck dissection versus observation for N0 neck of early tongue carcinoma. Head Neck. 2009;31(6):765–72.
Hosal AS, Carrau RL, Johnson JT, Myers EN. Selective neck dissection in the management of the clinically node-negative neck. Laryngoscope. 2000;110(12):2037–40.
Sivanandan R, Kaplan MJ, Lee KJ, Lebl D, Pinto H, Le QT, et al. Long-term results of 100 consecutive comprehensive neck dissections: implications for selective neck dissections. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;130(12):1369–73.
Genden EM, Ferlito A, Silver CE, Takes RP, Suarez C, Owen RP, et al. Contemporary management of cancer of the oral cavity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;267(7):1001–17.
Byers RM, Weber RS, Andrews T, McGill D, Kare R, Wolf P. Frequency and therapeutic implications of “skip metastases” in the neck from squamous carcinoma of the oral tongue. Head Neck. 1997;19(1):14–9.
Murer K, Huber GF, Haile SR, Stoeckli SJ. Comparison of morbidity between sentinel node biopsy and elective neck dissection for treatment of the n0 neck in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2010. [Epub ahead of print].
Rusthoven K, Ballonoff A, Raben D, Chen C. Poor prognosis in patients with stage I and II oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2008;112(2):345–51.
Hiratsuka H, Miyakawa A, Nakamori K, Kido Y, Sunakawa H, Kohama G. Multivariate analysis of occult lymph node metastasis as a prognostic indicator for patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Cancer. 1997;80(3):351–6.
Jang WI, Wu HG, Park CI, Kim KH, Sung MW, Kim MJ, et al. Treatment of patients with clinically lymph node-negative squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2008;38(6):395–401.
Shasha D, Harrison LB. Elective irradiation of the N0 neck in squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1998;31(5):803–13.
Bataini JP. Radiotherapy in N0 head and neck cancer patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1993;250(8):442–5.
Fidler IJ, Kumar R, Bielenberg DR, Ellis LM. Molecular determinants of angiogenesis in cancer metastasis. Cancer J Sci Am. 1998;4 Suppl 1:S58–66.
Atula T, Hunter KD, Cooper LA, Shoaib T, Ross GL, Soutar DS. Micrometastases and isolated tumour cells in sentinel lymph nodes in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009;35(5):532–8.
Leidenius MH, Vironen JH, Heikkila PS, Joensuu H. Influence of isolated tumor cells in sentinel nodes on outcome in small, node-negative (pT1N0M0) breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(1):254–62.
Kubuschok B, Passlick B, Izbicki JR, Thetter O, Pantel K. Disseminated tumor cells in lymph nodes as a determinant for survival in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(1):19–24.
Rosenberg R, Friederichs J, Gertler R, Hoos A, Mueller J, Nahrig J, et al. Prognostic evaluation and review of immunohistochemically detected disseminated tumor cells in peritumoral lymph nodes of patients with pN0 colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2004;19(5):430–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broglie, M.A., Haile, S.R. & Stoeckli, S.J. Long-Term Experience in Sentinel Node Biopsy for Early Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 18, 2732–2738 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1780-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1780-6