Abstract
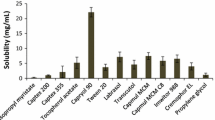
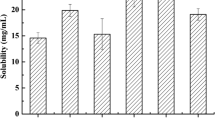
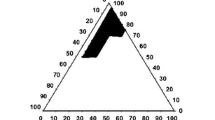
This study aims to formulate and evaluate bioavailability of a self-nanoemulsified drug delivery system (SNEDDS) of a poorly water-soluble herbal active component oleanolic acid (OA) for oral delivery. Solubility of OA under different systems was determined for excipient selection purpose. Four formulations, where OA was fixed at the concentration of 20 mg/g, were prepared utilizing Sefsol 218 as oil phase, Cremophor EL and Labrasol as primary surfactants, and Transcutol P as cosurfactant. Pseudo-ternary phase diagrams were constructed to identify self-emulsification regions for the rational design of SNEDDS formulations. Sefsol 218 was found to provide the highest solubility among all medium-chained oils screened. Efficient self-emulsification was observed for the systems composing of Cremophor EL and Labrasol. The surfactant to cosurfactant ratio greatly affected the droplet size of the nanoemulsion. Based on the outcomes in dissolution profiles, stability data, and particle size profiles, three optimized formulations were selected: Sefsol 218/Cremophor EL/Labrasol (50:25:25, w/w), Sefsol 218/Cremophor EL/Labrasol/Transcutol P (50:20:20:10, w/w), and Sefsol 218/Cremophor EL/Labrasol/Transcutol P (50:17.5:17.5:15, w/w). Based on the conventional dissolution method, a remarkable increase in dissolution was observed for the SNEDDS when compared with the commercial tablet. The oral absorption of OA from SNEDDS showed a 2.4-fold increase in relative bioavailability compared with that of the tablet (p < 0.05), and an increased mean retention time of OA in rat plasma was also observed compared with that of the tablet (p < 0.01). These results suggest the potential use of SNEDDS to improve dissolution and oral bioavailability for poorly water-soluble triterpenoids such as OA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. T. Tian, L. Ma, and N. S. Du. Survey of pharmacology of oleanolic acid. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 27:884–886 (2002).
J. Liu. Pharmacology of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid. J. Ethnopharmacol. 49:57–68 (1995).
B. Claude, P. h. Morin, M. Lafosse, and P. Andre. Evaluation of apparent formation constants of pentacyclic triterpene acids complexes with derivatized β- and χ-cyclodextrins by reversed phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 1049:37–42 (2004).
H. H. Tong, H. B. Wu, Y. Zheng, J. Xi, H. L. Chow, and C. K. Chan. Physical characterization of oleanolic acid nonsolvate and solvates prepared by solvent recrystallization. Int. J. Pharm. 355:195–202 (2008).
M. Song, T. Hang, Y. Wang, L. Jiang, X. Wu, Z. Zhang, J. Shen, and Y. Zhang. Determination of oleanolic acid in human plasma and study of its pharmacokinetics in Chinese healthy male volunteers by HPLC tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 40:190–196 (2006).
D. W. Jeong, Y. H. Kim, H. H. Kim, H. Y. Ji, S. D. Yoo, W. R. Choi, S. M. Lee, C. K. Han, and H. S. Lee. Dose-linear pharmacokinetics of oleanolic acid after intravenous and oral administration in rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 28:51–57 (2007).
Y. D. Yan, B. Feng, X. J. Huang, and Z. G. Zhou. Study on β-cyclodextrin inclusion compound of oleanolic acid. Chin. Tradit. Patent Med. 6:2–4 (1995).
D. X. Xiang, Y. F. Tao, F. Wang, and H. D. Li. Studies on formation and solubilizing mechanism of oleanolic acid solid dispersion. Chin. Tradit. Herb Drugs. 33:311–314 (2002).
M. Q. Guo, S. Q. Zhang, F. R. Song, D. W. Wang, Z. Q. Liu, and S. Y. Liu. Studies on the non-covalent complexes between oleanolic acid and cyclodextrins using electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 38:723–731 (2003).
V. T. Neu Yen Thi, and H. R. Zhao. Preparation of oleanolic acid solid dispersion systems and their dissolution in vitro. J. Chin. Pharm. Univ. 34:236–239 (2003).
A. A. Date, and M. S. Nagarsenker. Design and evaluation of self-nanoemulsified drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) for cefpodoxime proxetil. Int. J. Pharm. 329:166–172 (2007).
P. P. Constantinides. Lipid microemulsions for improving drug dissolution and oral absorption: physical and biopharmaceutical aspects. Pharm. Res. 12:1561–1572 (1995).
S. Shafiq, F. Shakeel, S. Talegaonkar, F. J. Ahmad, R. K. Khar, and M. Ali. Development and bioavailability assessment of ramipril nanoemulsion formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 662:227–243 (2007).
T. R. Kommuru, B. Gurley, M. A. Khan, and I. K. Reddy. Self-emulsified drug delivery systems (SEDDS) of coenzyme Q10: formulation development and bioavailability assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 212:233–246 (2001).
K. Kawakami, Y. Yoshikawa, E. Moroto, K. Kanaoka, Y. Takaashi, K. Nishihara, and K. Masuda. Microemulsion formulation for enhanced absorption of poorly soluble drugs II. In vivo study. J. Control Release. 81:75–82 (2002).
Y. Chen, J. Liu, X. Yang, X. Zhao, and H. Xu. Oleanolic acid nanosuspensions: preparation, in-vitro characterization and enhanced hepatoprotective effect. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 57:259–264 (2005).
P. Li, A. Ghosh, R. F. Wagner, S. Krill, Y. M. Joshi, and A. T. M. Serajuddin. Effect of combined use of nonionic surfactant on formation of oil-in-water microemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 288:27–34 (2005).
Z. G. Gao, H. G. Choi, H. J. Shin, K. M. Park, S. J. Lim, K. J. Hwang, and C. K. Kim. Physicochemical characterization and evaluation of a microemulsion system for oral delivery of cyclosphorin A. Int. J. Pharm. 161:75–86 (1998).
S. Nazzal, I. I. Smalyukh, O. D. Lavrentovich, and M. A. Khan. Preparation and in vitro characterization of a eutectic based semisolid self-nanoemulsified drug delivery system (SNEDDS) of ubiquinone: mechanism and progress of emulsion formation. Int. J. Pharm. 235:247–265 (2002).
S. A. Charman, W. N. Charman, M. C. Rogge, T. D. Wilson, F. J. Dutko, and C. W. Pouton. Self-emulsified drug delivery systems: formulation and biopharmaceutic evaluation of an investigational lipophilic compound. Pharm. Res. 9:87–93 (1992).
P. Zhang, Y. Liu, N. P. Feng, and J. Xiu. Preparation and evaluation of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of oridonin. Int. J. Pharm. 355:269–276 (2008).
E. Atef, and A. A. Belmonte. Formulation and in vitro and in vivo characterization of a phenytoin self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 35:257–263 (2008).
Y. Y. Chiu, K. Higaki, B. L. Neudeck, J. L. Barnett, L. S. Welage, and G. L. Amidon. Human jejunal permeability of cyclosporin A: influence of surfactants on P-glycoprotein efflux in Caco-2 cells. Pharm. Res. 20:749–756 (2003).
M. J. Lawrence, and G. D. Ress. Microemulsion-based media as novel drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 45:89–121 (2000).
D. Q. M. Craig, S. A. Barker, D. Banning, and S. W. Booth. An investigation into the mechanisms of self-emulsification using particle size analysis and low frequency dielectric spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 114:103–110 (1995).
S. M. Khoo, A. J. Humberstone, C. J. H. Porter, G. A. Edwards, and W. N. Charman. Formulation design and bioavailability assessment of lipidic self-emulsifying formulations of halofantrine. Int. J. Pharm. 167:155–164 (1998).
A. Priev, S. Zalipsky, R. Cohen, and Y. Barenholz. Determination of critical micelle concentration of lipopolymers and other amphiphiles: comparison of sound velocity and fluorescent measurements. Langmuir. 18:612–617 (2002).
L. A. Smith, R. B. Hammond, K. J. Roberts, D. Machin, and G. McLeod. Determination of the crystal structure of anhydrous sodium dodecyl sulphate using a combination of synchrotron radiation powder diffraction and molecular modeling techniques. J. Mol. Struct. 554:173–182 (2000).
P. K. Ghosh, and R. S. R. Murthy. Microemulsions: a potential drug delivery system. Curr. Drug Deliv. 3:167–180 (2006).
N. J. Kale, and L. V. Allen. Studies on microemulsions using Brij 96 as surfactant and glycerin, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol as cosurfactants. Int. J. Pharm. 57:87–93 (1989).
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Research Council of the University of Macau (Research Grant RG 072/05-06S/07R for YZ) and the Macao Science and Technology Development Fund (FDCT Fund Project No: 005/2007/A1 for HHYT & 008/2007/A1 for YZ) is gratefully acknowledged. Valuable comments from Mr. Zhao Yi are highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, J., Chang, Q., Chan, C.K. et al. Formulation Development and Bioavailability Evaluation of a Self-Nanoemulsified Drug Delivery System of Oleanolic Acid. AAPS PharmSciTech 10, 172–182 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-009-9190-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-009-9190-9