Abstract.
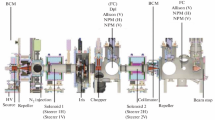
The SPES Radioactive Ion Beam (RIB) facility, now in the construction phase at INFN-LNL, has the aim to provide high-intensity and high-quality beams of neutron-rich nuclei for nuclear physics research as well as to develop an interdisciplinary research center based on the cyclotron proton beam. The SPES system is based on a dual-exit high-current cyclotron, with tunable proton beam energy 35-70MeV and 0.20-0.75mA. The first exit is used as proton driver to supply an ISOL system with an UCx Direct Target able to sustain a power of 10kW. The expected fission rate in the target is of the order of \( 10^{13}\) fissions per second. The exotic isotopes will be re-accelerated by the ALPI superconducting LINAC at energies of 10 A MeV and higher, for masses around \( A=130\) amu, with an expected beam intensity of \( 10^7\) - \( 10^9\) pps. The second exit will be used for applied physics: radioisotope production for medicine and neutrons for material studies. Fast neutron spectra will be produced by the proton beam interaction with a conversion target. A production rate in excess of \( 10^{14}\) n/s can be achieved: this opens up the prospect of a high-flux neutron irradiation facility (NEPIR) to produce both discrete and continuous energy neutrons. A direct proton beam line is also envisaged. NEPIR and the direct proton line would dramatically increase the wide range of irradiation facilities presently available at LNL. We also present LENOS, a proposed project dedicated to accurate neutron cross-sections measurements using intense, well-characterized, broad energy neutron beams. Other activities already in operation at LNL are briefly reviewed: the SIRAD facility for proton and heavy-ion irradiation at the TANDEM-ALPI accelerator and the BELINA test facility at CN van de Graaff accelerator.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Prete et al., EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 11030 (2014)
T. Lamy et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75, 1624 (2004)
A. Dainelli et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 382, 100 (1996)
J. Esposito, The LARAMED project at INFN Legnaro National labs, poster contribution to NRC-8EuCheMS International Conference on Nuclear and Radiochemistry, September 2012, Como (Italy), https://indico.cern.ch/event/183405/session/26/contribution/69
J. Esposito, The IFMIF EVEDA Low Power Beam Dump (LPBD) Design for LIPAc commissioning tests, LNL annual report 2014
JEDEC, Measurement and reporting of alpha particle and terrestrial cosmic ray-induced soft errors in semiconductor devices, JEDEC Standard JESD89A (2006) available at: http://www.jedeq.org/
S. Kamada, T. Itoga, Y. Unno, W. Takahashi, T. Oishi, M. Baba, Measurement of energy-angular neutron distribution of ^7Li, ^9Be(p,nx) reaction at $E_p=70$MeV and 11MeV, in Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology (2010)
R. Nolte et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 476, 369 (2002)
J.M. Sisterson et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 240, 617 (2005)
S. Pomp, D.T. Barlett, S. Mayer, G. Reitz, S. Röttger, M. Silari, F.D. Smit, H. Vincke, H. Yasuda, High-energy quasi-monoenergetic neutron fields: existing facilities and future needs, EURADOS Report 2013-02
D. Bisello, J. Esposito, P. Mastinu, G. Prete, L. Silvestrin, J. Wyss, Phys. Proc. 60, 271 (2014)
D.B. Pelowitz, M.R. James, G.W. McKinney, J.W. Durkee, MCNPX 2.7.A Extensions (LANL, 2008)
HeatWave Labs model HWEG-1079, provided by Atlair Technologies
C. Ceballos, J. Esposito, S. Agosteo, P. Colautti, V. Conte, D. Moro, A. Pola, Appl. Radiat. Isot. 69, 1660 (2011)
A. Pisent, M. Comunian, A. Palmieri, E. Fagotti, G.V. Lamanna, S. Mathot, The TRASCO SPES-RFQ, in Proceedings of LINAC 2004 conference, JaCoW, Lubeck, Germany (2005) pp. 69--71
P.F. Mastinu, G. Martín Hernández, J. Praena, Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 601, 333 (2009)
G. Martín-Hernández, P.F. Mastinu, J. Praena, N. Dzysiuk, R. Capote Noy, M. Pignatari, Appl. Radiat. Isot. 70, 1583 (2012)
P. Mastinu, S. Marigo, Method for producing a heat exchanger and relevant heat exchanger, Patent Application Number PCT/IB2014/067156
B. Bayanov, V. Belov, V. Kindyuk, E. Oparin, S. Taskaev, Appl. Radiat. Isot. 61, 817 (2004)
S. Halfon et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85, 056105 (2014)
S. Halfon et al., Appl. Radiat. Isot. 88, 238 (2014)
D. Bisello, A. Candelori, P. Giubilato, A. Kaminski, D. Pantano, R. Rando, M. Tessaro, J. Wyss, The SIRAD irradiation facility for bulk damage and single event effect studies, in Proceedings of RADECS (2003) p. 451
J. Wyss, D. Bisello, D. Pantano, Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 462, 426 (2001)
J.F. Ziegler, SRIM, Stopping and range of ions in matter, available at http://www.srim.org
D. Bisello et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 231, 65 (2005)
D. Bisello, P. Giubilato, S. Mattiazzo, M. Nigro, D. Pantano, R. Rando, L. Silvestrin, M. Tessaro, J. Wyss, Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 266, 2142 (2008)
S. Mattiazzo, D. Bisello, P. Giubilato, A. Kaminsky, D. Pantano, L. Silvestrin, M. Tessaro, J. Wyss, Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 685, 125 (2011)
G. Busatto et al., Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 1995 (2011)
L. Silvestrin, D. Bisello, G. Busatto, P. Giubilato, F. Iannuzzo, S. Mattiazzo, D. Pantano, A. Sanseverino, M. Tessaro, F. Velardi, J. Wyss, Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 273, 234 (2012)
S. Gerardin, M. Bagatin, A. Paccagnella, D. Bisello, P. Giubilato, S. Mattiazzo, D. Pantano, L. Silvestrin, M. Tessaro, J. Wyss, V. Ferlet-Cavrois, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 60, 4136 (2013)
A. Dainelli et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 382, 100 (1996)
Webpage of LNL accelerators, http://www.lnl.infn.it/accelerators/accelerators.html
General Electric’s Inspection Technologies (formerly Seifert), www.gemeasurement.com
D. Bisello, A. Candelori, A. Kaminski, A. Litovchenko, E. Noha, L. Stefanutti, Rad. Phys. Chem. 71, 713 (2004)
R. Rando, A. Bangert, D. Bisello, A. Candelori, P. Giubilato, M. Hirayama, R. Johnson, H.F.-W. Sadrozinsky, M. Sugizaki, J. Wyss, M. Ziegler, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 51, 1067 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silvestrin, L., Bisello, D., Esposito, J. et al. SPES and the neutron facilities at Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 131, 72 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16072-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16072-0