Abstract
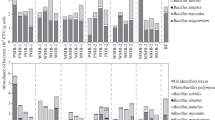
Differences in the functional structure of streptomycete complexes isolated from ecotopes with varying degrees of contamination by heavy metals (HMs) have been revealed using data on the growth kinetics of representatives of the genus Streptomyces in the presence of lead, zinc, and copper ions. Streptomycete complexes isolated from moderately polluted soils (residential areas and garden plots in the city) and highly polluted soils (transport and industrial areas) are enriched in representatives reacting to metal ions (3 mg/L) by an increase in radial growth relative to the complex isolated from the soil of the control site, while the accumulation of biomass in a liquid medium containing 10 mg/L Pb2+ is less intensive in the former complexes than in the latter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, A. and Edwards, C., Effects of metals on a range of Streptomyces species, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1989, vol. 55, pp. 2030–2035.
Albarracín, V.H., Ávila, A.L., Amoroso, M.J., and Abate, C.M., Copper removal ability by Streptomyces strains with dissimilar growth patterns and endowed with cupric reductase activity, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2008, vol. 288, pp. 141–148.
Alvarez, A., Catalano, S.A, and Amoroso, M.J., Heavy metal resistant strains are widespread along Streptomyces phylogeny, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.11.025
Amoroso, M.-J., Schubert, D., Mitscherlich, P., Schumann, P., and Kothe, E., Evidence for high affinity nickel transporter genes in heavy metal resistant Streptomyces sp., J. Basic Microbiol., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 295–301.
De, J., Ramaiah, N., Mesquita, A., and Verlekar, X.N., Tolerance to various toxicants by marine bacteria highly resistant to mercury, Mar. Biotechnol., 2003, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 185–193.
Evdokimova, G.A. and Mozgova, N.P., Restoration of properties of cultivated soils polluted by copper and nickel, J. Environ. Monit., 2003, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 667–670.
Gauze, G.F., Preobrazhenskaya, T.P., Sveshnikova, M.A., Terekhova, L.P., and Maksimova, T.S., Opredelitel’ aktinomitsetov. Rody Sreptomyces, Streptoverticillium, Chainia (Guide to Identification of Actinomyces: Genera Sreptomyces, Streptoverticillium, and Chainia), Moscow: Nauka, 1983.
Guo, J.K., Lin, Y.B., Zhao, M. L., Ran Sun, Wang, T.T., Tang, M., and Wei, G.H., Streptomyces plumbiresistens sp. nov., a leadresistant actinomycete isolated from lead-polluted soil in north-west China, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 59, pp. 1326–1330.
Haferburg, G., Groth, I., Möllmann, U., Kothe, E., and Sattler, I., Arousing sleeping genes: shifts in secondary metabolism of metal tolerant actinobacteria under conditions of heavy metal stress, Biometals, 2009, vol. 22, pp. 225–234.
Haferburg, G. and Kothe, E., Microbes and metals: interactions in the environment, J. Basic Microbiol., 2007, vol. 47, pp. 453–467.
Haferburg, G., Reinicke, M., Merten, D., Schmidt, A., Schmidt, T., and Schütze, E., Microbes adapted to acid mine drainage as source for strains active in retention of aluminum or uranium, J. Geochem. Explor., 2007, vol. 92, pp. 196–204.
Hopwood, D.A., Streptomyces in Nature and Medicine: the Antibiotic Makers, New York: Oxford Univ. Press, 2007.
Kothe, E., Bergman, H., and Büchel, G., Molecular mechanisms in bio-geo-interactions: from a case study to general mechanisms, Geochemistry, 2005, vol. 65, pp. 7–27.
Lin, Y.B., Wang, X.Y., Li, H.F., Wang, N.N., Wang, H.X., Tang, M., and Wei, G.H., Streptomyces zinciresistens sp. nov., a zinc-resistant actinomycete isolated from soil from a copper and zinc mine, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 61, pp. 616–620.
Majzlik, P., Strasky, A., Adam, V., Nemec, M., Trnkova, L., Zehnalek, J., Hubalek, J., Provaznik, I., and Kizek, R., Influence of zinc (II) and copper (II) ions on Streptomyces bacteria revealed by electrochemistry, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2011, no. 6, pp. 2171–2191.
Rho, J. and Kim, J., Heavy metal biosorption and its significance to metal tolerance of Streptomycetes, J. Microbiol., 2002, vol. 40, pp. 51–54.
Riccardi, G., Milano, A., Pasca, M.R., and Nies, D.H., Genomic analysis of zinc homeostasis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, FEMS Microbiol Lett., 2008, vol. 287, pp. 1–7.
Schmidt, A., Haferburg, G., Merten, D., Gherghel, F., Buchel, G., and Kothe, E., Heavy metal resistance to the extreme: Streptomyces strains from a former uranium mining area, Chemie Erde., 2009, vol. 69, no. 2, pp. 35–44.
Schütze, E. and Kothe, E., Heavy metal-resistant Streptomycetes in soil, in Bio-Geo Interactions in Metal-Contaminated Soils, in Soil Biology Series, New York: Springer, 2012, vol. 31, pp. 163–182.
Shirokikh, I.G., Shirokikh, A.A., and Ashikhmina, T.Y., Specificity of actinomycetal complexes in urbanozems of the city of Kirov, Eurasian Soil Sci., 2011, vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 180–185.
Smirnova, G.F., Distribution of bacteria resistant to oxygen-containing xenobiotics, Mikrobiol. Zh. Kyiv, 2005, vol. 67, no. 5, pp. 11–18.
So, N.W., Rho, J.Y., Lee, S.Y., Hancock, I.C., and Kim, J.H., A lead-absorbing protein with superoxide dismutase activity from Streptomyces subrutilus, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2001, vol. 194, pp. 93–98.
Vorob’eva, L.A., Teoriya i praktika khimicheskogo analiza pochv (Theory and Practice of the Chemical Analysis of Soils), Moscow: GEOS, 2006.
Weinberg, E.D., Roles of trace metals in transcriptional control of microbial secondary metabolism, Biol. Met., 1990, vol. 2, pp. 191–196.
Yaneva, O.D., Resistance mechanisms of bacteria to ions of heavy metals, Mikrobiol. Zh. Kyiv, 2009, vol. 71, no. 6, pp. 54–65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.G. Shirokikh, E.S. Solovyeva, T.J. Ashihmina, 2015, published in Sibirskii Ekologicheskii Zhurnal, 2015, No. 1, pp. 154–162.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirokikh, I.G., Solovyeva, E.S. & Ashihmina, T.J. Functional and structural features of streptomycete complexes isolated from soils with varying degrees of heavy-metal contamination. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 8, 125–132 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425515010138
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425515010138