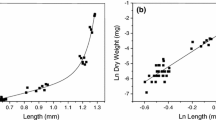
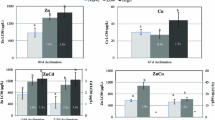
Abstract
The chronic effects of cadmium, naphthalene, and DDVP on the growth of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus Peters) exposed to concentrations corresponding to 1/30 LC50 for 24 h (cadmium and DDVP) and 1/15 LC50 for 24 h (naphthalene) have been studied. The fish are kept in toxicant solutions for 60 days and then for 60 more days in clean water. It is found that the studied toxicants affect fish-growth indices to varying extents. Organic compounds have no significant effect on the linear and mass growth of tilapia. Cadmium most strongly suppresses tilapia growth, and the toxic effect of this metal is irreversible: all fish die after being transferred to clean water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerasimov, Yu.V., Pavlov, D.F., and Chuiko, G.M., Foraging behavior of the bream under chronic exposure to cadmium, in Tr. Vsesoyuz. Soveshch. po voprosam povedeniya ryb (Proc. All-Union Congr. on the Behavior of Fish), Moscow: Inst. Evol. Morfol. Ekol. Zhivotn. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 1991, pp. 196–203.
Mina, M.V. and Klevezal’, G.A., Rost zhivotnykh (Growth of Animals), Moscow: Nauka, 1976.
Pavlov, D.F., Dynamics of acetylcholinesterase activity and protein content in the brain of fish under the influence of pollutants, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation,: Borok, 1992.
Pavlov, D.F., Chuiko, G.M., and Gerasimov, Yu.V., The protein content and the activity of acetylcholinesterase in the bream brain under chronic exposure to cadmium, in Biologiya vnutrennikh vod: Inform. Byul. (Inland Water Biology: Information Bulletin), Leningrad, 1990, vol. 89, pp. 72–77.
Stroganov, N.S., The biological criteria of toxicity in aquatic toxicology, in Kriterii toksichnosti i printsipy metodik po vodnoi toksikologii (Toxicity Criteria and Principles of Methodologies for Aquatic Toxicology), Moscow: Izd. Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1971, pp. 14–28.
Chuiko, G.M., Pavlov, D.F., Podgornaya, V.A., and Stepanova, V.M., Changes in the activity of acetylcholinesterase and the soluble protein content in the brain of the Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus (Peters, 1852) under chronic exposure to cadmium, naphthalene, and dichlophos, Biol. Vnutr. Vod, 2001, no. 3, pp. 72–79.
Frumin, G.T., Chuiko, G.M., Pavlov, D.F., and Menzikova, O.V., New rapid method to evaluate median effect concentrations of xenobiotics in hydrobionts, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1992, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 361–367.
Golovanova, I.L., Pavlov, D.F., and Chuiko, G.M., Effects of cadmium, naphthalene and DDVP on gut carbohydrase activity in bream (Abramis brama L.) and mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus Peters), Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1994, vol. 52, pp. 338–345.
Heg, D., Shürch, R., and Rothenberg, S., Behavioral type and growth rate in a cichlid fish, Behav. Ecol., 2011, vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 1227–1233.
James, R. and Sampath, K., Effect of the ion-exchanging agent, zeolite, on reduction of cadmium toxicity: an experimental study on growth and elemental uptake in Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch), J. Aquacult. Trop., 1999, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 65–74.
James, R., Sampath, K., and Edward, D.S., Effect of copper toxicity on growth and reproductive potential in an ornamental fish, Xiphophorus helleri, Asian Fish. Sci., 2003, vol. 16, pp. 317–326.
James, R., Sivakumar, V., Sampath, K., and Rajendran, P., Individual and combined effects of zinc, cadmium and copper on growth of Oreochromis mossambicus, Indian J. Fish., 1991, vol. 38, pp. 198–200.
Kooijman, S.A.L. and Bedaux, J.J.M., Analysis of toxicity tests on fish growth, Water. Res., 1996, vol. 30, no. 7, pp. 1633–1644.
Kuz’mina, V.V., Chuiko, G.M., and Pavlov, D.F., Effects of DDVP, naphthalene and cadmium on intestinal proteolytic activity in Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus Peters), Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1999, vol. 62, pp. 193–198.
Pavlov, D.F., Chuiko, G.M., Gerassimov, Yu.V., and Tonkopiy, V.D., Feeding behavior and brain acetylcholinesterase activity in bream (Abramis brama L.) as affected by DDVP, an organophosphorus insecticide, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C, 1992, vol. 103C, no. 3, pp. 563–568.
Pihalova, L., Macova, S., Haluzova, I., et al., Terbutryn toxicity to Danio rerio: effects of subchronic exposure on fish growth, Neuro Endocrinol. Lett., 2009, vol. 30, suppl. 1, pp. 242–247.
Rypel, A.L. and Bayne, D.R., Do fish growth correlate with PCB body burdens?, Environ. Pollut., 2010, vol. 158, no. 8, pp. 2533–2536.
Saima, Naz., Javed, M., Hayat, S., et al., Long term effects of lead (Pb) on the growth performance, nitrogen conversion ratio and yield of major carps, Pakistan. J. Agri. Sci., 2008, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 53–58.
Sandheinrich, M.B. and Atchison, G.J., Sublethal toxicant effects on fish foraging behavior: empirical vs. mechanical approaches, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 1990, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 107–119.
Sokal, R.R. and Rohlf, F.J., Biometry: The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, New York: W. H. Freeman and Co, 1995.
Tsaij, W. and Liao, C.M., Mode of action and growth toxicity of arsenic to tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus can be determined bioenergetically, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2006, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 144–152.
Vinodhini, R. and Narayanan, M., Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in organs of fresh water fish Cyprinus carpio (common carp), Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 2008, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 179–182.
Voslarova, E., Pistekova, V., Svobodova, Z., and Bedanova, I., Nitrite toxicity to Danio rerio: effects of subchronic exposure on fish growth, Acta. Vet. Brno., 2008, vol. 77, pp. 455–460.
Woltering, D.M., The growth response in fish chronic and early life stage toxicity tests: a critical review, Aquat. Toxicol., 1984, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 1–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.F. Pavlov, G.M. Chuiko, D.D. Pavlov, 2014, published in Biologiya Vnutrennikh Vod, 2014, No. 1, pp. 103–107.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlov, D.F., Chuiko, G.M. & Pavlov, D.D. Growth of mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus Peters) chronically exposed to cadmium, naphthalene, and DDVP. Inland Water Biol 7, 97–100 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082913040135
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082913040135