Abstract
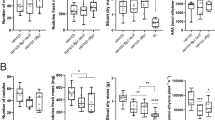
Factor analysis has been conducted for the data on the interaction between the genes of the root nodule bacteria (rhizobia), which influence the efficiency of symbiosis with leguminous plants, including dctA (encoding succinate permease), dctBD (activating the dctA gene due to binding its enhancer in the presence of succinate), rpoN (activating the promoters of dctA and nitrogenase genes nifHDK), and nifA (activating the nitrogenase genes due to binding their enhancers). The analysis of the alfalfa rhizobia (Sinorhizobium meliloti) recombinants that contain additional copies of these genes suggested the antagonistic (epistatic) interaction between nifA and rpoN. It may be associated either with the competition for C compounds imported into the nodules between the energy production and nitrogen assimilation processes or with the competition for redox potentials between the oxidative phosphorylation and nitrogen fixation processes. Since the phenotypic effects of the studied genes depend on the activity of nitrogen export into the aerial parts of plants, we suppose that its accumulation in bacteroids impairs the activation of the nifHDK genes by the NifA protein due to its interaction with the GlnB protein (the nitrogen metabolism regulator) or with the FixLJ and ActSR proteins (the redox potential regulators).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Franche, C., Lindstrom, K., and Elmerich, C., Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria Associated with Leguminous and Non-Leguminous Plants, Plant Soil, 2009, vol. 321, pp. 35–59.
Kretovich, V.L., Biokhimiya usvoeniya azota vozdukha rasteniyami (Biochemistry of the Airborne Nitrogen Assimilation by Plants), Moscow: Nauka, 1994.
Shtark, O.Y., Borisov, A.Y., Zhukov, V.A., et al., Intimate Associations of Beneficial Soil Microbes with Host Plants, Soil Microbiology and Sustainable Crop Production, Dixon, R. and Tilston, E., Eds., Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2010, pp. 119–196.
Fisher, H.M., Genetic Regulation of Nitrogen Fixation in Rhizobia, Microbiol. Rev., 1994, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 352–386.
Kaminski, P., Batut, Zh., and Boistard, P., Control of Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in Rhizobia, Rhizobiaceae: Molekulyarnaya biologiya bakterii, vzaimodeistvuyushchikh s rasteniyami (Rhizobiaceae. Molecular Biology of Model Plant-Associated Bacteria), Spaink, G., Kondoroshi, A., and Khukas, P., Eds., St. Petersburg: Biont, 2002, pp. 465–492.
Bobik, C., Meilhoc, E., and Batut, J., FixJ: A Major Regulator of the Oxygen Limitation Response and Late Symbiotic Functions of Sinorhizobium meliloti, J. Bacteriol., 2006, vol. 188, pp. 4890–4902.
Elsen, S., Swem, L.R., Swem, D.L., and Bauer, C.E., RegB/RegA, a Highly Conserved Redox-Responding Global Two-Component Regulatory System, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2004, vol. 68, no. 2, pp. 263–279.
Arsene, F., Kaminski, P.A., and Elmerich, C., Modulation of NifA Activity by PII in Azospirillum brasilense: Evidence for a Regulatory Role of the NifA N-Terminal Domain, J. Bacteriol., 1996, vol. 178, no. 16, pp. 4830–4838.
Jording, D., Uhde, C., Schmidt, R., and Phler, A., The C4-Dicarboxylate Transport System of Rhizobium meliloti and Its Role in Nitrogen Fixation during Symbiosis with Alfalfa (Medicago sativa), Experientia, 1994, vol. 5, pp. 874–883.
Onishchuk, O.P., Vorob’ev, N.I., Provorov, N.A., and Simarov, B.V., Symbiotic Activity of Alfalfa Rhizobia (Sinorhizobium meliloti) Strains with Genetically Modified Transport of Dicarboxylic Acids, Ekol. Genet., 2009, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 3–10.
Kulaichev, A.P., Metody i sredstva kompleksnogo analiza dannykh (Methods and Facilities of the Complex Data Analysis), Moscow: FORUM—INFRA-M, 2006.
Mironov, A.A., Vinokurova, N.P., and Gelfand, M.S., Software for Analysis of Bacterial Genomes, Mol. Biol., 2000, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 222–231.
Jalovaja (Chuklina), J., Tsoy, O., and Gelfand, M., Comparative-Genomic Reconstruction of the NifA Regulon Evolution in Alphaproteobacteria, Abstracts of Papers, 17th International Nitrogen Fixation Congress, Fremanle, 2011, p. 32.
Drepper, T., Role of GlnB and GlnK in Ammonium Control of Both Nitrogenase Systems in the Phototrophic Bacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus, Microbiology, 2003, vol. 149, no. 8, pp. 2203–2212.
Romanov, V.I., Chetkova, S.A., Tikhonovich, I.A., et al., Nitrogen Fixation in Chlorophyllic Pea Mutants, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1987, vol. 294, no. 5, pp. 1277–1280.
Dombrecht, B., Marchal, K., Vanderleyden, J., and Michiels, J., Prediction and Overview of the RpoN-Regulon in Closely Related Species of the Rhizobiales, Genome Biol., 2002, vol. 3, no. 12, pp. 1–11.
Dixon, R., Austin, S., Eydmann, T., et al., Regulation of Nitrogen Fixation Genes by the NIFA and NIFL Regulatory Proteins, Biological Nitrogen Fixation for Ecology and Sustainable Agriculture, Legocki, A., Bothe, G., and Puhler, A., Eds., NATO ASI Ser., 1997, vol. G29, pp. 245–249.
Prell, J. and Poole, P., Metabolic Changes of Rhizobia in Legume Nodules, Trends Microbiol., 2006, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 161–168.
de Bruijn, F., Chen, R., Fujimoto, S.Y., et al., Regulation of Nodulin Gene Expression, Plant Soil, 1994, vol. 161, pp. 59–68.
Pini, F., Galardini, M., Bazzicalupo, M., and Mengoni, A., Plant-Bacteria Association and Symbiosis: Are There Common Genomic Traits in Alphaproteobacteria?, Genes, 2011, vol. 2, pp. 1017–1032.
Masson-Boivin, C., Giraud, E., Perret, X., and Batut, J., Establishing Nitrogen-Fixing Symbiosis with Legumes: How Many Rhizobium Species?, Trends Microbiol., 2009, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 458–466.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.A. Provorov, J. Chuklina, N.I. Vorobyov, O.P. Onishchuk, B.V. Simarov, 2013, published in Genetika, 2013, Vol. 49, No. 4, pp. 448–453.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Provorov, N.A., Chuklina, J., Vorobyov, N.I. et al. Factor analysis of interactions between alfalfa nodule bacteria (Sinorhizobium meliloti) genes that regulate symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Russ J Genet 49, 388–393 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795413030150
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795413030150