Abstract
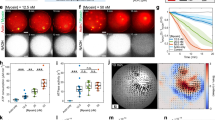
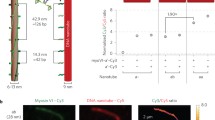
We introduce here an ATP (adenosine triphosphate)-fueled nano-biomachine constructed from actin and myosin gels. Various types of chemically cross-linked actin gel, which are tens of times larger in size than native actin filaments (F-actin), were formed by complexing with cation-polymers and placed on a chemically cross-linked myosin gel. By adding dilute solution of ATP, they moved along the myosin gel with a velocity as high as that of native F-actin by coupling to ATP hydrolysis. Formation mechanism and structure of actin complexes as well as those of myosin gels were studied in detail and elucidated with the specific characteristics of the motility. These results demonstrate that one can construct nano-biomachines fueled by chemical energy of ATP with controlled motility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. E. Huxley, Science (Washington, D. C.) 164, 1356 (1969).
A. F. Huxley, Reflections on Muscle (Liverpool Univ. Press, Liverpool, 1980).
G. H. Pollack, Cells, Gels and the Engines of Life (Ebner, Seattle, 2001).
K. Kitamura, M. Tokunaga, A. H. Iwane, and T. Yanagida, Nature (London) 397, 129 (1999).
Y. Osada, H. Okuzaki, and H. Hori, Nature (London) 355, 242 (1992).
T. Mitsumata, K. Ikeda, J. P. Gong, and Y. Osada, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2366 (1998).
Y. Osada and A. Matsuda, Nature (London) 376, 219 (1995).
Y. Osada and S. B. Ross-Murphy, Sci. Am. 268, 82 (1993).
E. W. H. Jager, E. Smela, and O. Inganas, Science (Washington, D. C.) 290, 1540 (2000).
D. J. Beebe, J. S. Moore, J. M. Bauer, et al., Nature (London) 404, 588 (2000).
S. R. Quake and A. Scherer, Science (Washington, D. C.) 290, 1536 (2000).
A. Kakugo, S. Sugimoto, J.P. Gong, and Y. Osada, Adv. Mater. (Weinheim, Fed. Repub. Ger.) 14, 1124 (2002).
A. Kakugo, K. Shikinaka, K. Matsumoto, et al., Bioconjugate Chem. 14, 1185 (2003).
A. Kakugo, S. Sugimoto, K. Shikinaka, et al., J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed. 16, 203 (2005).
A. Kakugo, K. Shikinaka, N. Takekawa, et al., Biomacromolecules 6, 845 (2005).
K. Hayakawa, J. P. Santerre, and J. C. Kwak, Macromolecules 16, 1642 (1983).
J. P. Gong, T. Mizutani, and Y. Osada, Polym. Adv. Technol. 7, 797 (1996).
I. Satake and J. T. Yang, Biopolymers 15, 2263 (1976).
H. J. Kwon, A. Kakugo, K. Shikinaka, et al., Biomacromolecules 6, 3005 (2005).
J. Howard, Mechanics of Motor Proteins and the Cytoskeleton (Sinauer, Massachusetts, 2001).
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshitz, Theory of Elasticity (Nauka, Moscow, Pergamon, Oxford, 1986).
K. Shikinaka, H.J. Kwon, A. Kakugo, et al., Biomacromolecules 9, 537 (2008).
H. J. Kwon, Y. Tanaka, A. Kakugo, et al., Biochemistry 45, 10313 (2006).
H. J. Kwon, A. Kakugo, T. Ura, et al., Langmuir 23, 6257 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The text was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osada, Y., Gong, J.P. Nano-biomachine from actin and myosin gels. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 51, 689–700 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X09060145
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X09060145