Abstract
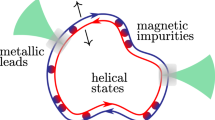
We study theoretically helical edge states of 2D and 3D topological insulators (TI) tunnel-coupled to metal leads and show that their transport properties are strongly affected by contacts as the latter play a role of a heat bath and induce damping and relaxation of electrons in the helical states of TI. A simple structure that produces a pure spin current in the external circuit is proposed. The current and spin current delivered to the external circuit depend on relation between characteristic lengths: damping length due to tunneling, contact length and, in case of 3D TI, mean free path and spin relaxation length caused by momentum scattering. If the damping length due to tunneling is the smallest one, then the electric and spin currents are proportional to the conductance quantum in 2D TI, and to the conductance quantum multiplied by the ratio of the contact width to the Fermi wavelength in 3D TI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Pesin and A. H. MacDonald, Nature Mater. 11, 409 (2012).
S. Modak, K. Sengupta, and D. Sen, Phys. Rev. B 86, 205114 (2012).
C. Brüne, A. Roth, H. Buhmann, et al., Nature Phys. 8, 485 (2012).
A. A. Sukhanov and V. A. Sablikov, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 24, 405301 (2012).
T. Pareek, Phys. Rev Lett. 92, 76601 (2004).
F. Dolcini, Phys. Rev. B 83, 165304 (2011).
M. König, H. Buhmann, L. W. Molenkamp, et al., J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 77, 031007 (2008).
H. Zhang, C.-X. Lium, X.-L. Qi, et al., Nature Phys. 5, 438 (2009).
M. Z. Hasan and C. L. Kane, Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 3045 (2010).
L. V. Keldysh, Sov. Phys. JETP 20, 1018 (1965).
N. B. Kopnin and A. S. Melnikov, Phys. Rev. B 84, 064524 (2011).
T. D. Stanescu and S. Tewari, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 25, 233201 (2013).
P. G. Silvestrov, P. W. Brouwer, and E. G. Mishchenko, Phys. Rev. B 86, 075302 (2012).
P. Schwab, R. Raimondi, and C. Gorini, Europhys. Lett. 93, 67004 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aseev, P.P., Artemenko, S.N. Spin injection from topological insulator tunnel-coupled to metallic leads. Jetp Lett. 98, 285–288 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364013180045
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364013180045