Abstract
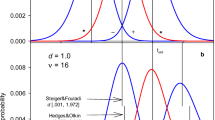
Approximative confidence intervals for a common standardized mean difference from a series of independent experiments are reasonably accurate when effect sizes are less than 1.5 in absolute magnitude and the sample sizes in each group are at least 10. In this article, we derive an exact confidence interval for this effect size where the bounds have to be determined by solving nonlinear equations. As a by-product, we obtain a median unbiased estimator of the common effect size.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Hartung, J., and G. Knapp. 2001. On tests of the overall treatment effect in the meta-analysis with normally distributed responses. Statistics in Medicine 20:1771–82.
Hartung, J., and G. Knapp. 2011. Statistical inference in adaptive group sequential trials with the standardized mean difference as effect size. Sequential Analysis 30:94–113.
Hartung, J., G. Knapp, and B.K. Sinha. 2008. Statistical meta-analysis with applications. New York NY: Wiley.
Hedges, L. V. 1981. Distribution theory for Glass’s estimator of effect size and related estimators. Journal of Educational Statistics 6:107–28.
Hedges, L. V., and I. Olkin. 1985. Statistical methods for meta-analysis. Boston MA: Academic Press.
Hollands, G. J., I. Shemilt, T. M. Marteau, S. A. Jebb, H. B. Lewis, Y. Wei, J. P. T. Higgins, D. Ogilvie. 2015. Portion, package or tableware size for changing selection and consumption of food, alcohol and tobacco. Database of Systematic Reviews 14(9):CD011045. doi:10.1002/14651858. CD011045.pub2.
R Development Core Team. 2016. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. https://doi.org/www.R-project.org/.
Singh, K., M. Xie, and W. E. Strawderman. 2005. Combining information from independent sources through confidence distributions. Annals of Statistics 33:159–83.
Veroniki, Α. Α., D. Jackson, W. Viechtbauer, R. Bender, J. Bowden, G. Knapp, O. Kuß, J.P.T. Higgins, D. Langan, and G. Salanti. 2016. Methods to estimate the between-study variance and its uncertainty in meta-analysis. Research Synthesis Methods 7:55–79.
Wiksten, Α., G. Rücker, and G. Schwarzer. 2016. Hartung-Knapp method is not always conservative compared with fixed-effect meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine 35:2503–515.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knapp, G. An exact confidence interval for a common effect size. J Stat Theory Pract 12, 3–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/15598608.2016.1278060
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15598608.2016.1278060
Keywords
- Meta-analysis
- parameterized p value
- standardized difference of normal means
- homogeneity of effect sizes