Abstract
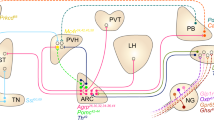
The hypothalamus is a region of the brain that plays a critical role in feeding regulation. It has been revealed by various physiological experiments that the feeding-regulating center is confined to the ventromedial hypothalamus, lateral hypothalamus (LH) and arcuate nucleus (ARC). Many kinds of neurons in these areas of the hypothalamus express factors such as melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), neuropeptide Y (NPY), proopiomelanocortin (POMC), orexin (OX) and ghrelin, which have been implicated in feeding regulation. In tissues of the periphery, two critical factors involved in feeding regulation, leptin and ghrelin, have been identified. Both hormone peptides are secreted mainly from adipose and stomach tissue, respectively, and are considered to function via their receptors mainly through several hypothalamic nuclei that play important roles in the regulation of appetite. The present review looks mainly at the functional significance of feeding-regulation factors, such as those described above, and the humoral and neuronal interactions among these compounds in the hypothalamus by drawing on published reports of morphological and physiological analyses. Immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization experiments indicate that both leptin and ghrelin receptors are distributed in the hypothalamus and that there are reciprocal interactions between MCH and OX neurons in the LH. Morphological and physiological studies on single living cells isolated from fresh rat hypothalamus or with receptor agonist and antagonist combined with immunohistochemisry clearly demonstrate that both leptin and OX reciprocally regulate NPY- and POMC-containing neurons in the ARC and that ghrelin may regulate feeding status independently through direct OX and NPY pathways. In this way, cross-talking systems in the hypothalamus play a role in determining feeding states.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen YS, Adrian TE, Allen JM et al. (1983) Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science 221, 877–9.
Anand BK, Brobeck JR (1951) Localization of a ‘feeding center’ in the hypothalamus of the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 77, 323–4.
Ariyasu H, Tanaka K, Tagami T et al. (2001) Stomach is a major source of circulating ghrelin, and feeding state determines plasma ghrelin-like immunoreactivity levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86, 4753–8.
Asakawa A, Inui A, Kaga T et al. (2001) Ghrelin is an appetite-stimulatory signal from stomach with structural resemblance to motilin. Gastroenterology 120, 337–45.
Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Huang W, Jaspan JB, Maness LM (1996) Leptin enters the brain by a saturable system independent of insulin. Peptides 17, 305–11.
Banks WA, Tschöp M, Robinson SM, Heiman ML (2002) Extent and direction of ghrelin transport across the blood-brain barrier is determined by its unique primary structure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302, 822–7.
Baskin DG, Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ et al. (1999) Leptin receptor long-form splice-variant protein expression in neuron cell bodies of the brain and co-localozation with neuropeptide Y mRNA in the arcuate nucleus. J Histochem Cytochem 47, 353–62.
Beck B, Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Burlet A, Chapleur-Chateau M, Leibowitz SF, Burlet C (1990) Rapid and localized alterations of neuropeptide Y in discrete hypothalamic nuclei with feeding status. Brain Res 528, 245–9.
Bittencourt JC, Presse F, Arias C et al. (1992) The melanin-concentrating hormone system of the rat brain: An immuno and hibridization histochemical characterization. J Comp Neurol 319, 218–45.
Blevins JE, Schwartz MW, Baskin DG (2002) Peptide signals regulating food intake and energy homeostasis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 80, 396–406.
Blomqvist AG, Herzog H (1997) Y-receptor subtypes: How many more? Trends Neurosci 20, 294–8.
Broberger C, Landry M, Wong H, Walsh JN, Hokfelt T (1997) Subtypes Y1 and Y2 of the neuropeptide Y receptor are respectively expressed in pro-opiomelanocortin- and neuropeptide-Y-containing neurons of the rat hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. Neuroendocrinology 66, 393–408.
Broberger C, Johansen J, Schalling M, Hokfelt T (1998) The neuropeptide Y/agouti gene-related protein (AGRP) brain circuitry in normal, anoretic, and monosodium glutamate-treated mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 15043–8.
Campfield LA, Smith FJ, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P (1995) Recombinant mouse OB protein: Evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science 269, 546–9.
Casanueva FF, Dieguez C (1999) Neuroendocrine regulation and actions of leptin. Front Neuroendocrinol 20, 317–63.
Chen H, Charlat O, Tartaglia LA et al. (1996) Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: Identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice. Cell 84, 491–5.
Chronwall BM, DiMaggio DK, Massari VJ, Pickel VM, Ruggiero DA, O’Donohue TL (1985) The anatomy of neuropeptide Y neurons in rat brain. Neuroscience 15, 1159–81.
Clark JT, Kalra PS, Crowley WR, Kalra SP (1984) Neuropeptide Y and human pancreatic polypeptide stimulate feeding behavior in rats. Endocrinology 115, 427–9.
Clement K, Vaisse C, Lahlou N et al. (1998) A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary dysfunction. Nature 392, 398–401.
Cochet M, Chang AC, Cohen SN (1982) Characterization of the structural gene and putative 5’-regulatory sequences for human melanocortin. Nature 297, 335–9.
Coleman DL (1978) Obese and diabetes: Two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia 14, 141–8.
Coleman DL, Hummel KP (1969) Effects of parabiosis of normal with genetically diabetic mice. Am J Physiol 217, 1298–304.
Couce ME, Burguera B, Parisi JE, Jensen MD, Lloyd RV (1997) Localization of leptin receptor in the human brain. Neuroendocrinology 66, 145–50.
Date Y, Ueta Y, Yamashita H et al. (1999) Orexins, orexigenic hypothalamic peptides, interact with autonomic, neuroendocrine and neuroregulatory systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96, 748–53.
Date Y, Mondel MS, Matsukura S et al. (2000a) Distribution of orexin/hypocretin in the rat median eminence and pituitary. Mol Brain Res 76, 1–6.
Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H et al. (2000b) Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology 141, 4255–61.
Date Y, Murakami N, Kojima M et al. (2000c) Central effects of a novel acylated peptide, ghrelin, on growth hormone release in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275, 477–80.
Date Y, Murakami N, Toshinai K et al. (2002) The role of the gastric afferent vagal nerve in ghrelin-induced feeding and growth hormone secretion. Gastroenterology 123, 1120–8.
Date Y, Nakazato M, Murakami N, Kojima K, Matsukura S (2001) Ghrelin acts in the central nervous system to stimulate gastric acid secretion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 280, 904–7.
De Lecca L, Kilduff TS, Peyrin C et al. (1998) The hypocretins: Hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 322–7.
Della-Zuana O, Presse F, Ortola C, Duhault J, Nahon JL, Levens N (2002) Acute and chronic administration of melanin-concentrating hormone enhances food intake and body weight in Wistar and Sprague-Dawley rats. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 26, 1289–95.
Elias CF, Lee C, Kelly J et al. (1998a) Leptin activates hypothalamic CART neurons projecting to the spinal cord. Neuron 21, 1375–85.
Elias CF, Saper CB, Maratos-Flier E et al. (1998b) Leptin activates distinct projections from the dorsomedial and ventromedial hypothalamic nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 741–6.
Elias CF, Saper CB, Maratos-Flier E et al. (1998c) Chemically defined projections linking the mediobasal hypothalamus and the lateral hypothalamic area. J Comp Neurol 402, 442–59.
Elmquist JK, Elias CF, Saper CB (1999) From lesions to leptin: Hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron 22, 221–32.
Fan W, Boston BA, Kesterson RA, Hruby VJ, Cone RD (1997) Role of melanocortinergic neurons in feeding and the agouti obesity syndrome. Nature 385, 165–8.
Friedman JM, Halaas JL (1998) Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 395, 763–70.
Funahashi H, Yada T, Muroya S et al. (1999) The effect of leptin on feeding-regulating neurons in the rat hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett 264, 117–20.
Funahashi H, Hori T, Shimoda Y et al. (2000) Morphological evidence for neural interactions between leptin and orexin in the hypothalamus. Regul Pept 92, 31–5.
Funahashi H, Yamada S, Kageyama H, Takenoya F, Guan JL, Shioda S (2003) Co-existence of leptin- and orexin-receptors in feeding-regulating neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: A triple labeling study. Peptides (in press).
Ghilardi N, Skoda RC (1997) The leptin receptor activates janus kinase 2 and signals for proliferation in a factor-dependent cell line. Mol Endocrinol 11, 393–9.
Ghilardi N, Ziegler S, Wiestner A, Stoffel R, Heim MH, Skoda RC (1996) Defective STAT signaling by the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 6231–5.
Gold RM (1973) Hypothalamic obesity: The myth of the ventro-medial nucleus. Science 182, 488–90.
Guan XM, Yu H, Palyha OC, McKee KK et al. (1997) Distribution of mRNA encoding the growth hormone secretagogue receptor in brain and peripheral tissues. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 48, 23–9.
Guan JL, Saotome T, Wang QP et al. (2001) Orexinergic innervation of POMC-containing neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus. Neuroreport 12, 547–51.
Guan JL, Suzuki R, Funahashi H et al. (2002a) Ultrastructural localization of orexin-1 receptor in pre- and post-synaptic neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus. Neurosci Lett 329, 209–12.
Guan JL, Uehara K, Lu S et al. (2002b) Reciprocal synaptic relationships between orexin- and melanin-concentrating hormone-containing neurons in the rat lateral hypothalamus: A novel circuit implicated in feeding regulation. Int J Obesity 26, 1523–32.
Gundlach AL (2002) Galanin/GALP and galanin receptors: Role in central control of feeding, body weight/obesity and reproduction? Eur J Pharmacol 440, 255–68.
Håkansson ML, Brown H, Ghilardi N, Skoda RC, Meister B (1998) Leptin receptor immunoreactivity in chemically defined target neurons of the hypothalamus. J Neurosci 18, 559–72.
Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M et al. (1995) Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 269, 543–6.
Hamilton BS, Paglia D, Kwan AY, Deitel M (1995) Increased obese mRNA expression in omental fat cells from massively obese humans. Nat Med 1, 953–6.
Haynes AC, Jackson B, Chapman H et al. (2000) A selective orexin-1 receptor antagonist reduces food consumption in male and female rats. Regul Pept 22, 45–51.
Heinrichs SC, Menzaghi F, Pich EM, Hauger RL, Koob GF (1993) Corticotropin-releasing factor in the paraventricular nucleus modulates feeding induced by neuropeptide ay. Brain Res 611, 18–24.
Hervieu GJ, Cluderay DC, Harrison JC, Leslie RA (2001) Gene expression and protein distribution of the orexin-1 receptor in the rat brain spinal cord. Neuroscience 103, 777–97.
Horvath T, Diano S, Anthony N, van den Pol AN (1999) Synaptic interaction between hypocretin (orexin) and neuropeptide Y cells in the rodent and primate hypothalamus: A novel circuit implicated in metabolic and endocrine regulations. J Neurosci 19, 1072–87.
Huszar D, Lynch CA, Fairchilled-Huntress V et al. (1998) Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell 88, 131–41.
Ingalls AM, Dickie MM, Snell GD (1950) Obese, a new mutation in the house mouse. J Hered 41, 317–18.
Iqbal J, Pompolo S, Murakami T, Clarke IJ (2000) Localization of long-form leptin receptor in the somatostatin-containing neurons in the sheep hypothalamus. Brain Res 887, 1–6.
Iqbal J, Pompolo S, Murakami T et al. (2001) Immunohisto-chemical characterization of localization of long-form leptin receptor (OB-Rb) in the ovine hypothalamus. Brain Res 920, 55–64.
Jaccobowitz DM, O’Donohue TL (1978) Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone: Immunohistochemical identification and mapping in neurons of rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75, 6300–4.
Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Beck B, Jhanwar YS, Burlet C, Leibowitz SF (1993) Neuropeptide Y projection from arcuate nucleus to parvocellular division of paraventricular nucleus: Specific relation to the ingestion of carbohydrate. Brain Res 631, 97–106.
Jolicoeur FB, Michaud JN, Rivest R et al. (1991) Neurobehavioral profile of neuropeptide Y. Brain Res Bull 26, 265–8.
Jureus A, Cunningham MJ, McClain ME, Cliton DK, Steiner RA (2000) Galanin-like peptide (GALP) is a target for regulation by leptin in the hypothalamus of the rat. Endocrinology 141, 2703–6.
Kalra SP, Dube MG, Kalra PS (1988) Continuous intraventricular infusion of neuropeptide Y evokes episodic food intake in satiated female rats: Effects of adrenalectomy and cholecytokinin. Peptides 9, 723–8.
Kamegai J, Tamura H, Shimizu T, Ishii S, Sugihara H, Wakabayashi I (2001) Chronic central infusion of ghrelin increases hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and agouti-related protein mRNA levels and body weight in rats. Diabetes 50, 2438–43.
Kawauchi H, Kawazoe I, Tsubokawa M, Kishida M, Baker BI (1983) Characterization of melanin-concentrating hormone in chum salmon pituitaries. Nature 305, 321–3.
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kanagawa K (1999) Ghrelin is a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402, 656–60.
Kristensen P, Judge ME, Thim L et al. (1998) Hypothalamic CART is a new anorectic peptide regulated by leptin. Nature 393, 72–6.
Lawrence CB, Baudoin FM, Luckman SM (2002a) Centrally administered galanin-like peptide modifies food intake in the rat: A comparison with galanin. J Neuroendocrinol 14, 853–60.
Lawrence CB, Snape AC, Baudoin FM, Luckman SM (2002b) Acute central ghrelin and GH secretagogues induce feeding and activate brain appetite centers. Endocrinology 143, 155–62.
Lee GH, Proenca R, Montez JM et al. (1996) Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature 379, 632–5.
Leibowitz SF, Sladek C, Spencer L, Tempel D (1988) Neuropeptide Y, epinephrine and norepinephrine in the paraventricular nucleus: Stimulation of feeding and the release of corticosterone, vasopressin and glucose. Brain Res Bull 21, 905–12.
Lollmann B, Gruninger S, Stricker-Krongrad A, Chiesi M (1997) Detection and quantification of the leptin receptor splice variants Ob-Ra, b, and e in different mouse tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 238, 648–52.
Lu S, Guan JL, Wang QP et al. (2002) Immunohistochemical observation of ghrelin-containing neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus. Neurosci Lett 321, 157–60.
Ludwig DS, Mountjoy KG, Tatro JB et al. (1998) Melanin-concentrating hormone: A functional melanocortin antagonist in the hypothalamus. Am J Physiol 274, E627–33.
Ludwig DS, Tritos NA, Mastaitis JW et al. (2001) Melanin-concentrating hormone overexpression in transgenic mice leads to obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 107, 379–86.
Marcus JN, Aschkenasi CJ, Lee CE et al. (2001) Differential expression of orexin receptors 1 and 2 in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 435, 6–15.
Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Isse N et al. (1995a) Human obese gene expression. Adipocyte-specific expression and regional differences in the adipose tissue. Diabetes 44, 855–8.
Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Hosoda K, Kawada T, Fushiki T, Nakao K (1995b) Augmented expression of the obese gene in the adipose tissue from rats fed high-fat diet. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 216, 355–8.
Matsumoto Y, Watanabe T, Adachi Y et al. (2002) Galanin-like peptide stimulates food intake in the rat. Neurosci Lett 322, 67–9.
McCowen KC, Chow JC, Smith RJ (1998) Leptin signaling in the hypothalamus of normal rats in vivo. Endocrinology 139, 4442–7.
Mercer JG, Hoggard N, Williams LM et al. (1996) Coexpression of leptin receptor and preproneuropeptide Y mRNA in arcuate nucleus of mouse hypothalamus. J Neuroendocrinol 8, 733–5.
Mercer JG, Moar KM, Hoggard N (1998a) Localization of leptin receptor (Ob-R) messenger ribonucleic acid in the rodent hindbrain. Endocrinology 139, 29–34.
Mercer JG, Moar KM, Findlay PA, Hoggard N, Adam CL (1998b) Association of leptin receptor (OB-Rb), NPY and GLP-1 gene expression in the ovine and murine brainstem. Regul Pept 75-76, 271–8.
Michel MC, Beck-Sickinger A, Cox H et al. (1998) XVI International Union of Pharmacology recommendations for the nomenclature of neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide receptors. Pharmacol Rev 50, 143–50.
Mitchell V, Bouret S, Beauvillain JC et al. (2001) Comparative distribution of mRNA encoding the growth hormone secretagogue-receptor (GHS-R) in Microcebus murinus (Primate, lemurian) and rat forebrain and pituitary. J Comp Neurol 429, 469–85.
Morley JE, Levine AS, Gosnell BA, Kneip J, Grace M (1987) Effect of neuropeptide Y on ingestive behaviors in the rat. Am J Physiol 252, R599–609.
Muroya S, Yada T, Shioda S, Takigawa M (1999) Glucose-sensitive neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus contain neu-ropeptide Y. Neurosci Lett 264, 113–16.
Nagatani S, Guthikonda P, Thompson RC, Tsukamura H, Maeda KI, Foster DL (1998) Evidence for GnRH regulation by leptin: Leptin administration prevents reduced pulsatile LH secretion during fasting. Neuroendocrinology 67, 370–6.
Nakazato M, Murakami N, Date Y et al. (2001) A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 409, 194–8.
Nambu T, Sakurai T, Mizukami K, Hosoya Y, Yanagisawa M, Goto K (1999) Distribution of orexin neurons in the adult rat brain. Brain Res 827, 243–60.
Ohtaki T, Kumano S, Ishibashi Y et al. (1999) Isolation and cDNA cloning of a novel galanin-like peptide (GALP) from porcine hypothalamus. J Biol Chem 274, 37 041–5.
Ollmann MM, Wilson BD, Yang YK et al. (1997) Antagonism of central melanocortin receptors in vitro and in vivo by agouti-related protein. Science 278, 135–8.
Olney JW (1969) Brain lesions, obesity, and other disturbances in mice treated with monosodium glutamate. Science 164, 719–21.
Oomura Y, Yoshimatsu H (1984) Neural network of glucose monitoring system. J Auton Nerv Syst 10, 359–72.
Oomura Y, Ono T, Ooyama H, Wayner MJÅ, (1969) Glucose and osmosensitive neurons of the rat hypothalamus. Nature 222, 282–4.
Oomura Y, Ooyama H, Sugimori M, Nakamura T, Yamada Y (1974) Glucose inhibition of the glucose-sensitive neuron in the rat lateral hypothalamus. Nature 247, 284–6.
Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB et al. (1995) Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science 269, 540–3.
Poggioli R, Vergoni AV, Bertolini A (1986) ACTH(1-24) and alpha-MSH antagonize feeding behavior stimulated by kappa opiate agonists. Peptides 7, 843–8.
Qu D, Ludwig DS, Gammeltoft S et al. (1996) A role of melanin-concentrating hormone in the central regulation of feeding behavior. Nature 380, 243–7.
Rossi M, Choi SJ, O’Shea D, Miyoshi T, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (1997) Melanin-concentrating hormone acutely stimulates feeding, but chronic administration has no effect on body weight. Endocrinology 138, 351–5.
Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M et al. (1998) Orexins and orexin receptors: A family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 92, 573–85.
Saladin R, De Vos P, Guerre-Millo M et al. (1995) Transient increase in obese gene expression after food intake or insulin administration. Nature 377, 527–9.
Schwartz MW, Baskin DG, Bukowski TR et al. (1996) Specificity of leptin action on elevated blood glucose levels and hypothalamic neuropeptide Y gene expression in ob/ob mice. Diabetes 45, 531–5.
Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ, Woods SC et al. (1997) Leptin increases hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin mRNA expression in the rostral arcuate nucleus. Diabetes 46, 2119–23.
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte Jr D, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG (2000) Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404, 661–71.
Shaver SW, Pang JJ, Wainman DS, Wall KM, Gross PM (1992) Morphology and function of capillary networks in subregions of the rat tuber cinereum. Cell Tissue Res 267, 437–48.
Shibasaki T, Oda T, Imaki T, Ling N, Demura H (1993) Injection of anti-neuropeptide Y γ-globulin into hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus decreases food intake in rats. Brain Res 601, 313–16.
Shimada M, Tritos NA, Lowell BB, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E (1998) Mice lacking melanin-concentrating hormone are hypophagic and lean. Nature 396, 670–4.
Shintani M, Ogawa Y, Ebihara K et al. (2001) Ghrelin, an endogenous growth hormone secretagogue, is a novel orexigenic peptide that antagonizes leptin action through the activation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y/Y1 receptor pathway. Diabetes 50, 227–32.
Shioda S, Funahashi H, Nakajo S, Yada T, Maruta O, Nakai Y (1998) Immunohistochemical localization of leptin receptor in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 243, 41–4.
Stanley BG, Leibowitz SF (1984) Neuropeptide Y injected in the paraventricular hypothalamus: A powerful stimulant of feeding behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82, 3940–3.
Stellar E (1954) The physiology of motivation. Psychol Rev 101, 301–11.
Stephens TW, Basinski M, Bristow PK et al. (1995) The role of neuropeptide Y in the antiobesity action of the obese gene product. Nature 377, 530–2.
Stunkard AJ, Harris JR, Pedersen NL, McClearn GE (1990) The body-mass index of twins who have been reared apart. N Engl J Med 322, 1483–7.
Suzuki R, Shimojima H, Funahashi H et al. (2002) Orexin-1 receptor in chemically identified target neurons in the rat hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett 324, 5–8.
Takatsu Y, Matsumoto H, Ohtaki T et al. (2001) Distribition of galanin-like peptide in the rat brain. Endocrinology 142, 1626–34.
Takenoya F, Funahashi H, Matsumoto H et al. (2002) Galanin-like peptide is co-localized with α-melanocyte stimulating hormone but not with neuropeptide Y in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 331, 119–22.
Takenoya F, Aihara K, Funahashi H et al. (2003) Galanin-like peptide is target for regulation by orexin in the rat hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett 340, 209–12.
Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X et al. (1995) Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell 83, 1263–71.
Tatemoto K, Carlquist M, Mutt V (1982) Neuropeptide Y, a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature 296, 659–60.
Toshinai K, Date Y, Murakami N et al. (2003) Ghrelin-induced food intake is mediated via the orexin pathway. Endocrinology 144, 1506–12.
Trivedi P, Yu H, MacNeil DJ, Van der Ploeg LH, Guan XM (1998) Distribution of orexin receptor mRNA in the rat brain. FEBS Lett 438, 72–5.
Tschöp M, Smiley DL, Heiman M (2000) Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 407, 908–13.
Tschöp M, Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Devanarayan V, Ravussin E, Heiman ML (2001) Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes 50, 707–9.
Vaisse C, Halaas JL, Horvath CM, Darnell JE, Stoffel M, Friedman JM (1996) Leptin activation of Stat3 in the hypothalamus of wild-type and ob/ob mice but not db/db mice. Nat Genet 14, 95–7.
Wabitsch M, Jensen PB, Blum WF et al. (1996) Insulin and cortisol promote leptin production in cultured human fat cells. Diabetes 45, 1435–8.
Wren AM, Small CJ, Ward HL et al. (2000) The novel hypothalamic peptide ghrelin stimulates food intake and growth hormone secretion. Endocrinology 141, 4325–8.
Wren AM, Small CJ, Abbott CR et al. (2001) Ghrelin causes hyperphagia and obesity in rats. Diabetes 50, 2540–7.
Yamanaka A, Kunii K, Nambu T et al. (2000) Orexin-induced food intake involves neuropeptide Y pathway. Brain Res 859, 404–9.
Yamanaka A, Tsujino N, Funahashi H et al. (2002) Orexins activate histaminergic neurons via orexin 2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290, 1237–45.
Yarnell DO, Knight DS, Hamilton K, Tulp O, Tso P (1998) Localization of leptin receptor immunoreactivity in the lean and obese Zucker rat brain. Brain Res 85, 80–90.
Zamir N, Skofitsch G, Bannon MJ, Jacobowitz DM (1986a) Melanin-concentrating hormone: Unique peptide neuronal system in the rat brain and pituitary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83, 1528–31.
Zamir N, Skofitsch G, Jacobowitz DM (1986b) Distribution of immunoreactive melanin-concentrating hormone in the central nervous system of the rat. Brain Res 373, 240–5.
Zarjevski N, Cusin I, Vettor R, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Jeanrenaud B (1993) Chronic intracerebroventricular neuropeptide-Y administration to normal rats mimics hormonal and metabolic changes of obesity. Endocrinology 133, 1753–8.
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM (1994) Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372, 425–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Funahashi, H., Takenoya, F., Guan, JL. et al. Hypothalamic neuronal networks and feeding-related peptides involved in the regulation of feeding. Anato Sci Int 78, 123–138 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0022-7722.2003.00055.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0022-7722.2003.00055.x