Abstract
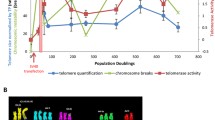
Some immortalized cell lines maintain their telomeres in the absence of detectable telomerase activity by an alternative (ALT) mechanism. To study how telomere maintenance is controlled in ALT cells, we have fused an ALT cell line GM847 (SV40 immortalized human skin fibroblasts) with normal fibroblasts or with telomerase positive immortal human cell lines and have examined their proliferative potential and telomere dynamics. The telomeres in ALT cells are characteristically very heterogeneous in length, ranging from very short to very long. The ALT×normal hybrids underwent a rapid reduction in telomeric DNA and entered a senescence-like state. Immortal segregants rapidly reverted to the ALT telomere phenotype. Fusion of ALT cells to telomerase-positive immortal cells in the same immortalization complementation group resulted in hybrids that appeared immortal and also exhibited repression of the ALT telomere phenotype. In these hybrids, which were all telomerase-positive, we observed an initial rapid loss of most long telomeres, followed either by gradual loss of the remaining long telomeres at a rate similar to the rate of telomere shortening in normal telomerase-negative cells, or by maintenance of shortened telomeres. These data indicate the existence of a mechanism of rapid telomere deletion in human cells. They also demonstrate that normal cells and at least some telomerase-positive immortal cells contain repressors of the ALT telomere phenotype.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allsopp RC, Vaziri H, Patterson C, Goldstein S, Younglai EV, Futcher AB, Greider CW and Harley CB. . 1992 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 10114–10118.
Allsopp RC and Harley CB. . 1995 Exp. Cell Res. 219: 130–136.
Bacchetti S and Counter CM. . 1995 Int. J. Oncol. 7: 423–432.
Blackburn EH. . 1991 Nature 350: 569–573.
Bryan TM, Englezou A, Gupta J, Bacchetti S and Reddel RR. . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 4240–4248.
Bryan TM, Englezou A, Dalla-Pozza L, Dunham MA and Reddel RR. . 1997 Nat. Med. 3: 1271–1274.
Bryan TM and Reddel RR. . 1997 Eur. J. Cancer 33A: 767–773.
Bryan TM, Englezou A, Dunham MA and Reddel RR. . 1998 Exp. Cell Res. 239: 370–378.
Bryan TM and Reddel RR. . 1994 Crit. Rev. Oncogenesis 5: 331–357.
Bunn CL and Tarrant GM. . 1980 Exp. Cell Res. 127: 385–396.
Cooke HJ and Smith BA. . 1986 Cold. Spring. Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 51: 213–219.
Greider CW and Blackburn EH. . 1985 Cell 43: 405–413.
Harley CB, Futcher AB and Greider CW. . 1990 Nature 345: 458–460.
Hastie ND, Dempster M, Dunlop MG, Thompson AM, Green DK and Allshire RC. . 1990 Nature 346: 866–868.
Jones CJ, Soley A, Skinner JW, Gupta J, Haughton MF, Wyllie FS, Schlumberger M, Bacchetti S and Wynford-Thomas D. . 1998 Exp. Cell Res. 240: 333–339.
Katoh M, Katoh M, Kameyana M, Kugoh H, Shimizu M and Oshimura M. . 1998 Mol. Carcinog. 21: 17–25.
Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley CB, West MD, Ho PLC, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL and Shay JW. . 1994 Science 266: 2011–2015.
Levy MZ, Allsopp RC, Futcher AB, Greider CW and Harley CB. . 1992 J. Mol. Biol. 225: 951–960.
Li B and Lustig AJ. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 1310–1326.
Lindsey J, McGill NI, Lindsey LA, Green DK and Cooke HJ. . 1991 Mutat. Res. 256: 45–48.
Lundblad V and Blackburn EH. . 1993 Cell 73: 347–360.
Makarov VL, Hirose Y and Langmore JP. . 1997 Cell 88: 657–666.
McEachern MJ and Blackburn EH. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 1822–1834.
McElligott R and Wellinger RJ. . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 3705–3714.
Moy EL, Duncan EL, Hukku B and Reddel R. . 1997 Exp. Gerontol. 32: 663–670.
Muggleton-Harris AL and DeSimone DW. . 1980 Somatic Cell Genet. 6: 689–698.
Murnane JP, Sabatier L, Marder BA and Morgan WF. . 1994 EMBO J. 13: 4953–4962.
Nakabayashi K, Ogata T, Fujii M, Tahara H, Ide T, Wadhwa R, Kaul SC, Mitsui Y and Ayusawa D. . 1997 Exp. Cell Res. 235: 345–353.
Ogata T, Ayusawa D, Namba M, Takahashi E, Oshimura M and Oishi M. . 1993 Mol. Cell. Biol. 13: 6036–6043.
Ogata T, Oshimura M, Namba M, Fujii M, Oishi M and Ayusawa D. . 1995 Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 86: 35–40.
Olovnikov AM. . 1971 Doklady Akademii Nauk SSR 201: 1496–1499.
Pereira-Smith OM and Smith JR. . 1983 Science 221: 964–966.
Pereira-Smith OM and Smith JR. . 1988 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 6042–6046.
Reddel R. . 1998 BioEssays 20: 977–984.
Rogan EM, Bryan TM, Hukku B, Maclean K, Chang AC-M, Moy EL, Englezou A, Warneford SG, Dalla-Pozza L and Reddel RR. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 4745–4753.
Shore D. . 1997 Trends Biochem. Sci. 22: 233–235.
Watson JD. . 1972 Nat. New Biol. 239: 197–201.
Whitaker NJ, Bryan TM, Bonnefin P, Chang AC-M, Musgrove EA, Braithwaite AW and Reddel RR. . 1995 Oncogene 11: 971–976.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Peter Rowe for his comments on the manuscript. These studies were supported by a project grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, and the Carcinogenesis Fellowship of the New South Wales Cancer Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perrem, K., Bryan, T., Englezou, A. et al. Repression of an alternative mechanism for lengthening of telomeres in somatic cell hybrids. Oncogene 18, 3383–3390 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202752
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202752
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Non-invasive assessment of telomere maintenance mechanisms in brain tumors
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Diagnosis and treatment of ALT tumors: is Trabectedin a new therapeutic option?
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2017)
-
Switch telomerase to ALT mechanism by inducing telomeric DNA damages and dysfunction of ATRX and DAXX
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
In Japanese patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma, TERT promoter mutation is associated with poor prognosis, in contrast to BRAF V600E mutation
Virchows Archiv (2016)
-
Suppression of the alternative lengthening of telomere pathway by the chromatin remodelling factor ATRX
Nature Communications (2015)