Abstract
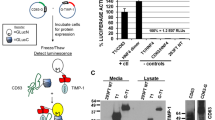
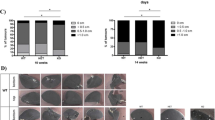
We recently identified, cloned, and characterized a novel human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-4, TIMP-4 (Greene et al., 1996). To determine if TIMP-4 can modulate the in vivo growth of human breast cancers, we transfected a full-length TIMP-4 cDNA into MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cells and studied the orthotopic growth of TIMP-4-transfected (TIMP4-435) versus control (neo-435) clones in the mammary fat pad of athymic nude mice. TIMP4-435 clones expressed TIMP-4 mRNA and produced anti-metalloproteinase (MMP) activity, while neo-435 clones did not express TIMP-4 mRNA or produce detectable anti-MMP activity. Overexpression of TIMP-4 inhibited the invasion potential of the cells in the in vitro invasion assay. When injected orthotopically into nude mice, TIMP-4 transfectants were significantly inhibited in tumor growth by 4 – 10-fold in primary tumor volumes; and in an axillary lymph node and lung metastasis as compared with controls. These results suggest the therapeutic potential of TIMP-4 in treating cancer malignant progression
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Liu, Y., Greene, J. et al. Inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis of human breast cancer cells transfected with tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 4. Oncogene 14, 2767–2774 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201245
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201245
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of expression, prognosis and immune infiltration for TIMPs in glioblastoma
BMC Neurology (2021)
-
WNT ligands control initiation and progression of human papillomavirus-driven squamous cell carcinoma
Oncogene (2018)
-
TIMPs: versatile extracellular regulators in cancer
Nature Reviews Cancer (2017)
-
TIMP-3 -1296 T>C and TIMP-4 -55 T>C gene polymorphisms play a role in the susceptibility of hepatocellular carcinoma among women
Tumor Biology (2014)
-
TIMP-4 and CD63: new prognostic biomarkers in human astrocytomas
Modern Pathology (2010)