Abstract
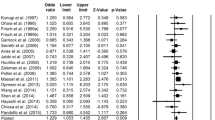
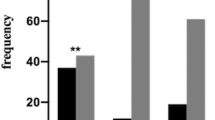
The available data from preclinical and pharmacological studies on the role of the C-O-methyl transferase (COMT) support the hypothesis that abnormal catecholamine transmission has been implicated in the pathogenesis of mood disorders (MD). We examined the relationship of a common functional polymorphism (Val108/158Met) in the COMT gene, which accounts for four-fold variation in enzyme activity, with ‘early-onset’ (EO) forms (less than or equal to 25 years) of MD, including patients with major depressive disorder (EO-MDD) and bipolar patients (EO-BPD), in a European multicenter case–control sample. Our sample includes 378 MDD (120 EO-MDD), 506 BPD (222 EO-BPD) and 628 controls. An association was found between the high-activity COMT Val allele, particularly the COMT Val/Val genotype and EO-MDD. These findings suggest that the COMT Val/Val genotype may be involved in EO-MDD or may be in linkage disequilibrium with a different causative polymorphism in the vicinity. The COMT gene may have complex and pleiotropic effects on susceptibility and symptomatology of neuropsychiatric disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Risch N, Merikangas K . The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science 1996; 273: 1516–1517.
Mendlewicz J . Juvenile and late onset forms of depressive disorder: genetic and biological characterization of bipolar and unipolar illness-a review. Maturitas 1979; 1: 229–234.
Strober M, Morrell W, Burroughs J, Lampert C, Danforth H, Freeman R . A family study of bipolar I disorder in adolescence: early onset of symptoms linked to increased familial loading and lithium resistance. J Affect Disord 1988; 15: 255–268.
Leboyer M, Bellivier F, McKeon P, Albus M, Borrman M, Perez-Diaz F et al. Age at onset and gender resemblance in bipolar siblings. Psychiatry Res 1998; 81: 125–131.
Grigoroiu-Serbanescu M, Martinez M, Nöthen MM, Grimberg M, Sima D, Propping P et al. Different familial transmission patterns in bipolar I disorder with onset before and after age 25. Am J Med Genet 2001; 105: 765–773.
Grigoroiu-Serbanescu M, Wickramaratne PJ, Hodge SE, Milea S, Mihailescu R . Genetic anticipation and imprinting in bipolar I illness. Br J Psychiatry 1997; 170: 162–166.
Lindblad K, Nylander PO, De bruyn A, Sourey D, Zander C, Engstrom C et al. Detection of expanded CAG repeats in bipolar affective disorder using the repeat expansion detection (RED) method. Neurobiol Dis 1995; 2: 55–62.
Lindblad K, Nylander PO, Zander C, Yuan QP, Stahle L, Engstrom C et al. Two commonly expanded CAG/ CTG repeat loci: involvement in affective disorders? Mol Psychiatry 1998; 3: 405–410.
Mendlewicz J, Lindbald K, Souery D, Mahieu B, Nylander PO, De Bruyn A et al. Expanded trinucleotide CAG repeats in families with bipolar affective disorder. Biol Psychiatry 1997; 42: 1115–1122.
Pericak-Vance MA, Bebout JL, Gaskell Jr PC, Yamaoka LH, Hung WY, Alberts MJ et al. Linkage studies in familial Alzheimer disease: evidence for chromosome 19 linkage. Am J Hum Genet 1991; 48: 1034–1050.
Papolos DF, Faedda GL, Veit S, Goldberg R, Morrow B, Kucherlapati R et al. Bipolar spectrum disorders in patients diagnosed with velo-cardio-facial syndrome: does a hemizygous deletion of chromosome 22q11 result in bipolar affective disorder? Am J Psychiatry 1996; 153: 1541–1547.
Lotta T, Vidgren J, Tilgmann C, Ulmanen I, Melen K, Julkunen I et al. Kinetics of human soluble and membrane-bound catechol-O methyltransferase: a revised mechanism and description of the thermolabile variant of the enzyme. Biochemistry 1995; 34: 4202–4210.
Bertocci B, Miggiano V, Da Prada M, Dembic Z, Lahm HW, Malherbe P . Human catechol-O-methyltransferase, cloning and expression of the membrane-associated form. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 1416–1420.
Lundstrom K, Salminen M, Jalanko A, Savolainen R, Ulmanen I . Cloning and characterization of human placental catechol-O-methyltransferase cDNA. DNA Cell Biol 1991; 10: 181–189.
Tenhunen J, Salminen M, Lundstrom K, Kiviluoto T, Savolainen R, Ulmanen I . Genomic organization of the human catechol-O-methyltransferase gene and its expression from two distinct promoters. Eur J Biochem 1994; 223: 1049–1059.
Lachman HM, Papolos DF, Saito T, Yu YM, Szumlanski CL, Weinshilboum RM . Human catechol-O-methyltransferase pharmacogenetics: description of a functional polymorphism and its potential application to neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacogenetics 1996; 6: 243–250.
Aksoy S, Klener J, Weinshilboum RM . Catechol O-methyltransferase pharmacogenetics: photoaffinity labelling and western blot analysis of human liver samples. Pharmacogenetics 1993; 3: 116–122.
Fahndrich E, Coper H, Christ W, Helmchen H, Muller-Oerlinghausen B, Pietzcker A . Erythrocyte COMT-activity in patients with affective disorders. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1980; 61: 427–437.
Guldberg HC, Marsden CA . Catechol-O-methyl transferase: pharmacological aspects and physiological role. Pharmacol Rev 1975; 27: 135–206.
Papolos DF, Veit S, Faedda GL, Saito T, Lachman HM . Ultra-ultra rapid cycling bipolar disorder is associated with the low activity catecholamine-O-methytransferase allele. Mol Psychiatry 1998; 3: 346–349.
Ohara K, Nagai M, Suzuki Y, Ohara K . Low activity allele of catechol-o-methyltransferase gene and Japanese unipolar depression. Neuroreport 1998; 9: 1305–1308.
Li T, Vallada H, Curtis D, Arranz M, Xu K, Cai G et al. Catechol-O-methyltransferase Val158Met polymorphism: frequency analysis in Han Chinese subjects and allelic association of the low activity allele with bipolar affective disorder. Pharmacogenetics 1997; 7: 349–353.
Mynett-Johnson LA, Murphy VE, Claffey E, Shields DC, McKeon P . Preliminary evidence of an association between bipolar disorder in females and the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene. Psychiatr Genet 1998; 8: 221–225.
Rotondo A, Mazzanti C, Dell'Osso L, Rucci P, Sullivan P, Bouanani S et al. Catechol o-methyltransferase, serotonin transporter, and tryptophan hydroxylase gene polymorphisms in bipolar disorder patients with and without comorbid panic disorder. Am J Psychiatry 2002; 159: 23–29.
Kirov G, Murphy KC, Arranz MJ, Jones I, McCandles F, Kunugi H et al. Low activity allele of catechol-O-methyltransferase gene associated with rapid cycling bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 1998; 3: 342–345.
Schizophrenia Collaborative Linkage Group for Chromosome 22. A transmission disequilibrium and linkage analysis of D22S278 marker alleles in 574 families: further support for a susceptibility locus for schizophrenia at 22q12. Schizophr Res 1998; 32: 115–121.
Lachman HM, Kelsoe JR, Remick RA, Sadovnick AD, Rapaport MH, Lin M et al. Linkage studies suggest a possible locus for bipolar disorder near the velo-cardio-facial syndrome region on chromosome 22. Am J Med Genet 1997; 74: 121–128.
Kelsoe JR, Spence MA, Loetscher E, Foguet M, Sadovnick AD, Remick RA et al. A genome survey indicates a possible susceptibility locus for bipolar disorder on chromosome 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 585–590.
Souery D, Lipp O, Serretti A, Mahieu B, Rivelli SK, Cavallini C et al. European Collaborative Project on Affective Disorders, interactions between genetic and psychosocial vulnerability factors. Psychiatr Genet 1998; 8: 197–205.
Endicott J, Spitzer RL . A diagnostic interview: the schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1978; 35: 837–862.
Wing JK, Babor T, Brugha T, Burke J, Cooper JE, Giel R et al. SCAN: schedules for clinical assessment in neuropsychiatry. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1990; 47: 589–593.
Farmer A, Cosyns P, Leboyer M, Maier W, Mors O, Sargeant M et al. A SCAN–SADS comparison study of psychotic subjects and their first degree relatives. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 1993; 242: 352–357.
Bellivier F, Golmard JL, Rietschel M, Schulze TG, Malafosse A, Preisig M et al. Age at onset in bipolar I affective disorder: further evidence for three subgroups. Am J Psychiatry 2003; 160: 999–1001.
Andreasen NC, Endicott J, Spitzer RL, Winokur G . The family history method using diagnostic criteria. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1977; 34: 1229–1235.
Lahiri DK, Nurnberger JI . A rapid non-enzymatic method for the preparation of HMW DNA from blood for RFLP studies. Nucleic Acids Res 1991; 19: 5444.
Raymond M, Rousset F . Genepop (ver1.2), a population genetic software for exact test and ecuniscism. J Hered 1995; 95: 248–249.
Mantel N, Haenszel W . Statistical aspects of the analysis if data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 1959; 22: 719–748.
Breslow NE, Day NE . Statistical Methods in Cancer Research. Volume 1 – The analysis of case–control studies. IARC Scientific Publication No. 32: Lyon, 1980.
Bellivier F, Laplanche JL, Schurhoff F, Feingold J, Feline A, Jouvent R et al. Apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism in early and late onset bipolar patients. Neurosci Lett 1997; 233: 45–48.
Egan MF, Goldberg TE, Kolachana BS, Callicott JH, Mazzanti CM, Straub RE et al. Effect of COMT Val108/158 Met genotype on frontal lobe function and risk for schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 6917–6922.
Badner JA, Gershon ES . Meta-analysis of whole-genome linkage scans of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 405–411.
Eley TC, Tahir E, Angleitner A, Harriss K, McClay J, Plomin R et al. Association analysis of MAOA and COMT with neuroticism assessed by peers. Am J Med Genet 2003; 120: 90–96.
Glatt SJ, Faraone SV, Tsuang MT . Association between a functional catechol O-methyltransferase gene polymorphism and schizophrenia: meta-analysis of case–control and family-based studies. Am J Psychiatry 2003; 160: 469–476.
Rujescu D, Giegling I, Gietl A, Hartmann AM, Moller HJ . A functional single nucleotide polymorphism (V158M) in the COMT gene is associated with aggressive personality traits. Biol Psychiatry 2003; 54: 34–39.
Kunugi H, Vallada HP, Hoda F, Kirov G, Gill M, Aitchison KJ et al. No evidence for an association of affective disorders with high- or low-activity allele of catechol-o-methyltransferase gene. Biol Psychiatry 1997; 42: 282–285.
Frisch A, Postilnick D, Rockah R, Michaelovsky E, Postilnick S, Birman E et al. Association of unipolar major depressive disorder with genes of the serotonergic and dopaminergic pathways. Mol Psychiatry 1999; 4: 389–392.
Russ MJ, Lachman HM, Kashdan T, Saito T, Bajmakovic-Kacila S . Analysis of catechol-O-methyltransferase and 5-hydroxytryptamine transporter polymorphisms in patients at risk for suicide. Psychiatry Res 2000; 93: 73–78.
Cusin C, Serretti A, Lattuada E, Lilli R, Lorenzi C, Smeraldi E . Association study of MAO-A, COMT, 5-HT2A, DRD2, and DRD4 polymorphisms with illness time course in mood disorders. Am J Med Genet 2002; 114: 380–390.
Gutierrez B, Bertranpetit J, Guillamat R, Valles V, Arranz MJ, Kerwin R et al. Association analysis of the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene and bipolar affective disorder. Am J Psychiatry 1997; 154: 113–115.
Lachman HM, Kelsoe J, Moreno L, Katz S, Papolos DF . Lack of association of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) functional polymorphism in bipolar affective disorder. Psychiatr Genet 1997; 7: 13–17.
Biomed European Bipolar Collaborative Group. No association between bipolar disorder and alleles at a functional polymorphism in the COMT gene. Br J Psychiatry 1997; 170: 526–528.
Geller B, Cook Jr EH . Ultradian rapid cycling in prepubertal and early adolescent bipolarity is not in transmission disequilibrium with val/met COMT alleles. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 47: 605–609.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Association for Mental Health Research (AESM), the European Community Biomed Grant (Grant No CT 92-1217), the National Fund for Scientific Research (NFSR), the Fund for Scientific Research Flanders (FWO) and a concerted action grant of the Special Research Fund of the University of Antwerp, Belgium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massat, I., Souery, D., Del-Favero, J. et al. Association between COMT (Val158Met) functional polymorphism and early onset in patients with major depressive disorder in a European multicenter genetic association study. Mol Psychiatry 10, 598–605 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001615
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001615
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The importance of identifying functional Val158Met polymorphism in catechol-O- Methyltransferase when assessing MRI-based volumetric measurements in major depressive disorder
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2020)
-
Meta-Analysis of the COMT Val158Met Polymorphism in Major Depressive Disorder: Effect of Ethnicity
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2016)
-
Influence of Val108/158Met COMT Gene Polymorphism on the Efficacy of Modified Electroconvulsive Therapy in Patients with Treatment Resistant Depression
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2015)
-
Altersabhängige Symptomatik und latente Ausdrucksformen beachten
NeuroTransmitter (2013)
-
A novel SNP in COMT is associated with alcohol dependence but not opiate or nicotine dependence: a case control study
Behavioral and Brain Functions (2011)