Abstract
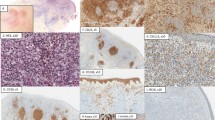
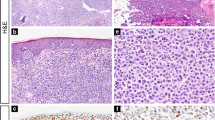
FOXP3 is a unique marker for CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells (Tregs). In solid tumours, high numbers of Tregs are associated with a poor prognosis. Knowledge about the implications of Tregs for the behaviour of haematological malignancies is limited. In this study, skin biopsies from 86 patients with mycosis fungoides (MF) and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) unspecified were analysed for the expression of FOXP3 on tumour cells and tumour-infiltrating Tregs. Labelling of above 10% of the neoplastic cells was seen in one case classified as an aggressive epidermotropic CD8+ cytotoxic CTCL. In the remaining 85 cases, the atypical neoplastic infiltrate was either FOXP3 negative (n=80) or contained only very occasional weakly positive cells (n=5). By contrast, all biopsies showed varying numbers of strongly FOXP3+ tumour-infiltrating Tregs. MF with early or infiltrated plaques had significantly higher numbers of FOXP3+ Tregs than CTCL unspecified or advanced MF with tumours or transformation to large cell lymphoma. An analysis of all patients demonstrated that increasing numbers of FOXP3+ Tregs were associated with improved survival in both MF and CTCL unspecified. In conclusion, our data indicate that the presence of FOXP3+ Tregs in CTCL is associated with disease stage and patient survival.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taams LS, Smith J, Rustin MH, Salmon M, Poulter LW, Akbar AN . Human anergic/suppressive CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells: a highly differentiated and apoptosis-prone population. Eur J Immunol 2001; 31: 1122–1131.
Zou W . Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 2006; 6: 295–307.
Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, Brunkow ME, Ferguson PJ, Whitesell L et al. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 20–21.
Shevach EM . CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nat Rev Immunol 2002; 2: 389–400.
Shevach EM . Fatal attraction: tumors beckon regulatory T cells. Nat Med 2004; 10: 900–901.
Beyer M, Schultze JL . Regulatory T cells in cancer. Blood 2006; 108: 804–811.
Alvaro T, Lejeune M, Salvado MT, Bosch R, Garcia JF, Jaen J et al. Outcome in Hodgkin's lymphoma can be predicted from the presence of accompanying cytotoxic and regulatory T cells. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 1467–1473.
Carreras J, Lopez-Guillermo A, Fox BC, Colomo L, Martinez A, Roncador G et al. High numbers of tumor infiltrating FOXP3-positive regulatory T-cells are associated with improved overall survival in follicular lymphoma. Blood 2006; 108: 2957–2964.
Berger CL, Tigelaar R, Cohen J, Mariwalla K, Trinh J, Wang N et al. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: malignant proliferation of T-regulatory cells. Blood 2005; 105: 1640–1647.
Klemke CD, Fritzsching B, Franz B, Kleinmann EV, Oberle N, Poenitz N et al. Paucity of FOXP3+ cells in skin and peripheral blood distinguishes Sezary syndrome from other cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1123–1129.
Tiemessen MM, Mitchell TJ, Hendry L, Whittaker SJ, Taams LS, John S . Lack of suppressive CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ T cells in advanced stages of primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol 2006; 126: 2217–2223.
Odum N, Hofmann B, Jakobsen B, Langhoff E, Morling N, Platz P et al. HLA-DP related suppression of mixed lymphocyte reaction with alloactivated lymphocytes. Tissue Antigens 1986; 27: 32–43.
Woetmann A, Lovato P, Eriksen KW, Krejsgaard T, Labuda T, Zhang Q et al. Non-malignant T cells stimulate growth of T-cell lymphoma cells in the presence of bacterial toxins. Blood 2007; 109: 3325–3332.
Kaltoft K, Bisballe S, Dyrberg T, Boel E, Rasmussen PB, Thestrup-Pedersen K . Establishment of two continuous T-cell strains from a single plaque of a patient with mycosis fungoides. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 1992; 28A: 161–167.
Odum N, Bregenholt S, Eriksen KW, Skov S, Ryder LP, Bendtzen K et al. The CC-chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) is a marker of, but not essential for the development of human Th1 cells. Tissue Antigens 1999; 54: 572–577.
Krejsgaard T, Vetter-Kauczok CS, Woetmann A, Lovato P, Labuda T, Eriksen KW et al. Jak3- and JNK-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1759–1766.
Gjerdrum LM, Sorensen BS, Kjeldsen E, Sorensen FB, Nexo E, Hamilton-Dutoit S . Real-time quantitative PCR of microdissected paraffin-embedded breast carcinoma—an alternative method for HER-2/neu analysis. J Mol Diagn 2004; 6: 42–51.
Ralfkiaer E, Willemze R, Meijer CJ, Dummer R, Jaffe ES, Swerdlow SH et al. Primary cutaneous peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified. In: Leboit PE, Burg G, Weedon D, Sarasin A (eds). Pathology and Genetics of Skin Tumors. IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2006, pp 184–188.
Woo EY, Chu CS, Goletz TJ, Schlienger K, Yeh H, Coukos G et al. Regulatory CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in tumors from patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and late-stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 4766–4772.
Woo EY, Yeh H, Chu CS, Schlienger K, Carroll RG, Riley JL et al. Cutting edge: regulatory T cells from lung cancer patients directly inhibit autologous T cell proliferation. J Immunol 2002; 168: 4272–4276.
Chen ML, Pittet MJ, Gorelik L, Flavell RA, Weissleder R, von BH et al. Regulatory T cells suppress tumor-specific CD8T cell cytotoxicity through TGF-beta signals in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 419–424.
Wolf AM, Wolf D, Steurer M, Gastl G, Gunsilius E, Grubeck-Loebenstein B . Increase of regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 606–612.
Sasada T, Kimura M, Yoshida Y, Kanai M, Takabayashi A . CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with gastrointestinal malignancies: possible involvement of regulatory T cells in disease progression. Cancer 2003; 98: 1089–1099.
Kono K, Kawaida H, Takahashi A, Sugai H, Mimura K, Miyagawa N et al. CD4(+)CD25 high regulatory T cells increase with tumor stage in patients with gastric and esophageal cancers. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2006; 55: 1064–1071.
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med 2004; 10: 942–949.
Wolf D, Rumpold H, Koppelstatter C, Gastl GA, Steurer M, Mayer G et al. Telomere length of in vivo expanded CD4(+)CD25 (+) regulatory T-cells is preserved in cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2006; 55: 1198–1208.
Hirahara K, Liu L, Clark RA, Yamanaka K, Fuhlbrigge RC, Kupper TS . The majority of human peripheral blood CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ regulatory T cells bear functional skin-homing receptors. J Immunol 2006; 177: 4488–4494.
Chong BF, Murphy JE, Kupper TS, Fuhlbrigge RC . E-selectin, thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine/CCL17, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 are constitutively coexpressed in dermal microvessels: a foundation for a cutaneous immunosurveillance system. J Immunol 2004; 172: 1575–1581.
Kakinuma T, Sugaya M, Nakamura K, Kaneko F, Wakugawa M, Matsushima K et al. Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17) in mycosis fungoides: serum TARC levels reflect the disease activity of mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol 2003; 48: 23–30.
Murakami M, Sakamoto A, Bender J, Kappler J, Marrack P . CD25+CD4+ T cells contribute to the control of memory CD8+ T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 8832–8837.
Trzonkowski P, Szmit E, Mysliwska J, Dobyszuk A, Mysliwski A . CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells inhibit cytotoxic activity of T CD8+ and NK lymphocytes in the direct cell-to-cell interaction. Clin Immunol 2004; 112: 258–267.
Miyara M, Sakaguchi S . Natural regulatory T cells: mechanisms of suppression. Trends Mol Med 2007; 13: 108–116.
Levings MK, Bacchetta R, Schulz U, Roncarolo MG . The role of IL-10 and TGF-beta in the differentiation and effector function of T regulatory cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2002; 129: 263–276.
Yang ZZ, Novak AJ, Ziesmer SC, Witzig TE, Ansell SM . Attenuation of CD8(+) T-cell function by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells in B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 10145–10152.
Chen S, Ishii N, Ine S, Ikeda S, Fujimura T, Ndhlovu LC et al. Regulatory T cell-like activity of Foxp3+ adult T cell leukemia cells. Int Immunol 2006; 18: 269–277.
Karube K, Ohshima K, Tsuchiya T, Yamaguchi T, Kawano R, Suzumiya J et al. Expression of FoxP3, a key molecule in CD4CD25 regulatory T cells, in adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma cells. Br J Haematol 2004; 126: 81–84.
Matsubara Y, Hori T, Morita R, Sakaguchi S, Uchiyama T . Phenotypic and functional relationship between adult T-cell leukemia cells and regulatory T cells. Leukemia 2005; 19: 482–483.
Roncador G, Garcia JF, Garcia JF, Maestre L, Lucas E, Menarguez J et al. FOXP3, a selective marker for a subset of adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma. Leukemia 2005; 19: 2247–2253.
Walsh PT, Benoit BM, Wysocka M, Dalton NM, Turka LA, Rook AH . A role for regulatory T cells in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; induction of a CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3+ T-cell phenotype associated with HTLV-1 infection. J Invest Dermatol 2006; 126: 690–692.
Hallermann C, Niermann C, Schulze HJ . Regulatory T-cell phenotype in association with large cell transformation of mycosis fungoides. Eur J Haematol 2007; 78: 260–263.
Jaffe ES, Ralfkiaer E . Mature T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (eds). Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2001, pp 189–235.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the Foundation of 17—12-1981, the Research Council, the Danish Foundation for Cancer Research and the Danish Cancer Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gjerdrum, L., Woetmann, A., Odum, N. et al. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: association with disease stage and survival. Leukemia 21, 2512–2518 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404913
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404913
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Peripheral T cell lymphomas: from the bench to the clinic
Nature Reviews Cancer (2020)
-
Prognostic role of regulatory T cells in lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2020)
-
Clinicopathologic and microenvironmental analysis of primary cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders: a 26 year experience from an academic medical center in Brazil
Diagnostic Pathology (2019)
-
Bone marrow infiltrated Lnc-INSR induced suppressive immune microenvironment in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Peripheral T cell lymphoma with a regulatory T cell phenotype: a Mexican case not associated with HTLV-1 virus infection
Journal of Hematopathology (2014)