Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Although the body mass index (BMI, kg/m2) is widely used as a surrogate measure of adiposity, it is a measure of excess weight, rather than excess body fat, relative to height. We examined the relation of BMI to levels of fat mass and fat-free mass among healthy 5- to 18-y-olds.
METHODS AND PROCEDURES:
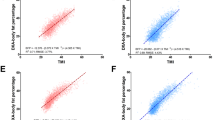
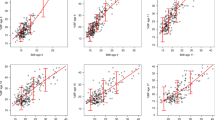
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry was used to measure fat and fat-free mass among 1196 subjects. These measures were standardized for height by calculating the fat mass index (FMI, fat mass/ht2) and the fat-free mass index (FFMI, fat-free mass/ht2).
RESULTS:
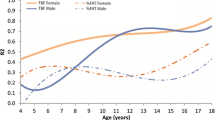
The variability in FFMI was about 50% of that in FMI, and the accuracy of BMI as a measure of adiposity varied greatly according to the degree of fatness. Among children with a BMI-for-age ≥85th P, BMI levels were strongly associated with FMI (r=0.85–0.96 across sex–age categories). In contrast, among children with a BMI-for-age <50th P, levels of BMI were more strongly associated with FFMI (r=0.56–0.83) than with FMI (r=0.22–0.65). The relation of BMI to fat mass was markedly nonlinear, and substantial differences in fat mass were seen only at BMI levels ≥85th P.
DISCUSSION:
BMI levels among children should be interpreted with caution. Although a high BMI-for-age is a good indicator of excess fat mass, BMI differences among thinner children can be largely due to fat-free mass.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Johnson CL . Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999–2000. JAMA 2002; 288: 1728–1732.
Franklin MF . Comparison of weight and height relations in boys from 4 countries. Am J Clin Nutr 1999; 70: 157S–162S.
Horlick M . Body mass index in childhood—measuring a moving target. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 4059–4060.
Gallagher D, Visser M, Sepulveda D, Pierson RN, Harris T, Heymsfield SB . How useful is body mass index for comparison of body fatness across age, sex, and ethnic groups? Am J Epidemiol 1996; 143: 228–239.
Deurenberg P, Yap M, van Staveren WA . Body mass index and percent body fat: a meta analysis among different ethnic groups. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998; 22: 1164–1171.
Gallagher D, Heymsfield SB, Heo M, Jebb SA, Murgatroyd PR, Sakamoto Y . Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index. Am J Clin 2000; 72: 694–701.
Jackson AS, Stanforth PR, Gagnon J, Rankinen T, Leon AS, Rao DC, Skinner JS, Bouchard C, Wilmore JH . The effect of sex, age and race on estimating percentage body fat from body mass index: the Heritage Family Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26: 789–796.
Hannan WJ, Wrate RM, Cowen SJ, Freeman CP . Body mass index as an estimate of body fat. Int J Eat Disord 1995; 18: 91–97.
Goulding A, Gold E, Cannan R, Taylor RW, Williams S, Lewis–Barned NJ . DEXA supports the use of BMI as a measure of fatness in young girls. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1996; 20: 1014–1021.
Daniels SR, Khoury PR, Morrison JA . The utility of body mass index as a measure of body fatness in children and adolescents: differences by race and gender. Pediatrics 1997; 99: 804–807.
Schaefer F, Georgi M, Wuhl E, Scharer K . Body mass index and percentage fat mass in healthy German schoolchildren and adolescents. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998; 22: 461–469.
Pietrobelli A, Faith MS, Allison DB, Gallagher D, Chiumello G, Heymsfield SB . Body mass index as a measure of adiposity among children and adolescents: a validation study. J Pediatr 1998; 132: 204–210.
Sarria A, Garcia–Llop LA, Moreno LA, Fleta J, Morellon MP, Bueno M . Skinfold thickness measurements are better predictors of body fat percentage than body mass index in male Spanish children and adolescents. Eur J Clin Nutr 1998; 52: 573–576.
Bray GA, DeLany JP, Harsha DW, Volaufova J, Champagne CC . Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10–y–old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children's Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2001; 73: 687–702.
Widhalm K, Schonegger K, Huemer C, Auterith A . Does the BMI reflect body fat in obese children and adolescents? A study using the TOBEC method. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: 279–285.
Lindsay RS, Hanson RL, Roumain J, Ravussin E, Knowler WC, Tataranni PA . Body mass index as a measure of adiposity in children and adolescents: relationship to adiposity by dual energy X–ray absorptiometry and to cardiovascular risk factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 4061–4067.
Maynard LM, Wisemandle W, Roche AF, Chumlea WC, Guo SS, Siervogel RM . Childhood body composition in relation to body mass index. Pediatrics 2001; 107: 344–350.
Mast M, Langnase K, Labitzke K, Bruse U, Preuss U, Muller MJ . Use of BMI as a measure of overweight and obesity in a field study on 5–7 year old children. Eur J Nutr 2002; 41: 61–67.
Taylor RW, Jones IE, Williams SM, Goulding A . Body fat percentages measured by dual–energy X–ray absorptiometry corresponding to recently recommended body mass index cutoffs for overweight and obesity in children and adolescents aged 3–18 y. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 76: 1416–1421.
Mei Z, Grummer–Strawn LM, Pietrobelli A, Goulding A, Goran MI, Dietz WH . Validity of body mass index compared with other body–composition screening indexes for the assessment of body fatness in children and adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 75: 978–985.
Kerruish KP, O'Connor J, Humphries IR, Kohn MR, Clarke SD, Briody JN, Thomson EJ, Wright KA, Gaskin KJ, Baur LA . Body composition in adolescents with anorexia nervosa. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 75: 31–37.
VanItallie TB, Yang MU, Heymsfield SB, Funk RC, Boileau RA . Height–normalized indices of the body's fat–free mass and fat mass: potentially useful indicators of nutritional status. Am J Clin Nutr 1990; 52: 953–959.
Hattori K, Tatsumi N, Tanaka S . Assessment of body composition by using a new chart method. Am J Hum Biol 1997; 9: 573–578.
Wells JC . A critique of the expression of paediatric body composition data. Arch Dis Child 2001; 85: 67–72.
Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, Grummer–Strawn LM, Flegal KM, Mei Z, Wei R, Curtin LR, Roche AF, Johnson CL . CDC growth charts: United States. Adv Data 2000; 314: 1–27; (http://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpa/growthcharts/sas.htm).
Ogden CL, Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM, Mei Z, Guo S, Wei R, Grummer-Strawn LM, Curtin LR, Roche AF, Johnson CL . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2000 growth charts for the United States: improvements to the 1977 National Center for Health Statistics version. Pediatrics 2002; 109: 45–60.
Himes JH, Dietz WH . Guidelines for overweight in adolescent preventive services: recommendations from an expert committee. The Expert Committee on Clinical Guidelines for Overweight in Adolescent Preventive Services. Am J Clin Nutr 1994; 59: 307–316.
Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM . Criteria for definition of overweight in transition: background and recommendations for the United States. Am J Clin Nutr 2000; 72: 1074–1081.
Mazess RB, Barden HS, Bisek JP, Hanson J . Dual–energy X–ray absorptiometry for total–body and regional bone–mineral and soft–tissue composition. Am J Clin Nutr 1990; 51: 1106–1212.
Russell–Aulet M, Wang J, Thornton J, Pierson Jr RN . Comparison of dual–photon absorptiometry systems for total–body bone and soft tissue measurements: dual–energy X–rays versus gadolinium 153. J Bone Miner Res 1991; 6: 411–415.
Cleveland WS . The elements of graphing data. Wadsworth Advanced Books and Software: Monterey, CA; 1985. pp 170–178.
Harrell Jr FR . Regression modeling strategies with applications to linear models, logistic regression, and survival analysis. Springer-Verlag: New York; 2001. pp 16–26.
Wells JC . Body composition in childhood: effects of normal growth and disease. Proc Nutr Soc 2003; 62: 521–528.
Siervogel RM, Maynard LM, Wisemandle WA, Roche AF, Guo SS, Chumlea WC, Towne B . Annual changes in total body fat and fat free mass in children from 8 to 18 years in relation to changes in body mass index: the Fels Longitudinal Study. Ann NY Acad Sci 2000; 904: 420–423.
Ruxton CH, Reilly JJ, Kirk TR . Body composition of healthy 7–and 8–year–old children and a comparison with the ‘reference child’. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999; 23: 1276–1281.
Mast M, Kortzinger I, Konig E, Muller MJ . Gender differences in fat mass of 5–7-year old children. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998; 22: 878–884.
Schutz Y, Kyle UU, Pichard C . Fat-free mass index and fat mass index percentiles in Caucasians aged 18–98 y. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26: 953–960.
Wells JC, Cole TJ, ALSPAC study team. Adjustment of fat–free mass and fat mass for height in children aged 8 y. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26: 947–952.
Prentice AM, Jebb SA . Beyond body mass index. Obes Rev 2001; 2: 141–147.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by NIH Grant DK37352.
For overnight deliveries: Rhodes Bldg, Rm 5161, 3005 Chamblee-Tucker Rd, Atlanta, GA 30341-4133, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freedman, D., Wang, J., Maynard, L. et al. Relation of BMI to fat and fat-free mass among children and adolescents. Int J Obes 29, 1–8 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802735
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802735
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Clustering of lifestyle and health behaviours in Australian adolescents and associations with obesity, self-rated health and quality of life
BMC Public Health (2023)
-
Low skeletal muscle mass and liver fibrosis in children with cerebral palsy
European Journal of Pediatrics (2023)
-
Relationships of BMI, muscle-to-fat ratio, and handgrip strength-to-BMI ratio to physical fitness in Spanish children and adolescents
European Journal of Pediatrics (2023)
-
Novel type of references for BMI aligned for onset of puberty – using the QEPS growth model
BMC Pediatrics (2022)
-
BMI metrics and their association with adiposity, cardiometabolic risk factors, and biomarkers in children and adolescents
International Journal of Obesity (2022)