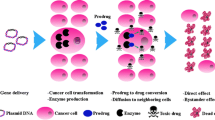
Abstract
Acetaminophen is oxidized by human CYP1A2 to the cytotoxic metabolite N-acetylbenzoquinoneimine (NABQI). Incubation of cells transfected with human CYP1A2 (H1A2 MZ cells) with 4–20 mM acetaminophen for 6 hours at 37°C caused extensive cytotoxicity (cell viability <10%). In contrast, nontransfected V79 MZ cells were unaffected (viability >95%). By mixing H1A2 MZ cells with V79 MZ cells in various proportions and incubating with 4 mM acetaminophen, it was shown that the NABQI released from H1A2 MZ cells also caused cytotoxicity of bystander cells. Thus, in a mixture containing 5% H1A2 MZ cells, exposure to 4 mM acetaminophen for 6 hours resulted in complete cell killing by 24 hours. A similar bystander effect was found by incubating the same proportion of CYP1A2-containing cells with ovarian tumor-derived SK-OV-3 cells or colon tumor-derived HCT116 cells. However, breast tumor-derived MDA-MB-361 cells displayed resistance to the cytotoxic effect of NABQI, and it was necessary to increase the proportion of H1A2 MZ cells to 50% to achieve complete cell killing. In conclusion, the use of acetaminophen as prodrug and CYP1A2 as an activating enzyme is a promising combination for gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thatcher, N., Edwards, R., Lemoine, N. et al. The potential of acetaminophen as a prodrug in gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 7, 521–525 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700165
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700165
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Enzyme prodrug therapy: cytotoxic potential of paracetamol turnover with recombinant horseradish peroxidase
Monatshefte für Chemie - Chemical Monthly (2021)
-
Use of horseradish peroxidase for gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy with paracetamol
British Journal of Cancer (2004)