Abstract
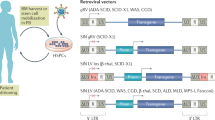
Genetic transfer and expression of drug-resistance functions into haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells is a promising means to overcome both the acute and long-term side-effects of cytotoxic drugs in bone marrow. Here, we describe a functional analysis of a retroviral vector that co-expresses human cDNAs for multidrug resistance 1/P-glycoprotein (MDR1) and a double mutant of O6-alkylguanine-alkyltransferase (hATPA/GA) to high levels. The hATPA/GA protein contains two amino acid substitutions that render it resistant to compounds such as O6-benzylguanine that inhibit the wild-type protein which is often overexpressed in resistant tumour cells. Evidence for simultaneous drug resistance of genetically modified primary murine progenitor cells to colchicine or the podophyllotoxin etoposide, both covered by MDR1-mediated efflux activity, and the nitrosourea BCNU, which is counteracted by hATPA/GA, is presented using in vitro colony assays. Bone Marrow Transplantation (2000) 25 , Suppl. 2, S71–S74.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baum, C., Peinert, S., Carpinteiro, A. et al. Genetic modification of haematopoietic cells for combined resistance to podophyllotoxins, other agents covered by MDR1-mediated efflux activity and nitrosoureas. Bone Marrow Transplant 25 (Suppl 2), S71–S74 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702359
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702359
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy with drug resistance genes: an update
Cancer Gene Therapy (2005)