As screen time becomes more and more present in the lives of children, parents need the best information to help to guide their decisions. By collating all of the meta-analytic evidence from across the field, we hope to provide that evidence.
References
The Lancet. Social media, screen time, and young people’s mental health. Lancet 393, 611 (2019). An editorial that summarizes the state of the field for screen time and mental health.
Screen time: how much is too much? Nature 565, 265–266 (2019). An editorial summarizing some of the weaknesses in screen time research.
United States Surgeon General. Social media and youth mental health. hhs.gov, https://www.hhs.gov/surgeongeneral/priorities/youth-mental-health/social-media/index.html (2023). Recent advice from the US Surgeon General regarding young people’s engagement with social media.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
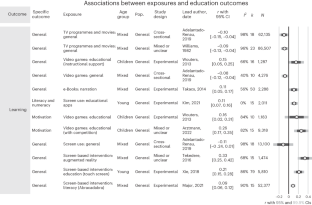
This is a summary of: Sanders, T. et al. An umbrella review of the benefits and risks associated with youths’ interactions with electronic screens. Nat. Hum. Behav. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-023-01712-8 (2023)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weighing the risks and benefits of screen time for children. Nat Hum Behav 8, 16–17 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-023-01713-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-023-01713-7
- Springer Nature Limited


